Xeloda for metastatic breast cancer is a crucial topic for those facing this challenging diagnosis. This guide delves into the specifics of Xeloda’s role in treatment, exploring its mechanism of action, efficacy, potential side effects, and patient considerations. We’ll examine how Xeloda fits into the broader treatment strategy, comparing it to other therapies and analyzing the factors influencing its effectiveness.
Understanding the details of Xeloda’s use in metastatic breast cancer is paramount for informed decision-making. This in-depth look at the drug’s properties, including dosage, potential side effects, and clinical trial data, aims to provide a comprehensive overview for patients and healthcare professionals alike.
Overview of Xeloda for Metastatic Breast Cancer
Xeloda, or capecitabine, is an oral chemotherapy drug used in the treatment of various cancers, including metastatic breast cancer. It works by targeting specific cellular processes involved in tumor growth and spread. Understanding its mechanism of action, role in different treatment approaches, and dosage regimens is crucial for effective patient management. This discussion will provide a comprehensive overview of Xeloda’s application in metastatic breast cancer.
Mechanism of Action
Xeloda works by converting into a form of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) inside the body. 5-FU disrupts the DNA replication process of rapidly dividing cancer cells, ultimately inhibiting their growth and proliferation. This targeted approach aims to slow or stop the spread of the cancer to other parts of the body.
Role in Treatment Approach
Xeloda is often used in combination with other therapies, such as hormone therapy or other chemotherapy agents, to achieve optimal outcomes in metastatic breast cancer. The specific treatment plan is tailored to the individual patient’s cancer stage, subtype, and overall health. For example, in patients with hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer, Xeloda may be combined with hormonal therapies to enhance treatment efficacy.
In other cases, Xeloda might be used as a single agent in patients who have previously received other therapies, depending on the individual response.
Dosage Regimens and Administration
The dosage and administration method of Xeloda are crucial for its effectiveness and to minimize side effects. It is typically administered orally, in the form of tablets, and the dosage is determined based on factors like the patient’s weight and overall health condition. The frequency of administration is also carefully considered. The specific regimen will be determined by the oncologist based on the patient’s specific needs and the overall treatment plan.
Comparison with Other Therapies
| Drug | Drug Class | Mechanism | Side Effects | Efficacy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xeloda (Capecitabine) | Antimetabolite | Converts to 5-fluorouracil, disrupting DNA replication in rapidly dividing cells | Common: Hand-foot syndrome, diarrhea, nausea, fatigue; less common: skin rash, mouth sores, hair loss. | Generally effective in some metastatic breast cancer subtypes, often used in combination with other therapies. |
| Paclitaxel | Microtubule inhibitor | Stabilizes microtubules, interfering with cell division | Common: Peripheral neuropathy, fatigue, alopecia; less common: hypersensitivity reactions. | Effective in certain metastatic breast cancer subtypes, commonly used in combination regimens. |
| Docetaxel | Microtubule inhibitor | Stabilizes microtubules, interfering with cell division | Common: Peripheral neuropathy, fatigue, alopecia; less common: hypersensitivity reactions. | Effective in certain metastatic breast cancer subtypes, commonly used in combination regimens. |
| Trastuzumab | Monoclonal antibody | Targets HER2 receptors, inhibiting tumor growth | Common: Fatigue, skin rash, diarrhea; less common: heart problems. | Effective in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. |
The table above presents a simplified comparison. Individual responses to these therapies can vary greatly, and the choice of treatment depends on the specific characteristics of the patient’s cancer. Consulting with an oncologist is crucial for determining the most appropriate treatment plan.
Efficacy and Outcomes
Xeloda, a medication used in the treatment of metastatic breast cancer, aims to improve patients’ quality of life and potentially extend their survival. Understanding its efficacy, however, requires careful consideration of various factors influencing treatment response. This section delves into the documented evidence supporting Xeloda’s effectiveness, along with potential influencing factors and key outcome measures.Xeloda’s impact on metastatic breast cancer patients is complex and multifaceted.
Dealing with metastatic breast cancer and Xeloda can be tough, but it’s important to consider all aspects of your health. While Xeloda helps manage the disease, it’s also crucial to maintain a healthy lifestyle. This includes understanding how many calories you burn sleeping, which can help with overall well-being. Learning about the how many calories do you burn sleeping can be a valuable piece of the puzzle in managing your energy levels and nutritional needs alongside Xeloda treatment.
Ultimately, a holistic approach, including understanding calorie expenditure, can make a difference in your journey with metastatic breast cancer and Xeloda.
While it can effectively target cancer cells, the extent of its benefit varies significantly based on individual patient characteristics, tumor properties, and concomitant therapies. Analyzing response rates and survival data provides crucial insights into the drug’s overall effectiveness and the potential for positive outcomes.
Documented Evidence of Effectiveness
Xeloda, containing the active ingredient capecitabine, works by interfering with DNA replication in cancer cells, effectively hindering their growth and proliferation. Clinical trials have demonstrated Xeloda’s ability to improve outcomes for some patients with metastatic breast cancer, albeit with varying degrees of success. Published studies frequently report improvements in progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) for certain patient subgroups.
Importantly, the effectiveness of Xeloda is often evaluated in conjunction with other therapies, like chemotherapy or hormone therapy, to determine its combined impact.
Factors Influencing Treatment Response
Several factors can influence how a patient responds to Xeloda therapy. Patient characteristics such as age, overall health, and pre-existing conditions can play a role. Tumor characteristics, including the specific type of breast cancer, its stage of progression, and the presence of specific genetic markers, also significantly impact treatment outcomes. Furthermore, the concurrent use of other therapies, such as chemotherapy or hormone therapy, can influence the effectiveness of Xeloda.
A thorough understanding of these factors is crucial for optimizing treatment strategies and predicting patient responses.
Response Rates and Progression-Free Survival
Data on overall response rates and progression-free survival for patients treated with Xeloda is available in various published clinical trials. These trials have shown that while not all patients experience a complete or partial response, Xeloda can effectively delay disease progression in some patients, resulting in longer periods of stable disease. Precise response rates and PFS durations depend heavily on factors like the patient’s specific tumor characteristics and the overall clinical context.
Long-Term Effects
| Side Effect | Frequency | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Diarrhea | Common | Moderate to severe, potentially requiring hospitalization in extreme cases |
| Hand-foot syndrome (pain, redness, swelling of hands and feet) | Common | Can be uncomfortable but usually manageable with supportive care |
| Mouth sores (stomatitis) | Occasional | Mild to moderate, manageable with local treatment |
| Fatigue | Common | Variable, can range from mild to severe, impacting daily activities |
| Nausea and vomiting | Common | Mild to moderate, often manageable with anti-emetics |
| Skin rash | Occasional | Mild to moderate, usually responsive to topical treatments |
Note: Frequency and severity can vary significantly among patients. The table above presents general observations based on available data. Individual experiences may differ. Regular monitoring and communication with healthcare professionals are crucial for managing potential side effects effectively.
Side Effects and Management
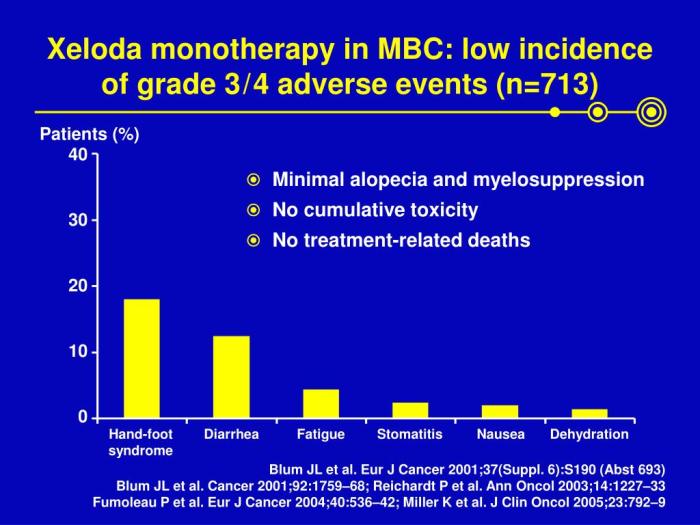
Unfortunately, Xeloda, like many cancer treatments, can cause a range of side effects. Understanding these potential side effects, how they are managed, and the importance of monitoring is crucial for patients undergoing this therapy. This section will delve into the common and severe side effects, strategies for mitigation, and the necessity of regular monitoring during treatment.
Common Side Effects
Many patients experience mild to moderate side effects, which often improve with time or with supportive care. Common side effects associated with Xeloda treatment frequently include gastrointestinal issues, fatigue, and skin reactions. Understanding these common side effects is vital for both patients and healthcare professionals in anticipating and managing them.
- Gastrointestinal issues: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and loss of appetite are common. These symptoms can be managed with antiemetics, antidiarrheal medications, and dietary adjustments. Maintaining adequate hydration is essential to prevent dehydration.
- Fatigue: Significant fatigue is a frequent side effect. It’s important to listen to the body and prioritize rest. Strategies for managing fatigue may include regular exercise (with physician approval), a balanced diet, and stress reduction techniques.
- Skin reactions: Skin rashes, dryness, or itching are potential side effects. Moisturizing the skin, using mild soaps, and avoiding harsh chemicals can help. Prompt reporting of skin changes to the healthcare team is crucial.
Potential Severe Side Effects
While less common, some severe side effects can occur. Recognizing the potential for these complications and knowing how to respond promptly is critical for patient safety. These include but are not limited to kidney problems, and liver issues.
- Kidney problems: Xeloda can potentially affect kidney function. Regular monitoring of kidney function through blood tests is crucial. Maintaining adequate hydration and reporting any unusual changes in urine output are vital steps.
- Liver problems: Liver toxicity is a possibility. Regular liver function tests are essential. Prompt reporting of symptoms like jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes), abdominal pain, or fatigue is critical.
- Neuropathy: Peripheral neuropathy, characterized by numbness, tingling, or pain in the hands and feet, can be a side effect. Prompt reporting of these symptoms to the healthcare team is vital. Managing blood sugar levels, if applicable, and consulting with a neurologist may be part of the management strategy.
Management Strategies
Proactive management of side effects is key to improving patient comfort and well-being. Strategies can range from preventative measures to supportive care. This involves a collaborative effort between the patient, healthcare team, and support systems.
- Preventative measures: Maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and managing stress levels can often lessen the impact of side effects. Regular check-ups with the medical team are important for early detection and management of potential problems.
- Supportive care: Pain medications, antiemetics, and other supportive therapies can effectively manage symptoms. Dietary adjustments, such as avoiding certain foods that exacerbate symptoms, can also be helpful.
Importance of Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring is essential to detect any adverse events early and intervene promptly. This includes blood tests to assess kidney and liver function, as well as regular assessments of overall health.
- Regular blood tests: Monitoring blood tests, including kidney and liver function tests, allows for early detection of potential complications.
- Symptom reporting: Patients should report any new or worsening symptoms promptly to their healthcare team. This allows for timely intervention and management.
Table of Common Side Effects
| Side Effect | Frequency | Management Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Nausea/Vomiting | Common | Antiemetics, dietary adjustments, hydration |
| Diarrhea | Common | Antidiarrheal medications, hydration, dietary changes |
| Fatigue | Common | Rest, balanced diet, stress reduction, exercise (with physician approval) |
| Skin Rash | Possible | Moisturizers, mild soaps, avoidance of harsh chemicals |
| Peripheral Neuropathy | Possible | Symptom reporting, neurologist consultation, blood sugar management (if applicable) |
| Kidney Problems | Possible | Regular kidney function tests, hydration, symptom reporting |
| Liver Problems | Possible | Regular liver function tests, symptom reporting, avoidance of alcohol and certain medications |
Patient Selection and Considerations
Choosing the right metastatic breast cancer patient for Xeloda therapy involves careful evaluation and consideration of various factors. This selection process is crucial to maximizing treatment efficacy and minimizing potential risks. Individualized treatment plans are essential to ensure the best possible outcomes, considering patient preferences and overall health.Patient selection for Xeloda involves a multifaceted approach, recognizing that treatment decisions must align with patient goals, preferences, and potential risks.
Factors beyond the tumor characteristics, such as comorbidities and patient motivation, significantly impact the success of Xeloda therapy. Understanding these factors allows healthcare professionals to tailor treatment strategies to individual patient needs.
Factors Influencing Xeloda Prescription
Several factors influence the decision to prescribe Xeloda for metastatic breast cancer patients. Tumor characteristics, such as the type of breast cancer, the presence of specific genetic mutations, and the extent of the disease’s spread, play a significant role. Patient-specific factors, such as age, overall health, and presence of other medical conditions, also need careful consideration. Furthermore, patient preferences and expectations concerning treatment duration, side effects, and quality of life must be acknowledged and incorporated into the treatment plan.
Importance of Patient Preferences, Comorbidities, and Other Factors
Patient preferences regarding treatment duration, potential side effects, and quality of life impact the decision-making process. Understanding these preferences is crucial for tailoring the treatment plan to the individual patient. Comorbidities, such as kidney or liver dysfunction, heart conditions, or diabetes, can affect the suitability of Xeloda. These factors must be assessed and managed proactively to minimize risks.
Furthermore, the patient’s overall health status, including nutritional status, functional abilities, and psychosocial factors, should be evaluated to determine their capacity to tolerate Xeloda therapy.
Patient Education and Counseling Materials
Comprehensive patient education and counseling are essential components of Xeloda therapy. Patients should receive detailed information about the medication, its mechanism of action, potential benefits, and risks. This includes information about possible side effects, their management, and reporting procedures. The importance of adherence to the treatment regimen and regular follow-up appointments should be emphasized. Educational materials should be presented in a clear, concise, and easily understandable format.
The materials should also include contact information for healthcare providers and support groups.
Dealing with Xeloda for metastatic breast cancer can be tough, but incorporating regular exercise, like the exercise to offset sitting recommendations, can really help. Staying active is crucial for overall well-being, and it can potentially complement the treatment’s effects. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including exercise, is important for managing the challenges of Xeloda therapy for metastatic breast cancer.
Patient Selection Criteria
| Criteria | Justification | Exceptions |
|---|---|---|
| Presence of HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer | Xeloda is not a standard treatment for HER2-positive breast cancer. | Rare cases with unusual HER2-negative characteristics, when clinically indicated and closely monitored by the oncologist. |
| Adequate organ function (liver and kidney) | Xeloda is primarily metabolized by the liver and excreted by the kidneys. Compromised organ function can increase the risk of toxicity. | Patients with mild to moderate impairment may be eligible, provided appropriate dose adjustments and close monitoring are implemented. |
| Absence of significant gastrointestinal issues | Xeloda can cause gastrointestinal side effects. Patients with pre-existing conditions may be at increased risk. | Patients with mild gastrointestinal conditions may be considered, provided careful monitoring and supportive care are implemented. |
| Patient understanding and willingness to adhere to treatment regimen | Effective treatment depends on patient cooperation and adherence to the prescribed regimen. | Patients with cognitive impairments or other barriers to adherence may be eligible, but close support and alternative strategies are needed. |
| Realistic expectations and goals | Xeloda’s effectiveness is not guaranteed in all patients. Patients need realistic expectations about treatment outcomes. | Patients with a high expectation of complete remission or cure, but understand the limitations of the therapy, may be eligible. |
Clinical Trials and Research: Xeloda For Metastatic Breast Cancer
Exploring the potential of Xeloda in metastatic breast cancer goes beyond the established treatments. Researchers are actively investigating its use in combination therapies and specific patient populations to optimize outcomes and identify the best treatment approaches. This research is crucial for improving the quality of life and survival rates for patients with this challenging disease.
Combination Therapies
Recent research emphasizes the potential benefits of combining Xeloda with other targeted therapies or chemotherapy regimens. This approach aims to enhance efficacy by targeting multiple pathways involved in cancer growth and spread. For instance, studies are examining the synergy between Xeloda and PARP inhibitors, aiming to exploit vulnerabilities in cancer cells.
Specific Patient Subsets
Researchers are also investigating whether Xeloda might be more effective in certain subgroups of metastatic breast cancer patients. Factors like specific hormone receptor status, HER2 status, or tumor genetic profiles are being examined to identify patients who may derive the greatest benefit from Xeloda. This personalized approach could lead to more tailored treatment strategies.
Recent Study Findings
Several recent studies have shown promising results regarding Xeloda’s role in combination therapies. One study, for example, demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in progression-free survival when Xeloda was combined with a specific chemotherapy agent in HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer patients. Another study highlighted the potential of Xeloda in delaying disease progression in patients with specific genetic mutations. These findings underscore the potential of Xeloda as a component of a broader treatment strategy.
Impact on Future Treatment
The research advancements surrounding Xeloda are reshaping the future of metastatic breast cancer treatment. By understanding how Xeloda interacts with other therapies and its potential effectiveness in specific patient populations, oncologists can develop more targeted and personalized treatment plans. This could lead to better outcomes and improved quality of life for patients.
Comparison of Clinical Trial Results
| Trial | Combination Therapy | Patient Subset | Primary Outcome (e.g., PFS, OS) | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trial 1 | Xeloda + Chemotherapy A | HER2-negative MBC | Progression-Free Survival (PFS) | Statistically significant improvement in PFS compared to chemotherapy A alone. |
| Trial 2 | Xeloda + PARP Inhibitor B | Triple-Negative MBC with specific BRCA mutations | Overall Survival (OS) | Trend towards improved OS, requiring further larger-scale studies. |
| Trial 3 | Xeloda + Endocrine Therapy | ER+/PR+ MBC with disease progression on prior endocrine therapy | Time to Progression | No significant difference in time to progression compared to endocrine therapy alone. |
Note: This table provides a simplified representation of clinical trial results. Specific details, including statistical significance levels, and other relevant data would be presented in full publications.
Drug Interactions and Contraindications
Navigating the complexities of cancer treatment often involves careful consideration of potential drug interactions. Xeloda, while effective in treating metastatic breast cancer, isn’t without its potential for interactions with other medications. Understanding these interactions and contraindications is crucial for ensuring patient safety and optimal treatment outcomes. A thorough medication reconciliation, encompassing all prescribed medications, supplements, and herbal remedies, is essential.
Potential Drug Interactions
Careful attention to drug interactions is paramount. Concurrent medications can alter Xeloda’s metabolism or affect its efficacy, potentially leading to adverse effects or treatment failure. It’s vital to recognize that interactions aren’t always immediately apparent, and ongoing monitoring is crucial.
Many medications, particularly those metabolized by the same liver enzymes as Xeloda, can influence its levels in the body. This can lead to either increased toxicity or reduced effectiveness. For example, certain antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs might impact Xeloda’s clearance, potentially raising the risk of side effects.
Important Considerations for Medication Reconciliation
Medication reconciliation is a crucial step in managing potential interactions. This involves a comprehensive review of all medications the patient is currently taking, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, supplements, and herbal remedies. Incomplete or inaccurate information can lead to errors in treatment planning.
Healthcare providers must diligently collect and verify all medications. A detailed patient history is necessary, including any prior adverse reactions to medications, to identify potential risk factors. This thorough assessment helps anticipate potential problems and tailor the treatment plan accordingly. This careful approach helps minimize the risk of unwanted interactions.
Contraindications for Xeloda Use
Certain conditions can make Xeloda unsuitable for certain patients. A thorough evaluation of a patient’s medical history is essential to identify any contraindications. For instance, severe kidney or liver dysfunction can increase the risk of side effects, and these conditions should be carefully considered before prescribing Xeloda.
Patients with a known hypersensitivity or allergy to Xeloda or its components are also contraindicated. A detailed allergy history is critical. In such cases, alternative treatment options should be explored.
Potential Interactions with Other Cancer Treatments
Xeloda can interact with other cancer treatments. For example, concomitant use with certain chemotherapy drugs may alter their effectiveness or increase the risk of side effects.
Xeloda, a common treatment for metastatic breast cancer, often comes with a range of side effects. One important consideration alongside treatment is the potential for fasting to lead to low blood pressure, which can be a concern for patients. Managing this alongside Xeloda treatment is crucial for a patient’s overall health. Learning more about how fasting can affect blood pressure is key, as is understanding how these factors relate to the treatment plan.
A good resource for exploring this is fasting low blood pressure. Ultimately, open communication with your healthcare team is vital when navigating these complex issues, and understanding the potential impacts of different lifestyle choices on your treatment for metastatic breast cancer.
Furthermore, specific targeted therapies used in conjunction with Xeloda may require careful monitoring and adjustment of dosages to mitigate potential adverse reactions. These interactions can significantly impact treatment outcomes and necessitate careful coordination between different specialists involved in the patient’s care.
Table of Potential Drug Interactions
| Interacting Drug | Mechanism | Precautions |
|---|---|---|
| Certain antibiotics (e.g., Ciprofloxacin) | May affect Xeloda metabolism, potentially increasing side effects. | Close monitoring of Xeloda levels and side effects is essential. Adjustments to Xeloda dosage may be necessary. |
| NSAIDs (e.g., Ibuprofen) | May increase risk of gastrointestinal complications when used with Xeloda. | Monitor for signs of gastrointestinal bleeding or ulceration. Alternative pain management strategies may be considered. |
| Certain chemotherapy drugs (e.g., 5-fluorouracil) | Potential for additive toxicity to the bone marrow and other organs. | Careful monitoring of blood counts and organ function is crucial. Close coordination between oncologists is vital. |
| Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) | May reduce Xeloda absorption, potentially decreasing efficacy. | Consider alternative medications where possible. Adjust Xeloda dosage if necessary, after consulting with the physician. |
Alternative Treatment Approaches
Choosing the right treatment for metastatic breast cancer is a complex decision, often involving careful consideration of various factors. Individual patient characteristics, tumor characteristics, and the specific stage and spread of the disease all play crucial roles in determining the most appropriate course of action. Xeloda, while effective for some, isn’t the only option, and understanding the landscape of alternative therapies is essential for informed decision-making.
Comparison with Other Targeted Therapies
Xeloda, a fluoropyrimidine, targets DNA replication. Other targeted therapies, like tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) or hormonal therapies, operate through different mechanisms. For example, TKIs like lapatinib or neratinib target specific proteins involved in cell growth and proliferation, while hormonal therapies like tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors target hormone receptors. The choice between these therapies hinges on the specific characteristics of the tumor and the patient.
For instance, tumors with HER2 amplification might respond better to TKIs. Understanding the molecular profile of the tumor can help predict which targeted therapies might be more effective.
Comparison with Chemotherapy Regimens
Chemotherapy regimens for metastatic breast cancer often involve combinations of drugs targeting rapidly dividing cells. Common regimens include anthracyclines, taxanes, and others. The efficacy and side effect profiles of these regimens can vary. For example, anthracyclines, while potent, can cause significant cardiac toxicity. The decision to use chemotherapy alongside or instead of Xeloda often depends on factors such as the patient’s overall health and the aggressiveness of the cancer.
Some patients may benefit from a combination approach, while others may respond better to targeted therapies.
Table Comparing Xeloda to Alternative Treatments
| Drug | Mechanism | Efficacy | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xeloda (Capecitabine) | Inhibits DNA synthesis by converting to 5-fluorouracil | Demonstrated efficacy in certain subtypes of metastatic breast cancer, particularly in those with deficient DNA repair mechanisms. | Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, hand-foot syndrome, and mucositis. Severe toxicity is less frequent compared to some chemotherapy regimens. |
| Lapatinib | Inhibits the growth of cancer cells by blocking the function of the HER2 protein | Effective for HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. | Potential side effects include skin rash, diarrhea, fatigue, and liver problems. |
| Tamoxifen | Blocks the estrogen receptor, preventing the growth of estrogen-receptor positive breast cancer cells. | Effective for hormone receptor positive metastatic breast cancer. | Potential side effects include hot flashes, nausea, and vaginal dryness. |
| Anthracycline-based chemotherapy | Disrupts DNA structure and function of cancer cells. | Effective for many metastatic breast cancer types, but with significant side effects. | Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, hair loss, and cardiac toxicity. |
Rationale for Choosing Xeloda, Xeloda for metastatic breast cancer
The rationale for selecting Xeloda over other treatments depends on the individual patient and their specific tumor characteristics. Patients with certain genetic mutations or specific subtypes of metastatic breast cancer may respond better to Xeloda. The less intense side effects compared to some chemotherapy regimens might make Xeloda a suitable choice for patients with comorbidities or those who prefer less aggressive treatment.
For example, a patient with a history of heart conditions might be a better candidate for Xeloda due to its lower risk of cardiac toxicity compared to anthracyclines.
Strengths and Limitations of Different Strategies
Each treatment strategy possesses unique strengths and limitations. Targeted therapies offer the potential for fewer side effects compared to chemotherapy, but their effectiveness depends on the specific genetic characteristics of the tumor. Chemotherapy regimens, while often effective, can lead to significant side effects. Xeloda, positioned as a targeted therapy, provides a balance between efficacy and side effect profile, but its effectiveness isn’t universal.
The decision-making process often involves a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s overall health, the tumor characteristics, and the potential benefits and risks of each treatment option.
Final Wrap-Up

In conclusion, Xeloda presents a valuable treatment option for some metastatic breast cancer patients, but it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. Careful consideration of individual patient factors, potential side effects, and alternative treatments is essential. The information presented here highlights the multifaceted nature of this therapy and encourages a collaborative approach between patients, doctors, and support systems. Continued research and clinical trials will undoubtedly shape the future of Xeloda’s use in this complex disease.




