What is antisocial personality disorder aspd – What is antisocial personality disorder (ASPD)? This complex condition, often characterized by a disregard for social norms and the rights of others, is a serious mental health concern that affects individuals and their relationships. Understanding its diagnostic criteria, potential causes, and treatment approaches is crucial for both those affected and those who want to support them.
This in-depth exploration delves into the various facets of ASPD, from its defining characteristics and potential risk factors to effective treatment strategies and the social and legal implications it presents. We’ll examine case studies to illustrate the complexities of the disorder and explore the challenges of living with ASPD, while also offering support strategies for those affected.
Defining Antisocial Personality Disorder (ASPD)

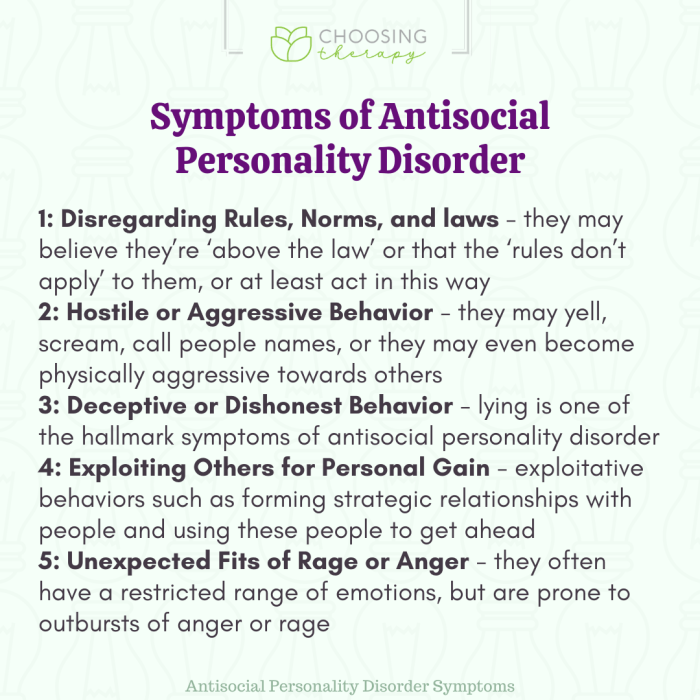
Antisocial personality disorder (ASPD) is a pervasive pattern of disregard for and violation of the rights of others, occurring since age 15. Individuals with ASPD exhibit a consistent pattern of manipulative, deceitful, and often criminal behavior. This pattern significantly impacts their relationships, employment, and overall well-being, as well as the well-being of those around them.This disorder is characterized by a profound lack of empathy and conscience, often leading to a disregard for the feelings and needs of others.
Individuals with ASPD typically fail to conform to social norms, engage in impulsive behaviors, and frequently disregard the consequences of their actions. Understanding the specific diagnostic criteria, traits, and behaviors associated with ASPD is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Diagnostic Criteria for ASPD
The diagnosis of ASPD is based on a set of specific criteria Artikeld in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). These criteria encompass various aspects of an individual’s behavior and personality. Crucially, these criteria must be present consistently over a significant period, usually since adolescence.
- A pervasive pattern of disregard for and violation of the rights of others, occurring since age 15, as indicated by three or more of the following:
- Failure to conform to social norms with respect to lawful behaviors, as indicated by repeatedly performing acts that are grounds for arrest.
- Deceitfulness, as indicated by repeated lying, use of aliases, or conning others for personal profit or pleasure.
- Impulsivity or failure to plan ahead.
- Irritability and aggressiveness, as indicated by repeated physical fights or assaults.
- Reckless disregard for safety of self or others.
- Consistent irresponsibility, as indicated by repeated failure to sustain consistent work behavior or financial obligations.
- Lack of remorse, as indicated by being indifferent to or rationalizing having hurt, mistreated, or stolen from another.
Common Traits and Behaviors Associated with ASPD
Individuals with ASPD often display a range of common traits and behaviors. These traits frequently contribute to their difficulties in maintaining healthy relationships and fulfilling societal expectations.
- Manipulative behavior: Individuals with ASPD frequently employ manipulative tactics to control situations and gain personal advantage. This manipulation can involve deception, emotional blackmail, or other forms of persuasion.
- Lack of empathy: A hallmark of ASPD is a diminished capacity for empathy. They may struggle to understand or share the feelings of others, often leading to disregard for their well-being.
- Impulsivity: Impulsive decision-making is a common characteristic, often leading to immediate gratification without considering long-term consequences.
- Disregard for rules and laws: A consistent pattern of violating social norms and legal regulations is often observed.
Examples of Behaviors Considered Characteristic of ASPD
Several examples illustrate the behaviors associated with ASPD. These examples highlight the consistent pattern of disregard for others’ rights and societal expectations.
- Repeatedly breaking laws, such as engaging in theft, assault, or property damage.
- Engaging in deceitful behavior, such as fraud, impersonation, or manipulation to gain personal profit.
- Failure to fulfill financial obligations, such as failing to pay bills or support family members.
- Engaging in reckless behaviors, such as dangerous driving or substance abuse, with disregard for the safety of themselves or others.
Comparison of ASPD with Other Personality Disorders
Differentiating ASPD from other personality disorders is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the key distinctions helps clinicians to tailor interventions to the specific needs of the individual.
| Characteristic | ASPD | Borderline Personality Disorder | Narcissistic Personality Disorder |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emotional Regulation | Often impulsive and lacks emotional control; displays callousness and lack of remorse | Marked instability in mood and interpersonal relationships; intense fear of abandonment | Grandiose sense of self-importance; lack of empathy; exploitative behavior |
| Interpersonal Relationships | Exploitative and manipulative; disregard for others’ feelings | Intense and unstable relationships; fear of abandonment | Relationships are used to enhance the self-image; relationships are often superficial and exploitative |
| Impulsivity | High impulsivity; often engages in risky behaviors | Impulsive behaviors, but often related to emotional dysregulation | Impulsivity may be present but often focused on satisfying self-esteem needs |
Causes and Risk Factors of ASPD
Understanding the causes of antisocial personality disorder (ASPD) is crucial for developing effective interventions and support systems for individuals affected by this complex condition. While a definitive cause remains elusive, research suggests a confluence of genetic predispositions, environmental influences, and developmental experiences play a significant role. This exploration will delve into the multifaceted factors contributing to ASPD, highlighting the importance of a holistic approach to understanding and addressing this disorder.
Understanding antisocial personality disorder (ASPD) involves recognizing a pattern of disregard for social norms and the rights of others. While the complexities of ASPD are significant, sometimes seemingly unrelated issues like persistent headaches can be a factor. For example, if you’re experiencing a lingering headache following a potential COVID infection, you might want to look into how long those headaches typically last, to see if they could be related to something else.
Checking out this resource on how long does covid headache last could be helpful in understanding the possible timeline. Ultimately, it’s crucial to remember that seeking professional help is key when dealing with potential mental health concerns like ASPD.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetic factors appear to play a role in the development of ASPD. Studies have indicated a potential link between certain genes and traits associated with the disorder, such as impulsivity and aggression. However, it’s important to emphasize that genetics alone do not determine ASPD. Environmental factors and experiences significantly interact with genetic predispositions, shaping the expression of these traits.
A genetic predisposition might make an individual more susceptible to developing ASPD, but it does not guarantee its development. The interplay between genes and environment is crucial in understanding the etiology of ASPD.
Environmental Influences
Environmental factors contribute substantially to the development of ASPD. Adverse childhood experiences, including neglect, abuse, and inconsistent parenting, can significantly impact a child’s development, potentially increasing the risk of ASPD later in life. The consistent lack of nurturing and support during crucial developmental stages can lead to difficulties in forming healthy attachments and regulating emotions, contributing to the manifestation of ASPD traits.
Childhood Experiences
Early childhood experiences hold substantial weight in the development of ASPD. These experiences, particularly those involving trauma and abuse, can create lasting emotional scars. A lack of consistent parental care and affection can disrupt the development of empathy and emotional regulation. These difficulties in emotional processing and attachment can lead to problems in interpersonal relationships and behaviors, increasing the likelihood of ASPD.
Trauma and Abuse
Experiences of trauma and abuse, such as physical, emotional, or sexual abuse, significantly increase the risk of developing ASPD. These traumatic events can profoundly impact the developing brain and psyche, leading to difficulties in emotional regulation, trust, and empathy. The resulting emotional dysregulation and heightened sense of vulnerability can contribute to antisocial behaviors and interpersonal difficulties, increasing the likelihood of ASPD.
Substance Abuse
Substance abuse is frequently observed in individuals with ASPD. This correlation suggests a complex relationship, with substance abuse potentially acting as a coping mechanism for underlying emotional distress or as a facilitator of antisocial behaviors. Individuals with ASPD may be more prone to substance abuse due to their impulsivity, risk-taking tendencies, and difficulties in managing emotions. Substance abuse can further exacerbate existing antisocial behaviors and make treatment more challenging.
Antisocial personality disorder (ASPD) is a complex condition characterized by a disregard for social norms and the rights of others. While not directly related, understanding the importance of a balanced diet, like avoiding certain foods that might contribute to macular degeneration, foods to avoid with macular degeneration , can be a part of a broader approach to overall well-being.
Ultimately, focusing on a healthy lifestyle, including mental health care, is key to managing ASPD and its related challenges.
Neurobiological Factors
Neurobiological factors may also play a role in the development of ASPD. Studies have indicated potential differences in brain structure and function in individuals with ASPD, particularly in areas associated with emotional regulation and decision-making. These neurobiological factors may interact with environmental influences to contribute to the manifestation of antisocial traits. Further research is needed to fully understand the intricate neurobiological mechanisms involved.
Summary of Risk Factors
| Risk Factor | Potential Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Predisposition | Increased susceptibility to developing ASPD | Family history of ASPD or related personality disorders |
| Adverse Childhood Experiences | Disruption in emotional development and attachment | Neglect, abuse, inconsistent parenting |
| Trauma and Abuse | Impaired emotional regulation and trust issues | Physical, emotional, or sexual abuse |
| Substance Abuse | Exacerbation of antisocial behaviors, and increased treatment challenges | Alcohol or drug dependence |
| Neurobiological Factors | Potential differences in brain structure and function impacting emotional regulation | Impaired amygdala function, reduced prefrontal cortex activity |
Diagnosis and Assessment of ASPD: What Is Antisocial Personality Disorder Aspd
Diagnosing Antisocial Personality Disorder (ASPD) is a complex process requiring careful consideration of various factors. It’s not simply identifying specific behaviors; rather, it necessitates a comprehensive evaluation of an individual’s patterns of thinking, feeling, and behaving over time. The process is designed to differentiate ASPD from other conditions with overlapping characteristics, ensuring an accurate and appropriate diagnosis.Accurate diagnosis relies heavily on the expertise of mental health professionals.
They must skillfully gather information from various sources and utilize their clinical judgment to form a nuanced understanding of the individual’s presentation. This process is crucial for determining the appropriate course of treatment and support.
Role of Mental Health Professionals
Mental health professionals play a vital role in the diagnosis of ASPD. Their expertise is essential in interpreting the individual’s behaviors and experiences within a broader context. Clinicians must consider the individual’s developmental history, current social circumstances, and potential co-occurring conditions. This holistic approach allows for a more accurate assessment of the disorder.
Thorough Clinical Evaluation
A thorough clinical evaluation is critical in the diagnosis of ASPD. This evaluation goes beyond simply observing symptoms; it delves into the individual’s history, including childhood experiences, relationships, and legal issues. The evaluation also assesses for potential co-occurring disorders, such as substance use disorders, anxiety, or depression. This comprehensive approach is vital for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment planning.
Assessment Process
A structured approach to assessment is crucial for maintaining objectivity and ensuring a thorough evaluation. This structured approach is often utilized in mental health settings.
| Step | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Gathering Information | Collecting detailed information from various sources, including the individual, family members, and previous clinicians. This may involve interviews, questionnaires, and reviewing medical records. | Interviewing the patient about their childhood experiences, relationships, and legal history. Reviewing previous therapy notes or court documents. |
| Clinical Interviews | Conducting structured interviews to assess the individual’s presentation, personality traits, and behaviors. These interviews are designed to elicit information about the individual’s past experiences and their impact on their current functioning. | Using the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 (SCID) to assess the presence of ASPD symptoms. |
| Psychological Testing | Administering standardized psychological tests to assess personality traits, cognitive abilities, and emotional functioning. | Using personality inventories (e.g., the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory-2, MMPI-2) to identify patterns in the individual’s personality. |
| Review of Past Records | Reviewing past medical records, court documents, and other relevant information to gain a comprehensive understanding of the individual’s history. | Reviewing school records, employment records, and police reports. |
| Differential Diagnosis | Identifying and ruling out other conditions that may have similar symptoms to ASPD. This step is essential to ensure the most accurate possible diagnosis. | Differentiating ASPD from borderline personality disorder (BPD), narcissistic personality disorder (NPD), or substance use disorders. |
Distinguishing ASPD from Other Conditions
Accurate diagnosis of ASPD requires differentiating it from other conditions that may present with overlapping symptoms. Careful consideration of the individual’s specific behaviors, patterns, and history is crucial. For example, impulsive behaviors, a disregard for social norms, and a lack of remorse might be seen in both ASPD and other conditions, but the context and underlying motivations differ.
A thorough clinical evaluation helps to identify these nuances.
Antisocial personality disorder (ASPD) is a complex condition marked by a disregard for social norms and the rights of others. Sometimes, a sudden dental emergency might arise, requiring a quick decision on whether to head to the hospital or visit a dentist. This guide can help you navigate such situations. Ultimately, though, understanding ASPD involves delving into the underlying psychological factors that drive the behavior, and it’s a crucial aspect of mental health awareness.
Treatment Approaches for ASPD
Antisocial personality disorder (ASPD) presents a significant challenge for treatment due to the inherent difficulties in motivating individuals with ASPD to engage in therapy. However, various approaches have shown some degree of success in managing symptoms and improving functioning. These strategies aim to address the underlying issues contributing to the disorder, including impulsivity, aggression, and disregard for social norms.Effective treatment for ASPD necessitates a multifaceted approach that integrates various modalities.
The goal is not to “cure” ASPD, but to help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their relationships with others and their overall well-being. This includes developing coping mechanisms, fostering empathy, and promoting prosocial behaviors.
Psychotherapy Modalities
Psychotherapy plays a crucial role in ASPD treatment. It provides a structured environment for exploring the roots of the disorder and developing healthier coping strategies. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is frequently used, helping individuals identify and modify maladaptive thought patterns and behaviors. Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) can be particularly helpful in addressing emotional regulation issues, interpersonal conflicts, and self-destructive behaviors.
Other forms of psychotherapy, such as psychodynamic therapy, can help explore early childhood experiences and their impact on current behaviors. The specific type of therapy employed should be tailored to the individual’s needs and preferences, in consultation with a mental health professional.
Medication Management
While medication alone cannot treat ASPD, it can play a supportive role in managing specific symptoms. For example, medications may be used to address co-occurring conditions like anxiety, depression, or substance use disorders. These co-occurring disorders often significantly impact the individual’s functioning and ability to engage in therapy. The appropriate medication and dosage should be determined by a psychiatrist, considering the individual’s specific needs and any potential side effects.
Therapeutic Techniques
Several therapeutic techniques are used in treating ASPD. These include:
- Cognitive restructuring: This involves identifying and challenging negative or distorted thought patterns that contribute to antisocial behaviors.
- Behavioral activation: This focuses on increasing positive and prosocial behaviors by reinforcing desired actions and reducing avoidance.
- Interpersonal skills training: This aims to enhance communication, empathy, and conflict resolution skills to improve relationships.
These techniques are often employed within a structured therapeutic framework, ensuring the individual receives consistent support and guidance.
Comparison of Therapeutic Approaches, What is antisocial personality disorder aspd
| Therapy Type | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) | Focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. | Structured, evidence-based, and often effective in addressing specific symptoms. | May not address underlying emotional or relational issues as deeply as other therapies. |
| Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) | Teaches coping skills for emotional regulation, interpersonal effectiveness, and distress tolerance. | Effective in managing impulsivity and emotional dysregulation, particularly helpful in crisis situations. | Requires significant commitment and time from the patient, may not be suitable for all individuals. |
| Psychodynamic Therapy | Explores the unconscious motivations and past experiences that may contribute to current behaviors. | Can provide insight into the origins of antisocial tendencies. | May be less structured and require more sessions, less evidence-based for ASPD. |
Patient Motivation in Treatment
Patient motivation is paramount for successful treatment of ASPD. Individuals with ASPD often exhibit a lack of insight into their behaviors and a reluctance to engage in change. Therapists need to employ motivational interviewing techniques to encourage active participation and commitment to the therapeutic process. Building a trusting relationship with the patient is essential to foster motivation and encourage them to take ownership of their recovery.
This often involves demonstrating empathy and patience, while simultaneously holding the patient accountable for their actions. Successful treatment relies heavily on the patient’s willingness to engage and work towards change.
Social and Legal Implications of ASPD
Antisocial personality disorder (ASPD) significantly impacts individuals’ lives, extending far beyond their personal struggles. The disorder’s pervasive disregard for social norms and the rights of others creates complex social and legal ramifications that affect families, communities, and the justice system. Understanding these implications is crucial for fostering empathy and promoting effective interventions.The core characteristics of ASPD – a pattern of disregard for and violation of the rights of others – manifest in a wide array of social interactions.
Individuals with ASPD often struggle to maintain meaningful relationships due to their manipulative behaviors, lack of empathy, and tendency toward exploitation. This creates a ripple effect, impacting not only the individual with ASPD but also their loved ones and the broader social environment.
Impact on Interpersonal Relationships
Individuals with ASPD frequently exhibit a pattern of superficial charm and manipulation. They may initially appear engaging and charismatic, which can lead to the development of close relationships, only to be eroded by a lack of genuine connection and a pattern of exploitation. This makes maintaining healthy, long-term relationships extremely challenging. Trust becomes a rare commodity, and partners and family members are often left feeling confused, hurt, and ultimately betrayed.
Challenges in Maintaining Healthy Relationships
The core issues contributing to relationship problems stem from the core traits of ASPD. These include a persistent pattern of deceitfulness, a disregard for social norms, and a lack of empathy. Individuals with ASPD struggle to recognize and respect boundaries. They may engage in manipulative behaviors, such as lying, gaslighting, or intimidation, to control others and achieve their goals.
This pattern consistently undermines trust and damages relationships.
Impact on Family Dynamics
The presence of ASPD within a family can cause considerable disruption and strain. Family members may experience emotional abuse, financial exploitation, or neglect. Children growing up in such environments can face significant emotional and psychological harm. The lack of accountability and responsibility often leads to a breakdown of communication and conflict. For example, a parent with ASPD might prioritize their own needs over the needs of their children, causing neglect and emotional damage.
Legal Ramifications of ASPD
ASPD is strongly linked to criminal behavior. The disorder’s characteristics – including a disregard for the law, impulsivity, and a lack of remorse – often lead to legal problems. The criminal justice system frequently encounters individuals with ASPD, dealing with the consequences of their actions.
Examples of Criminal Behavior Associated with ASPD
Common criminal behaviors associated with ASPD include theft, assault, fraud, and violent crimes. These acts reflect the disregard for the rights and well-being of others that is a defining feature of the disorder. For example, individuals with ASPD may engage in con artists schemes, stealing from others, or even committing violent acts without remorse.
Potential Legal Consequences of ASPD
| Legal Ramification | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Arrest and Prosecution | Individuals engaging in criminal activities associated with ASPD may be arrested and brought before the court for prosecution. | A person with ASPD who robs a bank faces arrest and prosecution for the crime. |
| Conviction and Sentencing | Upon conviction, individuals may face a range of sentencing options, from probation to imprisonment. | A convicted individual with ASPD might receive a prison sentence for assault. |
| Civil Litigation | Victims of actions by individuals with ASPD may pursue civil litigation to seek compensation for damages. | A person who was defrauded by someone with ASPD may file a civil lawsuit to recover financial losses. |
| Incarceration | Repeated criminal behavior often results in incarceration as a means of punishment and societal protection. | A person with a history of violent crimes and ASPD might be sentenced to lengthy periods in prison. |
Illustrative Case Studies of ASPD
Understanding antisocial personality disorder (ASPD) requires delving into real-life examples to grasp its complexities. While diagnostic criteria offer a framework, the manifestation of ASPD varies greatly from person to person. Each individual’s history, environment, and specific challenges shape their experience and the ways in which ASPD impacts their lives.ASPD often presents as a pattern of disregard for and violation of the rights of others.
This disregard manifests in various ways, from consistent deceitfulness to impulsive behaviors and a persistent disregard for safety. These behaviors can lead to significant challenges for the individual and those around them, requiring a multifaceted approach to understanding and addressing the issue.
A Case Study of Complex Manifestations
Case Study: Mark, a 32-year-old man, has a history of petty theft, escalating to more serious crimes over time. He consistently lies and manipulates others for personal gain. His relationships are marked by superficiality and a lack of empathy.
Symptoms: Mark exhibits a pattern of deceitfulness, a disregard for social norms, and a lack of remorse. He engages in impulsive behaviors, including risky financial investments and physical altercations. He shows a marked disregard for the safety of others and has a history of violating the law. He demonstrates a superficial charm and manipulates others to achieve his goals.
Diagnosis: After extensive psychological evaluation, including interviews and assessments, a diagnosis of ASPD was established. The assessment considered his persistent pattern of antisocial behavior, lack of empathy, and disregard for social norms over a significant period. Key indicators included repeated criminal activity, consistent deception, and a failure to conform to societal rules.
Treatment: Mark’s treatment plan involves a combination of therapy and potentially medication. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is crucial to address the underlying cognitive distortions and behavioral patterns that contribute to his antisocial behavior. Medication might be used to manage co-occurring conditions, such as anxiety or depression, which can often accompany ASPD. A crucial aspect of treatment is helping Mark develop empathy and remorse, a significant challenge given his history. Support groups can provide a safe space for Mark to connect with others facing similar challenges.
Variations in Manifestation
Mark’s case illustrates how ASPD can manifest differently. While deceitfulness and disregard for others are common, the specific ways in which these traits play out vary. Some individuals might exhibit more overt aggression, while others may be more cunning and manipulative. The severity of the symptoms can also differ greatly, impacting the individual’s life and the lives of those around them.
Living with ASPD and Supporting Those Affected
Navigating a relationship with someone exhibiting antisocial personality disorder (ASPD) can be exceptionally challenging. Understanding the complexities of this condition and developing strategies for support is crucial for both the individual with ASPD and those around them. This journey requires empathy, patience, and a strong commitment to self-care.Living with ASPD often involves a constant struggle with unpredictable behavior, a disregard for social norms, and a tendency toward manipulation and deceit.
The inherent instability and lack of empathy in ASPD can create significant emotional strain and instability in relationships.
Challenges of Living with Someone with ASPD
Individuals living with someone with ASPD face a unique set of challenges. These challenges stem from the inherent traits of the disorder, including a lack of remorse, a disregard for others’ feelings, and a tendency toward impulsive behavior. These behaviors can lead to feelings of betrayal, anger, and fear in those close to the individual with ASPD.
Strategies for Supporting Individuals with ASPD
Developing supportive strategies requires a multifaceted approach. Understanding the disorder’s core characteristics is essential for tailoring effective support. Maintaining clear boundaries and consistent expectations is critical. Communicating openly and honestly, while acknowledging the limitations imposed by the disorder, can be beneficial. Seeking professional guidance, including therapy or support groups, is often invaluable.
Coping Mechanisms for Individuals Living with ASPD
Developing healthy coping mechanisms is vital for individuals navigating relationships with those diagnosed with ASPD. Recognizing and acknowledging the impact of the disorder is a crucial first step. Practicing stress management techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, can be highly effective. Building a strong support system of friends and family who understand the situation can provide emotional respite.
Journaling can be a valuable tool for processing emotions and developing strategies for managing stress. Ultimately, self-care is paramount in navigating these complex relationships.
Importance of Self-Care for Supporters
Self-care is paramount for anyone supporting someone with ASPD. The demands of such a relationship can be emotionally draining and mentally taxing. Taking time for oneself is not selfish but essential for maintaining well-being. This includes activities that promote relaxation, such as hobbies, exercise, or spending time in nature. Seeking professional guidance from a therapist or counselor can provide valuable support and coping strategies for navigating the challenges of this situation.
Understanding that support is not a one-size-fits-all solution is important, and seeking personalized guidance is often beneficial.
Resources for Individuals and Families Affected by ASPD
| Resource Type | Description | Link/Contact Info |
|---|---|---|
| Support Groups | Provide a forum for sharing experiences and support among individuals and families affected by ASPD. | Search online for ASPD support groups in your area or online platforms. |
| Therapy | Professional guidance can provide coping mechanisms and strategies for managing the challenges of ASPD. | Contact your healthcare provider or search online for licensed therapists specializing in personality disorders. |
| Educational Materials | Understanding ASPD is crucial for effective support. Educational materials can provide insight into the disorder’s characteristics and impact. | Look for reputable websites, books, or articles on ASPD from recognized mental health organizations. |
| Crisis Hotlines | Providing immediate support during challenging periods. | Search online for crisis hotlines specializing in mental health or domestic violence. |
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, antisocial personality disorder (ASPD) is a multifaceted condition with profound implications for individuals and society. From its diagnostic criteria and potential causes to the available treatment options and the impact on interpersonal relationships and legal systems, this exploration highlights the importance of understanding and addressing this complex issue. By understanding the nuances of ASPD, we can better support those affected and foster a more compassionate and understanding approach to mental health.




