What is indeterminate colitis? This perplexing condition lies somewhere between Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, making it a unique and challenging digestive disorder. Understanding its intricacies, from defining characteristics to diagnostic procedures, is crucial for those affected and those seeking to learn more. This exploration delves into the complexities of this inflammatory bowel disease, providing insights into its causes, pathophysiology, and the various management strategies.
Indeterminate colitis presents a complex puzzle for both patients and healthcare professionals. Its symptoms can vary widely, from mild discomfort to debilitating pain, and its unpredictable nature makes diagnosis and treatment particularly challenging. This in-depth look will cover the spectrum of experiences, offering a comprehensive understanding of this often-misunderstood condition.
Definition and Overview
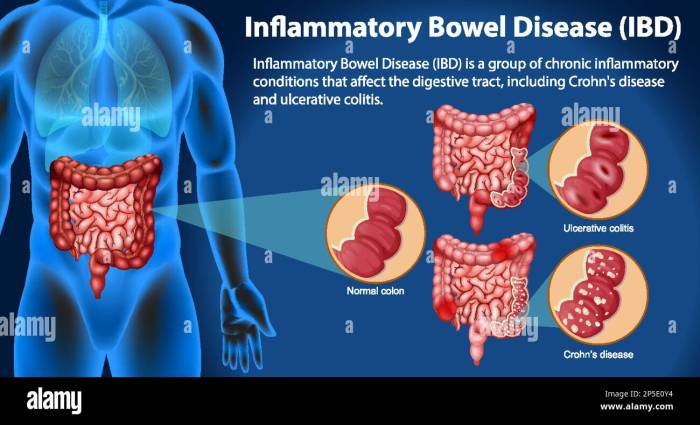
Indeterminate colitis is a frustrating and perplexing condition, often characterized by a diagnostic challenge for both patients and healthcare professionals. It represents a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that doesn’t neatly fit into the established categories of Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis. This ambiguity necessitates a thorough understanding of its characteristics and diagnostic process to provide effective management.This condition’s unpredictable nature makes it crucial to recognize the subtle differences in symptoms and responses to treatment.
Unlike Crohn’s disease, which can affect any part of the digestive tract, indeterminate colitis primarily involves the colon. Understanding these distinctions is vital for both early diagnosis and tailored treatment strategies.
Defining Indeterminate Colitis
Indeterminate colitis is a form of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that exhibits features of both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Its defining characteristic is the inability to definitively classify the disease as either Crohn’s or ulcerative colitis based on the initial presentation and endoscopic findings. The combination of these characteristics makes it a significant challenge in diagnosis. This lack of clear classification necessitates a careful evaluation of symptoms and diagnostic tests to distinguish it from other IBD forms.
Key Characteristics Distinguishing Indeterminate Colitis
The core characteristic of indeterminate colitis is its diagnostic ambiguity. It shares characteristics of both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, making it difficult to place it neatly into one category. These overlapping features often lead to initial diagnostic uncertainty. The unpredictable course and response to treatment further complicate the picture.
Symptoms of Indeterminate Colitis
Symptoms of indeterminate colitis can vary significantly in severity and presentation, mirroring the overlapping nature of the condition. Mild cases might present with infrequent episodes of mild abdominal discomfort and occasional loose stools, while severe cases can lead to frequent bloody diarrhea, severe abdominal pain, and significant weight loss. The presentation can vary across individuals and disease stages.
- Mild Symptoms: These might include intermittent abdominal discomfort, mild cramping, and infrequent loose stools. There might be limited or no blood in the stool.
- Moderate Symptoms: More frequent bowel movements, potentially with blood, are common. Abdominal pain and cramping become more pronounced. Mild to moderate weight loss may occur.
- Severe Symptoms: These can include frequent bloody diarrhea, severe abdominal pain, fever, and significant weight loss. Complications such as toxic megacolon might emerge.
Diagnostic Process for Indeterminate Colitis
The diagnostic process for indeterminate colitis relies on a combination of clinical evaluation, endoscopic examinations, and laboratory tests. A careful history, including symptom duration, frequency, and severity, is crucial for initial assessment.
- Colonoscopy: This procedure involves inserting a flexible tube with a camera into the colon to visualize the lining and identify any abnormalities. It allows for detailed examination of the colon’s entire length.
- Biopsy: Small tissue samples (biopsies) are taken during the colonoscopy to examine under a microscope for inflammation and other abnormalities.
- Blood Tests: These can help assess inflammation levels and rule out other conditions.
- Stool Tests: These tests can identify the presence of blood, infection, or other abnormalities in the stool.
Key Differences Between IBD Types
| Characteristic | Indeterminate Colitis | Crohn’s Disease | Ulcerative Colitis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Primarily colon, but can affect parts of the small intestine | Can affect any part of the digestive tract | Affects only the colon |
| Inflammation Pattern | Patches of inflammation, often both transmural and superficial | Transmural inflammation (through the wall of the intestine) | Superficial inflammation (limited to the lining of the colon) |
| Symptoms | Varied, overlapping with Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis | Abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, possible fistulas | Bloody diarrhea, rectal bleeding, abdominal pain |
Causes and Risk Factors
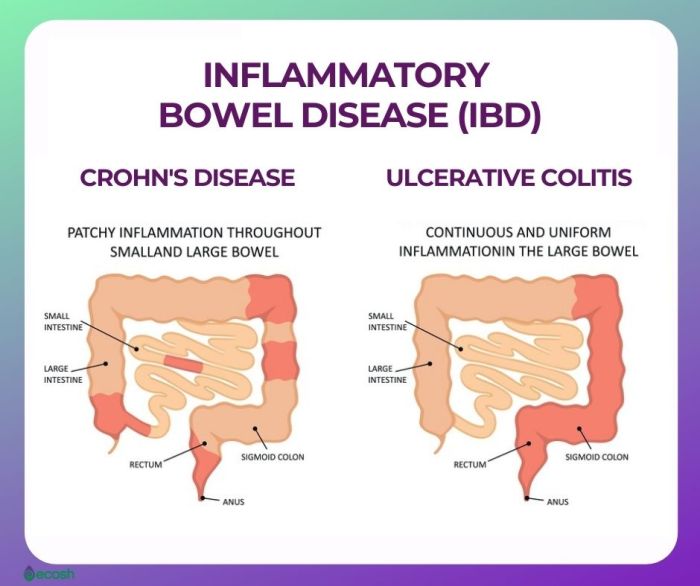
Indeterminate colitis, a perplexing inflammatory bowel disease, often presents a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. While the precise causes remain elusive, a combination of genetic predispositions and environmental triggers likely plays a crucial role in its development. Understanding these factors is essential for developing targeted prevention and treatment strategies.The multifactorial nature of indeterminate colitis underscores the complexity of this condition.
It’s not a simple case of one specific cause but rather a confluence of various elements interacting to initiate and perpetuate the inflammatory process. This intricate interplay between genetics and environmental factors makes pinpointing a single cause challenging.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetic factors are believed to play a significant role in the susceptibility to developing indeterminate colitis. Family history of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, often serves as a strong indicator of increased risk. Individuals with a family history of IBD may possess specific genetic variations that increase their likelihood of developing indeterminate colitis.
This suggests a potential link between shared genetic markers and the development of this condition.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as diet, lifestyle, and exposure to certain pathogens, may also contribute to the development of indeterminate colitis. Dietary habits, stress levels, and exposure to environmental toxins may influence the immune system’s response, potentially exacerbating the inflammatory process in genetically susceptible individuals. While these factors don’t directly cause the condition, they can act as triggers in those with a genetic predisposition.
Potential Triggers
Various factors can potentially trigger or worsen the symptoms of indeterminate colitis. These triggers can range from specific dietary components to infections or even stress. Identifying and avoiding these triggers is crucial in managing the condition effectively.
Risk Factors and Prevalence
The prevalence of indeterminate colitis may vary across different populations. Factors such as ethnicity, geographic location, and socioeconomic status could contribute to these variations. Further research is necessary to fully understand the distribution of indeterminate colitis across various demographics. This is crucial for targeted public health initiatives and early intervention strategies.
Potential Triggers and Risk Factors Table
| Category | Potential Triggers/Risk Factors | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Genetics | Family history of IBD | Presence of IBD in close relatives increases susceptibility. |
| Specific genetic variations | Certain genes may predispose individuals to the condition. | |
| Immune system variations | Variations in immune responses might increase susceptibility to inflammation. | |
| Environmental Factors | Dietary factors | Certain foods, dietary habits, and nutritional deficiencies might contribute. |
| Lifestyle factors | Stress, smoking, and lack of physical activity could exacerbate the condition. | |
| Infections/Toxins | Exposure to specific pathogens or environmental toxins might trigger inflammation. |
Pathophysiology
Indeterminate colitis, a perplexing inflammatory bowel disease, remains shrouded in mystery regarding its precise underlying mechanisms. While its clinical presentation often mimics both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, the exact pathophysiological pathways leading to its development and progression remain incompletely understood. This lack of clarity underscores the need for ongoing research to unravel the complexities of this enigmatic condition.The pathophysiology of indeterminate colitis is characterized by a complex interplay of genetic predisposition, environmental triggers, and aberrant immune responses.
This interplay fuels the chronic inflammation and tissue damage that are hallmarks of the disease. Understanding these intricate mechanisms is crucial for developing targeted therapies and improving patient outcomes.
Underlying Mechanisms
The precise triggers initiating the inflammatory cascade in indeterminate colitis remain elusive. However, it’s hypothesized that a combination of genetic susceptibility and environmental factors may contribute to the disease’s development. Genetic variations may predispose individuals to immune dysregulation, making them more susceptible to environmental stimuli. These environmental factors could include infections, dietary components, or even stress.
Immunological Processes
The immune system plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of indeterminate colitis. Aberrant immune responses, including dysregulated T cell activation and inappropriate cytokine production, are thought to contribute to the inflammatory cascade. An imbalance in the Th1/Th2/Th17 cell balance and an overproduction of inflammatory mediators such as TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, and IL-6 are implicated. Furthermore, an impaired regulatory T cell function may contribute to the chronic inflammatory response.
Inflammation and Tissue Damage
Chronic inflammation is a defining feature of indeterminate colitis. This inflammation results in significant tissue damage, characterized by mucosal ulcerations, crypt abscesses, and transmural inflammation, potentially extending throughout the bowel wall. The specific mechanisms leading to tissue injury in indeterminate colitis are not fully elucidated but are believed to involve a complex interplay of immune cells and inflammatory mediators.
Interplay of Immune System, Genetics, and Environmental Factors
The development of indeterminate colitis is a multifactorial process involving a complex interplay between genetic susceptibility, environmental triggers, and immune dysregulation. Genetic predisposition, possibly involving variations in genes related to immune response, inflammatory pathways, or intestinal barrier function, may increase the risk of developing the disease. Environmental factors, such as infections or dietary components, could then trigger or exacerbate the inflammatory response in genetically susceptible individuals.
This intricate interplay underscores the difficulty in predicting individual susceptibility and the need for further research.
Differences from Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis
Indeterminate colitis differs from Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis in its unpredictable pattern of inflammation. Unlike Crohn’s disease, which typically involves discontinuous inflammation affecting any layer of the bowel wall, indeterminate colitis displays a more diffuse pattern of inflammation. Furthermore, the inflammation in indeterminate colitis can affect both the colon and small intestine, unlike ulcerative colitis, which is typically limited to the colon.
Indeterminate colitis, a tricky digestive condition, can be a real pain. It’s basically when doctors can’t pinpoint the exact type of inflammatory bowel disease you have. This can make figuring out the right treatment a bit of a puzzle. Sometimes, the same symptoms that manifest in indeterminate colitis can be similar to those related to sleep paralysis.
To better understand the factors influencing these strange sensations, check out this insightful article on what causes sleep paralysis. But, regardless of the sleep issues, understanding the different factors contributing to indeterminate colitis is key to effective management.
This characteristic makes diagnosis and treatment more challenging.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Unraveling the mystery of indeterminate colitis requires a meticulous diagnostic journey and a personalized treatment approach. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for tailoring a strategy that addresses the specific needs of each patient, potentially preventing long-term complications. Treatment aims to alleviate symptoms, maintain remission, and prevent disease progression.The diagnostic process for indeterminate colitis often involves a combination of methods to gather comprehensive information and rule out other conditions.
This approach helps to pinpoint the underlying cause and guide the most effective treatment plan. Treatment strategies vary depending on the individual’s response to different therapies, and long-term management often requires ongoing monitoring and adjustments.
Diagnostic Procedures
A thorough evaluation is essential to distinguish indeterminate colitis from other inflammatory bowel diseases. This involves a combination of clinical assessments, laboratory tests, and imaging techniques. Physicians carefully consider the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and physical examination findings to formulate a preliminary diagnosis.
- Endoscopy and Colonoscopy: These procedures allow visualization of the colon’s lining, enabling the identification of inflammation, ulcerations, and other abnormalities. Biopsies are often taken during these procedures to examine tissue samples under a microscope for further analysis. This helps differentiate between different types of colitis and evaluate the extent of the inflammation.
- Imaging Studies: Imaging techniques such as CT scans and MRI scans can provide detailed images of the abdomen and pelvis. These can help assess the extent of inflammation and identify complications like strictures or abscesses. Imaging is especially helpful in evaluating the involvement of surrounding tissues or organs.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests can assess inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). These tests help indicate the level of inflammation in the body. Fecal calprotectin and lactoferrin levels can also provide insights into intestinal inflammation.
Treatment Options
Indeterminate colitis management often involves a multifaceted approach tailored to individual needs. The primary goal is to achieve and maintain remission, alleviate symptoms, and prevent complications.
Indeterminate colitis, a tricky digestive condition, can sometimes present with unusual symptoms. While often associated with general gut issues, it’s important to remember that some individuals experience other symptoms like those seen in “weeping legs and diabetes” weeping legs and diabetes. Ultimately, the precise cause and presentation of indeterminate colitis remain somewhat mysterious, making diagnosis and treatment challenging.
- Medications: Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are frequently used to reduce inflammation. Immunomodulators, such as azathioprine and 6-mercaptopurine, are often employed for long-term management and may be used alongside or in place of steroids to control inflammation and potentially prevent disease progression. Biologic therapies, like anti-TNF agents, are also considered in cases where other treatments are ineffective or not tolerated.
These medications target specific immune cells involved in the inflammatory process.
- Dietary Modifications: A tailored diet can play a supportive role in managing symptoms. A low-fiber diet might be recommended initially to minimize intestinal irritation, while later, a balanced diet tailored to individual needs and tolerance is encouraged to ensure adequate nutrition. Some patients may benefit from dietary restrictions for specific food intolerances or sensitivities.
- Surgical Interventions: Surgery may be necessary in severe cases with complications such as strictures, fistulas, or significant bleeding. Surgery aims to remove diseased segments of the colon and restore normal bowel function.
Comparison of Treatment Approaches
The effectiveness of different treatment approaches can vary significantly depending on the individual’s response. Corticosteroids provide rapid symptom relief but can have side effects. Immunomodulators may take several weeks or months to demonstrate their full effect. Biologic therapies offer targeted immune modulation but may come with their own set of potential side effects.
Personalized Treatment Plans
Tailoring treatment plans to the specific needs of each patient is crucial for optimal management of indeterminate colitis. Factors like disease severity, symptom presentation, and individual patient characteristics are taken into consideration when designing a personalized treatment strategy.
Indeterminate colitis is a tricky condition, right? It’s a type of inflammatory bowel disease where doctors can’t definitively pinpoint the exact cause. While exploring natural remedies, I’ve been fascinated by the potential benefits of L-theanine, and I’m currently diving deep into the topic in this comprehensive guide: l theanine everything you need to know. It’s interesting to see how different approaches might impact the overall health of someone with indeterminate colitis, although more research is needed to confirm any direct links.
| Diagnostic Test/Procedure | Description |
|---|---|
| Endoscopy/Colonoscopy | Visual inspection of the colon’s lining, tissue biopsies possible. |
| CT Scan/MRI Scan | Detailed imaging of the abdomen and pelvis, to evaluate inflammation extent. |
| Blood Tests (CRP, ESR) | Assess inflammatory markers in the blood. |
| Fecal Calprotectin/Lactoferrin | Assess intestinal inflammation levels in stool. |
Management and Prognosis: What Is Indeterminate Colitis
Indeterminate colitis, a perplexing inflammatory bowel disease, demands careful management and ongoing monitoring to ensure the best possible outcomes. Understanding the potential long-term implications and lifestyle adjustments is crucial for individuals facing this diagnosis. A personalized approach, integrating medical guidance, lifestyle modifications, and emotional support, plays a pivotal role in navigating the challenges of indeterminate colitis.Effective management of indeterminate colitis hinges on a comprehensive approach that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of the condition.
This involves regular check-ups, tailored dietary recommendations, and access to support networks to foster a positive outlook and maintain overall well-being. The journey toward managing indeterminate colitis requires proactive participation from both the patient and healthcare team.
Importance of Ongoing Monitoring and Follow-up
Regular monitoring and follow-up visits are essential for individuals with indeterminate colitis. These visits allow healthcare providers to track disease activity, assess response to treatment, and identify any potential complications early on. Early detection of flare-ups or worsening symptoms enables prompt intervention, preventing further damage to the colon and maintaining a stable condition. Monitoring also allows for adjustments to treatment plans as needed.
This proactive approach fosters better long-term outcomes.
Long-Term Prognosis and Potential Complications
The long-term prognosis for indeterminate colitis varies greatly depending on individual factors such as disease activity, response to treatment, and overall health. Some individuals may experience periods of remission, while others may face ongoing challenges. Potential complications include chronic inflammation, strictures (narrowing of the colon), and increased risk of colorectal cancer. The severity of complications can range from mild discomfort to life-altering conditions.
Understanding these potential issues empowers individuals to proactively manage their health.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Dietary Recommendations
Adopting healthy lifestyle choices can play a significant role in managing indeterminate colitis. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, while limiting trigger foods, can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health. Regular exercise, stress management techniques, and adequate sleep are also crucial components of a comprehensive management strategy. Specific dietary recommendations should be tailored to individual needs and in consultation with a registered dietitian or gastroenterologist.
Role of Support Groups and Mental Health Resources
Living with a chronic condition like indeterminate colitis can take an emotional toll. Support groups provide a safe space for individuals to share experiences, connect with others facing similar challenges, and gain emotional support. These groups offer a sense of community and shared understanding. Mental health resources, including counseling or therapy, can help individuals cope with the emotional aspects of the condition, develop coping mechanisms, and enhance their overall well-being.
Seeking professional guidance is a vital part of managing the emotional burden of indeterminate colitis.
Potential Complications and Long-Term Management Strategies
| Potential Complications | Long-Term Management Strategies |
|---|---|
| Chronic inflammation | Regular medical check-ups, adherence to treatment plans, and lifestyle modifications. |
| Strictures (narrowing of the colon) | Regular endoscopic surveillance, potential surgical interventions, and dietary modifications to prevent further narrowing. |
| Increased risk of colorectal cancer | Regular colonoscopies for early detection and removal of precancerous polyps, and close monitoring of disease activity. |
| Nutritional deficiencies | Regular blood tests to monitor nutrient levels and dietary supplements as needed. |
| Anxiety and depression | Seeking support from support groups, mental health professionals, and connecting with others who understand the condition. |
Living with Indeterminate Colitis
Living with indeterminate colitis is a complex journey marked by uncertainty and fluctuating symptoms. Beyond the physical challenges, the emotional and psychological toll can be significant. Navigating the healthcare system and finding reliable support are crucial for maintaining a positive quality of life. This section will explore the practical aspects of managing indeterminate colitis, from emotional well-being to accessing resources.
Challenges and Difficulties
Indeterminate colitis presents a unique set of difficulties. Patients often experience unpredictable flare-ups and symptom variations, making it hard to anticipate and manage their condition. This unpredictability can significantly impact daily routines, social activities, and overall well-being. The uncertainty surrounding the diagnosis itself can also be a source of anxiety and stress, as patients grapple with potential future health implications.
The need for ongoing medical monitoring and potential long-term treatment plans can also contribute to a sense of chronic illness.
Managing the Emotional and Psychological Impact
Coping with the emotional and psychological aspects of indeterminate colitis is crucial for overall well-being. Recognizing and acknowledging the emotional toll of the condition is a first step. Strategies such as stress-reduction techniques, mindfulness practices, and seeking support from mental health professionals can be very helpful. Joining support groups or online communities allows for shared experiences and validation.
Remember that emotional well-being is as important as physical health.
Importance of Patient Education and Self-Management
Patient education plays a critical role in improving quality of life. Understanding the condition, treatment options, and potential complications empowers individuals to actively participate in their healthcare. Self-management techniques, such as dietary modifications, stress reduction, and medication adherence, can significantly influence symptom control and overall well-being. By actively managing the condition, patients can gain a sense of control and independence.
Navigating Healthcare Systems and Accessing Support Services, What is indeterminate colitis
Successfully navigating the healthcare system is vital for managing indeterminate colitis effectively. Patients should develop a strong relationship with their gastroenterologist and other healthcare providers. Clearly communicating symptoms, concerns, and treatment goals to healthcare professionals is essential. Furthermore, understanding the specific healthcare system’s resources and support services available to patients with chronic conditions can be very beneficial.
Exploring options like support groups, community resources, and patient advocacy organizations can also be valuable.
Resources for Patients
Effective support networks are crucial for navigating indeterminate colitis. A strong support system can provide emotional encouragement and practical assistance. A list of potential resources is presented below:
- Support Groups: Local support groups or online forums can provide a safe space for sharing experiences and receiving emotional support from others who understand the challenges of living with indeterminate colitis. These groups often offer a sense of community and shared understanding.
- Online Communities: Online communities and forums dedicated to inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) can be valuable resources. These platforms offer access to information, advice, and encouragement from a wider network of individuals.
- Educational Materials: Numerous organizations provide educational materials on IBD. These materials can offer detailed information about indeterminate colitis, treatment options, and self-management strategies. Reliable sources include the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation of America and other reputable medical organizations.
Final Review
In conclusion, indeterminate colitis stands as a fascinating and challenging condition, demanding a personalized approach to diagnosis and management. Navigating the complexities of this illness requires a deep understanding of its multifaceted nature, from its underlying causes to the crucial role of ongoing monitoring and support. By exploring the various aspects of this condition, we aim to provide a clearer picture of indeterminate colitis and empower those affected to live fulfilling lives.




