IBS and diverticulosis what to do when you have both sets the stage for a deep dive into managing these two conditions together. Living with both Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and diverticulosis can be challenging, but with the right knowledge and strategies, you can effectively manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life. We’ll explore the differences and overlaps in symptoms, discuss various treatment options, and provide practical tips for dietary management, lifestyle changes, and medication use.
This guide is designed to empower you to take control of your health and well-being.
Understanding the unique interplay of IBS and diverticulosis requires a comprehensive approach. We’ll examine how symptoms might manifest differently or overlap, the importance of proper diagnosis, and the potential complications that can arise from having both conditions. This information will help you navigate the complexities of your health journey.
Introduction to IBS and Diverticulosis
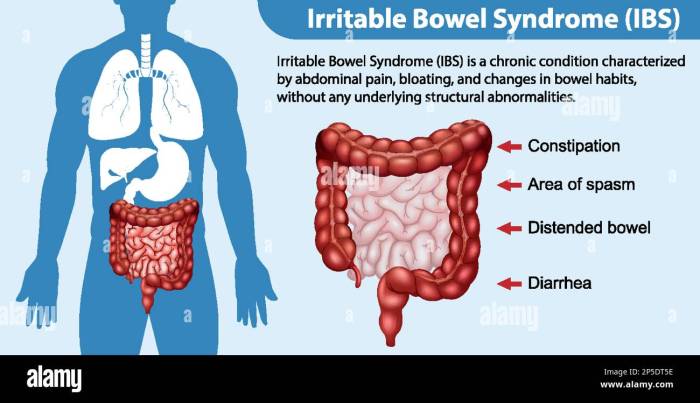
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and diverticulosis are two common gastrointestinal conditions that often affect individuals simultaneously. Understanding their distinct characteristics, overlapping symptoms, and potential complications is crucial for effective management. This exploration aims to provide a comprehensive overview of these conditions and their interactions.Diverticulosis is a condition where small pouches (diverticula) form in the lining of the colon.
IBS, on the other hand, is characterized by chronic abdominal pain, altered bowel habits, and other digestive symptoms, but without any structural damage to the intestines. While they have different root causes, their co-occurrence presents a unique set of challenges for diagnosis and treatment.
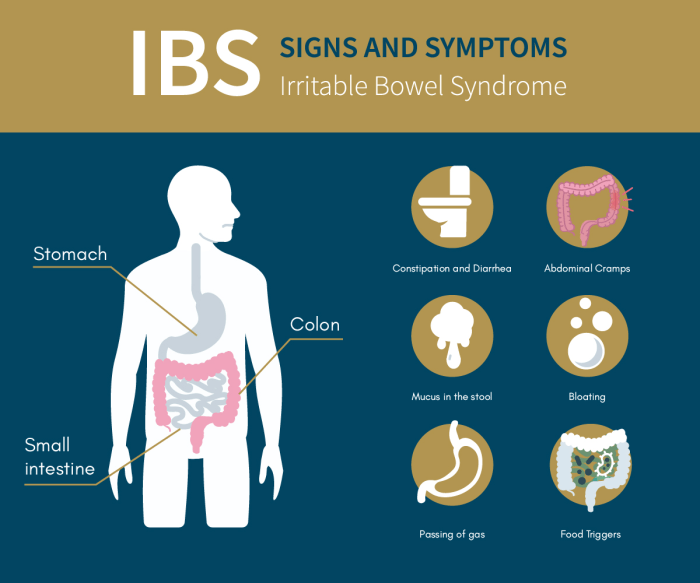
Symptoms of IBS and Diverticulosis
The overlapping symptoms of IBS and diverticulosis can often make diagnosis challenging. Distinguishing between the two necessitates careful consideration of the specific characteristics and patterns of each condition. Recognizing these differences is essential for appropriate medical intervention.
| Symptom | IBS | Diverticulosis |
|---|---|---|
| Abdominal pain | Often cramping, intermittent, and relieved by bowel movements. | May be mild or absent, or occur with bloating and cramping. |
| Changes in bowel habits | Diarrhea, constipation, or both. Frequency can vary. | Generally associated with constipation or infrequent bowel movements. |
| Bloating | Common, often accompanied by abdominal discomfort. | May occur with constipation or after meals. |
| Gas | Increased gas production and discomfort. | Gas can be a symptom, but not as prominent as in IBS. |
| Nausea and Vomiting | Possible, but not typical. | Less common than in IBS, but can occur. |
Overlap and Potential Complications
The coexistence of IBS and diverticulosis can lead to complex symptom presentations. For example, an individual might experience both the cramping pain associated with IBS and the bloating related to diverticulosis. This overlap can make diagnosis more challenging and necessitate a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional.
Challenges Faced by Individuals with Both Conditions
Managing both IBS and diverticulosis simultaneously presents several challenges. The symptoms can be intertwined, making it difficult to isolate the cause of discomfort. Additionally, dietary modifications and medication strategies must address both conditions, requiring careful consideration to avoid adverse effects. This often necessitates a multidisciplinary approach involving gastroenterologists, nutritionists, and other healthcare professionals.
Understanding the Symptoms
Living with both IBS and diverticulosis can be challenging, as symptoms can overlap and sometimes mimic each other. Understanding the nuances of each condition’s symptom presentation is crucial for effective management and communication with healthcare providers. This section delves into the diverse range of symptoms, how they may differ or overlap, and their impact on daily life.Symptoms of IBS and diverticulosis can vary significantly between individuals, and even within the same individual over time.
The interplay of these conditions can lead to a complex symptom picture, making accurate diagnosis and treatment planning essential.
Diverse Range of Symptoms
IBS and diverticulosis can manifest with a variety of symptoms. IBS is primarily characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits, such as diarrhea, constipation, or both. Diverticulosis, on the other hand, often presents with mild or no symptoms. However, when diverticula become inflamed (diverticulitis), symptoms can include severe abdominal pain, fever, and nausea.
Symptom Overlap and Differences
The overlap in symptoms can be confusing. Both conditions can cause abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits. For instance, cramping abdominal pain can be a symptom of both IBS and diverticulitis. However, the location and intensity of the pain, as well as the accompanying symptoms, can provide clues to the underlying condition.
Severity and Frequency of Symptoms
The severity and frequency of symptoms vary greatly. Some individuals experience mild, intermittent discomfort, while others experience debilitating symptoms that significantly impact their daily lives. The frequency and severity of symptoms can fluctuate, influenced by diet, stress, and other factors. For example, a person with IBS may experience more frequent and intense abdominal pain during periods of stress. A person with diverticulosis may experience little discomfort, except when they have a flare-up of diverticulitis.
Potential Interactions of Symptoms
The following table illustrates the potential interactions between symptoms of IBS and diverticulosis. It’s important to remember that this is not an exhaustive list, and individual experiences may vary.
| Symptom | IBS | Diverticulosis | Potential Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abdominal Pain | Cramping, intermittent, variable location | Localized, often lower left quadrant, sharp or dull | Overlap; differentiating based on location and intensity crucial |
| Bloating | Common, often associated with gas | Possible, but not a primary symptom | IBS bloating can be more persistent; diverticulosis bloating may be intermittent |
| Changes in Bowel Habits | Diarrhea, constipation, or both | Usually no significant change, unless diverticulitis is present | IBS can cause frequent or irregular bowel movements; diverticulitis can cause sudden, severe changes |
| Nausea | Possible, but less common | Common with diverticulitis | Nausea often indicates inflammation or infection, suggesting diverticulitis |
| Fever | Rare | Common with diverticulitis | Fever is a strong indicator of infection, potentially related to diverticulitis |
Impact on Daily Life
Symptoms of both IBS and diverticulosis can significantly impact daily life. They can affect work, social activities, and overall well-being. A flare-up of diverticulitis can lead to days or weeks of severe pain and discomfort, requiring rest and medical attention. Individuals with IBS may experience chronic discomfort and uncertainty about their digestive system, leading to anxiety and dietary restrictions.
Dietary changes, stress management techniques, and medication are often used to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Navigating the complexities of both Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and Diverticulosis requires a nuanced approach to diagnosis and treatment. While these conditions often share overlapping symptoms, distinguishing them and developing a tailored management plan is crucial for optimal well-being. The journey to effective treatment often involves a collaborative effort between patients and healthcare professionals.The diagnostic process typically begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination.
The doctor will inquire about the patient’s symptoms, their duration, frequency, and any potential triggers. This information, coupled with a physical assessment, helps narrow down the possibilities and guide the selection of appropriate diagnostic tests.
Diagnostic Process
The diagnostic process for IBS and Diverticulosis involves a combination of methods to accurately identify both conditions and differentiate them from other potential causes. A detailed medical history, including symptom patterns and potential triggers, is fundamental. A physical examination is performed to assess for any signs of inflammation or other abnormalities. Various tests, such as blood tests, stool tests, and imaging studies (e.g., colonoscopy), might be employed to rule out other conditions and confirm the presence of diverticula or identify specific IBS characteristics.
Colonoscopy is a crucial tool for detecting diverticulosis and assessing the overall health of the colon.
Treatment Approaches
Managing IBS and Diverticulosis, particularly when both are present, requires a multifaceted approach that considers both conditions’ specific needs. Treatment options can range from dietary modifications to medications and therapies. The effectiveness of different treatments can vary considerably among individuals.
Dietary Management
Dietary adjustments play a significant role in managing both IBS and Diverticulosis. Identifying trigger foods, such as certain types of fiber, dairy products, or processed foods, is crucial. A personalized dietary plan, potentially developed with the assistance of a registered dietitian, is often necessary. For example, a patient might benefit from a high-fiber diet to manage diverticulosis but needs to avoid certain types of fiber to control IBS symptoms.
Pharmacological Interventions, Ibs and diverticulosis what to do when you have both
Medications can help alleviate symptoms of both IBS and Diverticulosis. For IBS, various medications, including antispasmodics, antidepressants, and loperamide, may be prescribed to manage abdominal pain, bloating, and bowel movements. For diverticulosis, treatment primarily focuses on preventing complications. Pain relievers and other medications may be used to address any accompanying symptoms.
Therapies and Lifestyle Modifications
Beyond medication and diet, therapies like stress management techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can significantly impact symptom control in both IBS and Diverticulosis. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule, engaging in physical activity, and practicing stress-reducing techniques can all contribute to overall well-being and symptom management.
Successful Treatment Strategies
Individual responses to treatment vary, emphasizing the importance of personalized care. A patient with both conditions, for example, might find success through a combination of dietary modifications that address both conditions’ needs, along with the use of specific medications and stress-reducing therapies.
Dealing with both IBS and diverticulosis can be tricky. It’s crucial to find a doctor who understands the interplay of these conditions. While I’m no doctor, a key part of managing this double whammy is getting fully vaccinated, including the moderna covid 19 vaccine , to protect your overall health. This can significantly impact your digestive system’s well-being.
So, remember to focus on a personalized approach to diet, exercise, and medication, tailored to your specific needs, to manage both IBS and diverticulosis effectively.
Treatment Options Summary
| Condition | Dietary Changes | Medications | Therapies |
|---|---|---|---|
| IBS | Identify and eliminate trigger foods, adjust fiber intake | Antispasmodics, antidepressants, loperamide | Stress management, regular sleep, exercise |
| Diverticulosis | Increase fiber intake gradually, avoid certain foods | Pain relievers, antibiotics (if complications arise) | Stress management, regular sleep, exercise |
| IBS & Diverticulosis | Balanced approach addressing both conditions’ needs | Combination of medications targeting both conditions | Holistic approach combining stress reduction, regular habits |
Dietary Management
Dietary management plays a crucial role in mitigating symptoms and improving overall well-being for individuals with both IBS and diverticulosis. A tailored dietary approach can significantly reduce discomfort and flare-ups, allowing for a more comfortable and manageable lifestyle. This section will explore the importance of personalized dietary plans, common triggers, and practical strategies for implementing these changes.
Importance of Dietary Modifications
Dietary modifications are essential for managing both IBS and diverticulosis because certain foods can exacerbate symptoms in both conditions. By identifying and eliminating trigger foods, individuals can significantly reduce discomfort and improve their quality of life. This targeted approach helps manage the specific needs of each individual, rather than relying on a one-size-fits-all approach.
Dealing with both IBS and diverticulosis can be a real challenge. It’s crucial to pinpoint the exact cause of your symptoms, as some issues, like certain STDs that can mimic a UTI, like some STIs that can feel strikingly similar to a urinary tract infection , can complicate matters. Ultimately, a doctor’s diagnosis is key to developing a tailored treatment plan for your specific situation with IBS and diverticulosis.
Dietary Triggers for IBS and Diverticulosis
Numerous foods can act as triggers for IBS and diverticulosis symptoms. Common culprits often include high-fiber foods, certain types of carbohydrates, and processed foods. Identifying and eliminating these triggers is crucial for symptom control.
Dealing with both IBS and diverticulosis can be tricky. Finding the right dietary approach and lifestyle changes is key, but sometimes, medications like benzodiazepines, which have specific uses, types, and risks, as discussed here , might be suggested by your doctor. However, it’s essential to focus on the core of the issue: managing your IBS and diverticulosis symptoms with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress reduction techniques.
This approach will give you the best results in the long run.
Developing a Personalized Dietary Plan
Creating a personalized dietary plan requires careful consideration of individual needs and sensitivities. Working with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional is highly recommended. This specialized guidance ensures the plan addresses the specific needs of the individual and is tailored to their specific circumstances. It involves identifying foods that elicit symptoms in both IBS and diverticulosis.
Identifying and Eliminating Common Dietary Triggers
A comprehensive approach to identifying triggers involves keeping a detailed food diary. This diary tracks consumed foods and the corresponding symptoms experienced. Regular monitoring allows for the identification of patterns and the subsequent elimination of potential triggers. It’s important to be methodical and patient in this process.
Sample Dietary Plans for IBS and Diverticulosis
| Food Category | IBS-Friendly Options | Diverticulosis-Friendly Options | Potential Overlap |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fruits | Berries, bananas, melon (in moderation) | Berries, bananas, melon (in moderation) | Berries, bananas, melon |
| Vegetables | Leafy greens (cooked), carrots, zucchini | Leafy greens (cooked), carrots, zucchini | Leafy greens (cooked), carrots, zucchini |
| Grains | White rice, well-cooked oatmeal | White rice, well-cooked oatmeal | White rice, well-cooked oatmeal |
| Dairy | Yogurt (plain, low-sugar), cheese (in moderation) | Yogurt (plain, low-sugar), cheese (in moderation) | Yogurt (plain, low-sugar), cheese (in moderation) |
| Protein | Lean meats, fish, eggs | Lean meats, fish, eggs | Lean meats, fish, eggs |
| Processed Foods | Avoid | Avoid | Avoid |
| Sugary Drinks | Avoid | Avoid | Avoid |
Note: This is a simplified example, and individual needs may vary. Consulting a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is crucial for developing a personalized dietary plan.
Lifestyle Modifications
Living with both IBS and diverticulosis can be challenging, but adopting healthy lifestyle modifications can significantly improve symptom management and overall well-being. These changes aren’t just about diet, but also encompass stress reduction, regular exercise, and adequate sleep. By incorporating these strategies, you can take proactive steps to control your symptoms and enhance your quality of life.Effective management of both conditions requires a multifaceted approach, recognizing that each individual’s experience is unique.
Understanding how stress, exercise, and sleep impact your symptoms is crucial for developing a personalized plan. This section delves into specific lifestyle modifications, including strategies for stress reduction and the benefits of regular exercise.
Stress Management Strategies
Stress is a significant trigger for both IBS and diverticulosis symptoms. Chronic stress can exacerbate existing symptoms, leading to increased abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits. Therefore, incorporating stress-reduction techniques into your daily routine is vital. These techniques aim to calm the nervous system and promote relaxation.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practicing mindfulness and meditation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises and guided imagery, can help reduce stress levels and improve focus. Regular practice can help you become more aware of your body’s responses to stress, allowing you to manage them effectively.
- Yoga and Tai Chi: These practices combine physical postures, controlled breathing, and meditation to promote relaxation and reduce stress. They can also improve flexibility and balance, which can be beneficial for overall well-being.
- Journaling: Writing down your thoughts and feelings can be a powerful tool for processing stress and identifying triggers. This can help you understand your emotional responses better and develop coping mechanisms.
- Spending time in nature: Exposure to natural environments has been shown to reduce stress and improve mood. Even short walks in a park or spending time in a garden can have a significant impact.
The Impact of Exercise
Regular physical activity can significantly improve both IBS and diverticulosis symptoms. Exercise helps regulate bowel movements, improves digestion, and strengthens the abdominal muscles. Furthermore, it can contribute to better mood regulation and stress reduction.
- Choosing activities you enjoy: Select activities you find enjoyable, whether it’s brisk walking, swimming, cycling, or dancing. Consistency is key to experiencing the benefits.
- Gradual Progression: Start with short, low-intensity workouts and gradually increase the duration and intensity over time. This approach minimizes the risk of injury and promotes sustained participation.
- Types of exercise: Aerobic exercises like brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling are excellent choices. Strength training exercises, such as weightlifting or resistance bands, can also be beneficial.
Importance of Adequate Sleep
Adequate sleep is crucial for overall health and well-being, including managing symptoms of IBS and diverticulosis. Sleep deprivation can disrupt the body’s natural rhythms, leading to increased stress and impacting the digestive system.
- Establishing a regular sleep schedule: Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, including a regular bedtime and wake-up time, can help regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
- Creating a relaxing bedtime routine: Establish a relaxing bedtime routine to signal to your body that it’s time to sleep. This could include taking a warm bath, reading a book, or listening to calming music.
- Creating a sleep-conducive environment: Ensure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool to promote optimal sleep conditions. Avoid using electronic devices before bed.
Lifestyle Modifications Summary
| Lifestyle Modification | Impact on IBS | Impact on Diverticulosis |
|---|---|---|
| Stress Reduction Techniques (Mindfulness, Yoga) | Reduces stress-related symptoms, improves bowel regularity | Reduces stress-related symptoms, potentially improving gut health |
| Regular Exercise | Improves digestion, strengthens abdominal muscles, reduces stress | Improves digestion, strengthens abdominal muscles, reduces risk of complications |
| Adequate Sleep | Supports overall well-being, regulates digestive function | Supports overall well-being, strengthens immune system |
Medications and Supplements
Managing both IBS and diverticulosis often requires a multifaceted approach that includes medications, supplements, and lifestyle changes. Understanding the role of various medications and supplements in managing symptoms, and their potential interactions, is crucial for effective symptom relief and overall well-being. This section will delve into the use of common medications and supplements, exploring their potential benefits and drawbacks, particularly when both conditions are present.Medications and supplements can play a significant role in managing the symptoms of IBS and diverticulosis.
While they cannot cure these conditions, they can often alleviate discomfort and improve quality of life. It’s essential to remember that individual responses to medications and supplements can vary, and consulting with a healthcare professional is always recommended before starting any new treatment.
Common Medications for IBS
Several medications are used to manage the symptoms of IBS. These medications can address different aspects of the condition, such as abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, or constipation. Commonly prescribed medications include antispasmodics, which help relax the muscles in the intestines, and antidiarrheal medications, such as loperamide, for managing diarrhea. Some individuals find relief with antidepressants, which can help regulate the nervous system’s impact on gut motility.
Common Medications for Diverticulosis
Diverticulosis, in many cases, does not require specific medication. However, if diverticulitis (inflammation of the diverticula) occurs, antibiotics are commonly prescribed to treat the infection. The specific antibiotic and duration of treatment will depend on the severity and location of the infection. It’s important to note that the use of antibiotics should be carefully considered, and their potential side effects discussed with a healthcare professional.
Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics are live microorganisms, often beneficial bacteria, that can improve gut health. Prebiotics are non-digestible food ingredients that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. Both probiotics and prebiotics have shown promise in alleviating IBS symptoms, such as bloating and abdominal pain, and improving the overall gut microbiome. Research suggests that they may also potentially support gut health in individuals with diverticulosis.
However, the exact mechanisms and long-term effects are still under investigation.
Supplements for Both Conditions
Certain supplements, while not FDA-approved for treating IBS or diverticulosis, may potentially provide support for gut health. These include fiber supplements, which can help regulate bowel movements, and certain herbal remedies that are believed to have anti-inflammatory properties. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional before taking any supplements, especially if you have any underlying health conditions. Supplements should not be used as a substitute for a balanced diet and regular medical check-ups.
Potential Interactions and Side Effects
It is crucial to be aware of potential interactions between medications and supplements, particularly when managing both IBS and diverticulosis. Some medications may interact with certain supplements, altering their absorption or effectiveness. Furthermore, the combined use of medications for both conditions can lead to adverse side effects. Therefore, a thorough discussion with a healthcare professional is essential to determine the most appropriate and safest treatment plan.
Medication and Supplement Summary Table
| Medication/Supplement | Potential Effect on IBS | Potential Effect on Diverticulosis | Potential Side Effects | Important Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antispasmodics | Reduce intestinal muscle contractions, relieving pain and cramping | May not directly impact diverticulosis | Dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation | May interact with other medications |
| Antidiarrheals (e.g., loperamide) | Reduce diarrhea | May be helpful in managing diverticulitis | Constipation, abdominal cramping | May mask underlying causes of diarrhea |
| Antibiotics (for diverticulitis) | May cause temporary IBS-like symptoms | Treat infection | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, allergic reactions | Use only as prescribed |
| Probiotics | Potentially improve gut microbiota, reduce symptoms | Potentially improve gut microbiota | Gas, bloating, diarrhea | Choose strains specifically chosen for gut health |
| Prebiotics | Potentially improve gut microbiota, reduce symptoms | Potentially improve gut microbiota | Gas, bloating | May cause temporary digestive discomfort |
| Fiber supplements | Regulate bowel movements | Support healthy bowel movements | Bloating, gas, abdominal discomfort | Increase fiber intake gradually |
Potential Complications and Prevention: Ibs And Diverticulosis What To Do When You Have Both
Living with both IBS and diverticulosis can be challenging, but understanding potential complications and proactive prevention strategies can significantly improve your quality of life. This section delves into the specific risks associated with this combination and offers practical advice for mitigating them. Careful management and a proactive approach are key to minimizing the likelihood of complications.Co-existing conditions like IBS and diverticulosis can create a complex interplay, potentially leading to more frequent or severe symptoms.
This section will explore the specific complications that can arise, outlining preventive measures, and emphasizing the importance of ongoing medical care.
Potential Complications
The combination of IBS and diverticulosis can lead to a number of potential complications, some of which may be more serious than others. Common concerns include diverticulitis, which is an inflammation or infection of the diverticula. In severe cases, this can require hospitalization and antibiotics. Furthermore, the increased gut sensitivity associated with IBS can make it harder to manage flare-ups of diverticulitis.
Additionally, complications like bowel obstruction or bleeding are also possible. Symptoms may vary, and early detection is crucial.
Preventive Measures
Proactive measures can significantly reduce the risk of complications. A crucial aspect is maintaining a healthy diet. A high-fiber diet, while beneficial for diverticulosis, can sometimes exacerbate IBS symptoms. Therefore, a balanced approach is key. Furthermore, regular exercise and stress management techniques can play a significant role in overall gut health.
Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and practicing relaxation techniques are important.
Importance of Regular Medical Check-ups
Regular check-ups are essential for individuals with both IBS and diverticulosis. These visits allow your doctor to monitor your condition, assess any changes in symptoms, and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan. Early detection of potential complications, such as diverticulitis, is crucial for prompt and effective treatment. This monitoring also ensures that any changes in your health are addressed in a timely manner.
Adherence to Treatment Plans
Adherence to prescribed treatment plans is critical for managing both IBS and diverticulosis effectively. This includes following dietary recommendations, taking medications as directed, and participating in lifestyle modifications. Consistency in your approach helps prevent flare-ups and potential complications. This ongoing commitment contributes to a healthier and more stable overall condition.
Summary of Potential Complications and Preventive Strategies
| Potential Complications | Preventive Strategies |
|---|---|
| Diverticulitis (inflammation or infection of diverticula) | High-fiber diet (balanced with IBS), regular exercise, stress management |
| Bowel Obstruction | Dietary fiber intake adjusted to individual needs, regular bowel movements |
| Bleeding | Regular check-ups, adherence to treatment plan, monitoring of symptoms |
| Exacerbation of IBS Symptoms | Careful management of fiber intake, stress reduction, and regular medical care |
Managing Flare-Ups
Dealing with flare-ups of IBS and diverticulosis symptoms can be challenging, but understanding how to recognize and manage them is crucial for maintaining a good quality of life. These strategies can help you navigate these episodes effectively and prevent them from significantly disrupting your daily routines.Flare-ups, characterized by intensified symptoms, can be triggered by a variety of factors, including dietary indiscretions, stress, or changes in routine.
By learning to identify the patterns of your own symptoms, you can proactively implement strategies to mitigate discomfort and prevent prolonged episodes.
Recognizing Flare-Up Symptoms
Identifying the specific symptoms of a flare-up is the first step in effective management. Pay close attention to changes in bowel habits, abdominal pain intensity, and accompanying symptoms like bloating, gas, or nausea. These symptoms are often the first indicators of an upcoming flare-up.
Managing Flare-Up Symptoms
Effective management of flare-ups involves a multi-faceted approach that focuses on symptom relief and triggers identification. This includes dietary adjustments, stress management techniques, and medication as prescribed by your doctor. A personalized approach tailored to your individual needs is essential for optimal results.
Differentiating Flare-Ups from Other Conditions
Differentiating flare-ups from other gastrointestinal conditions is important for proper treatment. While some symptoms may overlap, distinct patterns and accompanying symptoms can help in diagnosis. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management. Consult your doctor if you suspect a condition other than IBS or diverticulosis.
Step-by-Step Guide for Managing Flare-Ups
This table provides a practical step-by-step guide for managing flare-ups. Following these steps can help you regain control and alleviate discomfort during an episode.
| Step | Action | Rationale | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Identify Trigger Foods | Note down foods that consistently trigger your symptoms. This allows you to make informed dietary choices during a flare-up. | |
| 2 | Adjust Diet | Introduce a bland diet, prioritizing easily digestible foods like rice, toast, and bananas. | This approach reduces the strain on your digestive system. |
| 3 | Increase Fluid Intake | Drink plenty of water or clear broths. | Hydration is crucial for overall well-being and preventing dehydration. |
| 4 | Manage Stress | Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation. | Stress can exacerbate symptoms. Managing stress helps to calm your body. |
| 5 | Monitor Symptoms | Keep a journal to track your symptoms and their relationship to specific triggers. | This helps you identify patterns and understand your body’s responses to different factors. |
| 6 | Seek Medical Attention | Consult your doctor if symptoms worsen or persist for an extended period. | Seek professional help for severe or persistent symptoms. |
Summary
In conclusion, coexisting with IBS and diverticulosis requires a multifaceted approach that integrates medical guidance, dietary adjustments, lifestyle modifications, and potentially, medication. By understanding the symptoms, the diagnostic process, and the range of treatment options, you can take control of your health and develop strategies to manage both conditions effectively. Remember, consistent communication with your healthcare provider is crucial to navigating your specific needs and achieving optimal health.




