What is a cortisone flare? This comprehensive guide delves into the complexities of these episodes, exploring the medical definitions, potential triggers, and effective management strategies. We’ll uncover the underlying physiological mechanisms, common symptoms, and even real-life case studies to paint a vivid picture of what it’s like to experience one.
From understanding the initial signs to navigating long-term management, this article will equip you with the knowledge to better comprehend and address cortisone flares. We’ll also explore the diagnostic procedures involved and the importance of a thorough medical history in the identification process.
Defining Cortisone Flare
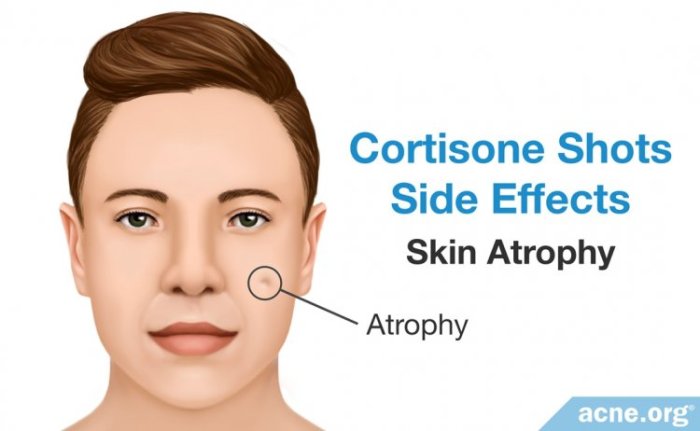
A cortisone flare, also known as a steroid flare, is a paradoxical reaction that can occur after the use of corticosteroid medications, like cortisone. These medications, often prescribed for inflammatory conditions, can sometimes trigger an inflammatory response in the body, leading to a temporary worsening of symptoms. It’s crucial to understand that this is not a sign of the medication failing but rather a complex interaction with the body’s immune system.Cortisone, while powerful in managing inflammation, can disrupt the delicate balance of the body’s immune response.
This disruption can manifest as a resurgence of symptoms, often similar to the original condition being treated. The symptoms, while generally temporary, can be quite distressing, highlighting the importance of close monitoring and communication with a healthcare professional.
Defining a Cortisone Flare (Medical Perspective)
A cortisone flare is a temporary exacerbation of symptoms, often inflammatory in nature, that arises in response to the use of corticosteroid medications. These medications, designed to suppress inflammation, can sometimes paradoxically trigger an inflammatory response. The key is that the flare is a response, not a failure, of the medication.
Typical Symptoms of a Cortisone Flare
Symptoms of a cortisone flare can vary significantly depending on the individual and the specific condition being treated. There’s no one-size-fits-all symptom profile. Some common symptoms, however, include joint pain, swelling, redness, and stiffness, mimicking the initial condition. Furthermore, fatigue, muscle aches, and fever are possible symptoms, highlighting the systemic nature of the response.
Physiological Mechanisms of a Cortisone Flare
The exact physiological mechanisms behind a cortisone flare are still being investigated, but several theories exist. One theory suggests that the abrupt cessation of the medication’s anti-inflammatory effect disrupts the body’s natural inflammatory response, leading to a rebound effect. Another theory focuses on the interplay between the immune system and the corticosteroid, potentially leading to an overreaction in certain individuals.
The body’s complex regulatory mechanisms may also play a role. This underscores the importance of gradual tapering of corticosteroid medications to minimize the risk of flares.
Cortisone Flare vs. Other Conditions
Distinguishing a cortisone flare from other inflammatory conditions can be challenging, particularly in the early stages. Symptoms overlap considerably, and a thorough medical evaluation is essential. Key differentiators often include the temporal relationship with corticosteroid use and the absence of other significant indicators of unrelated inflammatory processes. This emphasizes the need for medical professionals to consider the patient’s medication history when diagnosing inflammatory conditions.
A cortisone flare is basically when your body reacts negatively to the medication, causing inflammation and discomfort. Sometimes, to manage the intense symptoms, you might be prescribed benzodiazepines, like those detailed in the uses types and risks of benzodiazepines article. Understanding the potential side effects of these drugs is crucial for anyone dealing with a cortisone flare, as it helps manage the overall condition effectively.
Comparison Table: Common Symptoms of a Cortisone Flare
| Body System | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Musculoskeletal | Joint pain, swelling, stiffness, muscle aches |
| Integumentary | Redness, rash, skin sensitivity |
| Cardiovascular | Increased blood pressure, palpitations (less common) |
| Gastrointestinal | Nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort |
| Neurological | Headache, dizziness, fatigue |
Understanding the Causes of Cortisone Flares: What Is A Cortisone Flare
Cortisone flares, characterized by a sudden increase in symptoms, can be frustrating and unpredictable. Understanding the underlying triggers is crucial for effective management and prevention. This knowledge empowers individuals to take proactive steps towards minimizing flare-ups and improving their overall well-being.While the exact mechanisms triggering cortisone flares are not always fully understood, various factors play a role. These factors range from underlying medical conditions to lifestyle choices.
By identifying these potential triggers, individuals can work with their healthcare providers to develop personalized strategies for managing their cortisone-related symptoms.
Primary Factors Contributing to Cortisone Flare-ups
Numerous factors can contribute to cortisone flare-ups, making it challenging to pinpoint a single cause. These factors often interact and influence each other, making precise identification difficult. However, understanding these contributing elements is essential for personalized management strategies.
Role of Underlying Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can significantly increase the likelihood of cortisone flares. Autoimmune disorders, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, are frequently associated with heightened susceptibility to flare-ups. Infections, both acute and chronic, can also trigger or exacerbate these flares. Furthermore, hormonal imbalances, particularly in women, can play a significant role. For example, fluctuating estrogen levels during menstruation or pregnancy might contribute to increased symptom severity.
Impact of Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors exert a substantial influence on the frequency and severity of cortisone flares. Stressful situations, whether acute or chronic, can often trigger or worsen flare-ups. Poor sleep patterns and inadequate rest can also negatively impact the body’s ability to regulate inflammatory responses, increasing the risk of flares. Dietary choices and environmental factors, such as exposure to allergens or irritants, can also contribute.
For instance, certain foods or environmental pollutants might exacerbate inflammation in susceptible individuals.
Comparison of Flare Frequency and Severity in Different Patient Populations
The frequency and severity of cortisone flares can vary considerably between individuals and even within the same individual over time. Factors such as age, overall health, and the specific type of underlying condition play a role in influencing these variations. Research studies are ongoing to further elucidate these correlations. Patient populations with pre-existing inflammatory conditions often experience more frequent and severe flares compared to those without such conditions.
Moreover, individuals experiencing significant life stressors may encounter a higher frequency of flares.
Possible Triggers of Cortisone Flares
| Category | Possible Triggers |
|---|---|
| Medication | New medications, dosage changes, interactions with other medications |
| Stress | Significant life events, emotional distress, work-related pressure |
| Environment | Exposure to allergens, irritants, extreme temperatures, changes in humidity |
| Diet | Certain foods, alcohol consumption, dietary changes |
| Sleep | Poor sleep quality, lack of sleep, sleep disorders |
Recognizing the Symptoms of a Cortisone Flare
Understanding the signs and symptoms of a cortisone flare is crucial for managing the condition effectively. Early recognition allows for prompt intervention and potentially mitigates the severity of the flare. By paying close attention to the body’s signals, individuals can better understand their own reactions and seek appropriate medical care.Cortisone flares, while often associated with a particular trigger, can manifest in various ways, with the intensity and specific symptoms varying significantly from person to person.
This variability makes recognizing a flare a personalized journey. Understanding the typical progression of symptoms from initial signs to peak intensity is vital for timely management.
Initial Signs and Early Symptoms
The initial signs of a cortisone flare can be subtle and easily overlooked. These early indicators often mimic other, less serious conditions, leading to delayed recognition and treatment. Common initial symptoms include mild discomfort, fatigue, and a general sense of unease. These initial signs may not always be directly linked to the affected area.
Progression of Symptoms Over Time
Symptoms typically progress from mild to moderate and, if left unmanaged, can escalate to severe. The rate of progression varies greatly. For instance, some individuals might experience a gradual increase in symptoms over several days, while others might experience a sudden, rapid escalation within hours. This progression underscores the importance of ongoing self-monitoring and communication with a healthcare professional.
Severity and Variability of Symptoms
The severity of cortisone flare symptoms can range from mild discomfort to debilitating pain. Factors such as the individual’s overall health, the specific trigger, and the location of the flare significantly influence the intensity of the experience. For example, a flare affecting a joint might manifest as stiffness and limited range of motion, while a flare in the digestive system might lead to nausea and abdominal cramping.
Symptoms Indicating Worsening or More Severe Flare
Certain symptoms signal a worsening or more severe flare. These include an increase in pain intensity, the appearance of new symptoms, or a significant worsening of existing symptoms. Sudden and marked increases in inflammation, such as swelling or redness, are also indicators of a worsening flare. It is essential to be aware of these warning signs and to seek medical attention if they appear.
Symptom Severity Table
| Severity Level | Symptoms | Description | Potential Impact on Daily Activities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild | General discomfort, fatigue, slight stiffness | Symptoms are mild and manageable, and may not significantly interfere with daily activities. | Minimal impact; able to perform most daily tasks. |
| Moderate | Increased pain, swelling, redness, limited range of motion, nausea | Symptoms become more pronounced, impacting daily tasks and activities. | Reduced ability to perform daily tasks; may require adjustments or assistance. |
| Severe | Intense pain, severe swelling, significant limitations in movement, fever, difficulty breathing | Symptoms are debilitating and significantly impair daily functioning. | Inability to perform most daily tasks; requires immediate medical attention. |
Managing and Treating Cortisone Flares
Cortisone flares, characterized by a sudden worsening of symptoms, can significantly impact daily life. Effective management hinges on understanding the specific triggers and symptoms in each individual case. Prompt and appropriate treatment can help mitigate the severity and duration of the flare, allowing for a more comfortable experience.Effective treatment strategies for cortisone flares often involve a combination of approaches.
These methods can range from over-the-counter medications to more intensive therapies, and the choice of treatment will depend on the severity of the flare and the underlying cause. Understanding the potential benefits and risks of each approach is crucial for making informed decisions.
Common Treatment Options
Various treatments are available for managing cortisone flares. These options often target symptom relief and underlying causes. The choice of treatment often depends on the severity and individual response to different therapies.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help alleviate pain and inflammation. Prescription medications, including corticosteroids, may be necessary for more severe cases. It’s crucial to follow dosage instructions carefully and consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new medication.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help maintain range of motion, reduce pain, and improve strength and flexibility. Exercises and stretches tailored to individual needs can be beneficial. Physical therapists can create personalized routines to address specific areas of concern.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can play a significant role in managing cortisone flares. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep can help the body cope with inflammation. Stress management techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can also be beneficial.
- Complementary Therapies: Some individuals find relief through complementary therapies like acupuncture, massage therapy, or herbal remedies. These approaches can be used in conjunction with conventional treatments. However, it’s essential to discuss these therapies with a healthcare provider to ensure safety and avoid potential conflicts with other medications.
Potential Benefits and Risks
Each treatment option carries potential benefits and risks. Carefully weighing these factors is crucial when deciding on a course of action.
- Medications: While medications can provide rapid symptom relief, they can also carry side effects. Steroid medications, for example, may lead to increased blood sugar levels or fluid retention. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may cause stomach upset or ulcers.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can reduce pain and improve mobility, but it requires commitment and adherence to the prescribed exercises. Overexertion during therapy sessions can potentially exacerbate symptoms.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Healthy lifestyle choices, while beneficial in the long run, may not provide immediate relief from acute flares. Significant lifestyle changes may require time and effort to implement.
- Complementary Therapies: Complementary therapies often offer a non-pharmacological approach to symptom management. However, their efficacy for managing cortisone flares may vary, and their use should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
Effectiveness of Different Treatment Methods
The effectiveness of various treatment methods can differ significantly based on individual factors and the severity of the flare.
- Comparison: While over-the-counter pain relievers can provide initial relief, prescription medications might be necessary for more severe or persistent symptoms. Physical therapy and lifestyle modifications contribute to long-term management rather than immediate symptom relief.
- Individualized Approach: A healthcare professional can tailor a treatment plan based on the patient’s specific needs and responses. This personalized approach is crucial for maximizing effectiveness.
Strategies for Preventing Future Flares
Preventing future cortisone flares involves addressing the underlying causes and adopting proactive lifestyle changes.
A cortisone flare is basically when your body reacts negatively to a cortisone injection, sometimes causing inflammation and pain. This can sometimes mimic the symptoms of conditions like achilles tendonitis, which can be caused by overuse, poor footwear, or even flat feet. Understanding the causes and treatments for achilles tendonitis is key to managing these issues, and you can find a great resource on that here: achilles tendonitis causes and treatment.
Ultimately, recognizing the signs of a cortisone flare is important for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep are essential for reducing inflammation and strengthening the body’s natural defenses. Managing stress through relaxation techniques can also be beneficial.
- Trigger Avoidance: Identifying and avoiding known triggers, such as specific foods, environmental factors, or stress-inducing situations, can significantly reduce the risk of future flares. Keeping a journal to track potential triggers can be helpful.
Treatment Options Summary
| Treatment Option | Efficacy | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Over-the-counter pain relievers | Moderate, initial relief | Potential stomach upset, allergic reactions |
| Prescription medications (e.g., corticosteroids) | High, rapid relief | Increased blood sugar, fluid retention, potential for dependence |
| Physical therapy | Moderate, long-term improvement | Potential for soreness, discomfort during sessions |
| Lifestyle modifications | Low, gradual improvement | Requires commitment and adherence |
| Complementary therapies | Variable, often supportive | Potential interactions with other medications, efficacy not consistently proven |
Diagnostic Procedures and Considerations
Pinpointing the cause of a cortisone flare requires a multi-faceted approach. It’s not always straightforward, as symptoms can mimic other conditions. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and management. This section delves into the diagnostic procedures employed to identify and confirm a cortisone flare, emphasizing the importance of a thorough medical history and physical examination, alongside medical imaging and blood tests.
Medical History and Physical Examination
A comprehensive medical history plays a pivotal role in diagnosing a cortisone flare. The doctor will inquire about the patient’s overall health, pre-existing conditions, recent illnesses, medications (including over-the-counter drugs), and any relevant family history. This information helps to rule out other potential causes and identify any predisposing factors. A thorough physical examination is also essential. The doctor will assess the affected area for signs of inflammation, swelling, redness, and pain.
A cortisone flare is essentially a sudden increase in inflammation, often triggered by medications like cortisone. Understanding this can be crucial, especially when considering conditions like macular degenerations vs glaucoma, which can also impact vision. Learning about these eye conditions, like in this article about macular degenerations vs glaucoma , can help you better understand how different factors might influence your health and potentially lead to these types of flares.
Ultimately, a cortisone flare can manifest in various ways, impacting your overall well-being.
They will also evaluate the patient’s overall physical condition, noting any other symptoms or abnormalities.
Medical Imaging
Medical imaging techniques, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, can provide valuable insights into the underlying cause of a cortisone flare. X-rays are often the initial imaging modality used to visualize bone structures and detect any fractures or abnormalities. CT scans offer more detailed cross-sectional views, which can reveal soft tissue damage or inflammation. MRIs provide high-resolution images of soft tissues, allowing for detailed visualization of joints, muscles, and ligaments, aiding in the identification of potential sources of inflammation.
Blood Tests
Blood tests can be helpful in identifying potential systemic causes of cortisone flares. A complete blood count (CBC) can reveal signs of infection or inflammation. Other relevant blood tests might include inflammatory markers such as ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) or CRP (C-reactive protein). Elevated levels of these markers often indicate inflammation in the body. Additionally, tests specific to certain conditions that might mimic cortisone flares can also be performed.
Diagnostic Procedures Table
| Diagnostic Procedure | Relevance to Cortisone Flare |
|---|---|
| Medical History & Physical Examination | Essential for ruling out other conditions, identifying predisposing factors, and assessing the extent of inflammation. |
| X-rays | Useful for visualizing bone structures and detecting potential fractures or abnormalities. |
| CT Scans | Provide detailed cross-sectional views, revealing soft tissue damage or inflammation in deeper structures. |
| MRIs | Offer high-resolution images of soft tissues, enabling detailed visualization of joints, muscles, and ligaments. |
| Blood Tests (CBC, ESR, CRP) | Identify systemic inflammation, infection, or other underlying conditions that might be contributing to the flare. |
Illustrative Case Studies
Understanding cortisone flares requires looking at real-world examples. These case studies offer valuable insights into the diverse presentation, causes, and management strategies for cortisone flares. They highlight the impact these flares have on patients’ lives and the effectiveness of different treatment approaches.
Case Study 1: A Young Athlete’s Flare
“I was training for a marathon, and everything was going perfectly. Then, suddenly, I started experiencing severe joint pain in my knees. It was like someone was stabbing me with needles. The pain was so bad that I couldn’t even walk.”
This young athlete, in their prime physical condition, suffered a cortisone flare-up related to overuse. The intense pain, combined with the inflammation, made it nearly impossible to continue training. Treatment involved a combination of pain management, physical therapy, and rest. The athlete’s response to the treatment was encouraging, with the pain subsiding gradually over several weeks, allowing them to resume their training schedule, although with modifications to avoid exacerbating the issue.
Case Study 2: A Patient with Underlying Conditions
“I have lupus, and cortisone flares are a constant struggle. The pain radiates throughout my body, making even simple tasks challenging.”
This patient’s pre-existing condition, lupus, significantly influenced their experience with cortisone flares. The pain was widespread, affecting various parts of their body. Treatment involved a careful approach to manage both the flare and the underlying lupus. The patient’s response to a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments demonstrated that tailored strategies are crucial for managing flares in individuals with complex medical histories.
Case Study 3: A Patient with a Cortisone Injection Flare
“After receiving a cortisone injection for a persistent shoulder pain, I experienced an immediate, sharp increase in pain and inflammation. It was much worse than before the injection.”
This patient’s case highlights a potential adverse reaction to cortisone injections. The immediate worsening of symptoms following the injection underscored the importance of careful consideration and monitoring when administering cortisone. Treatment involved a different approach, focusing on reducing inflammation and managing the discomfort. The patient’s response was marked by a slower recovery period, emphasizing the need for individual patient monitoring and potential alternative treatment options in such situations.
Case Study 4: A Patient with Gastrointestinal Flare-ups, What is a cortisone flare
“Cortisone flares often trigger severe gastrointestinal issues, such as nausea and diarrhea. This makes it difficult to keep down any medication.”
This patient’s experience illustrates the potential for cortisone flares to trigger secondary symptoms. The digestive distress caused significant challenges in managing the flare effectively. Treatment involved a combination of anti-nausea medications and dietary adjustments to mitigate the gastrointestinal complications. The patient’s response highlighted the necessity of considering the holistic impact of cortisone flares and adjusting treatment plans accordingly.
Long-Term Management Strategies
Living with the potential for cortisone flares requires a proactive and comprehensive approach to long-term management. This involves more than just reacting to symptoms; it necessitates understanding the triggers and developing strategies to prevent future episodes. A personalized plan, tailored to individual needs, is crucial for maintaining well-being and quality of life.Proactive management hinges on understanding the factors that contribute to flares.
By identifying and addressing these triggers, patients can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of future episodes. This proactive approach involves lifestyle adjustments, consistent medical monitoring, and a strong emphasis on patient education and self-management.
Proactive Measures for Preventing Cortisone Flares
Proactive measures aim to reduce the likelihood of cortisone flares by addressing potential triggers. These strategies include consistent medication adherence, regular check-ups with healthcare providers, and diligent monitoring of potential triggers. Understanding the specific factors that influence individual susceptibility to flares is vital for developing a personalized approach.
Importance of Patient Education and Self-Management
Patient education plays a critical role in long-term management. A thorough understanding of the condition, including triggers, symptoms, and available treatment options, empowers individuals to take an active role in their health. Self-management techniques, such as stress reduction strategies and symptom tracking, further enhance control over the condition.
Lifestyle Adjustments to Reduce Flare Likelihood
Lifestyle adjustments can significantly impact the frequency and severity of cortisone flares. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management techniques are essential components of a proactive approach. Avoiding known triggers, such as certain foods or environmental factors, is also critical. A well-rounded approach that encompasses physical, emotional, and dietary factors is key to long-term management.
Role of Support Systems in Managing Long-Term Flare Issues
Support systems are crucial for managing long-term flare issues. The emotional and practical support provided by family, friends, or support groups can help individuals cope with the challenges of managing a chronic condition. Sharing experiences and learning from others who understand the specific struggles can be immensely helpful in navigating the complexities of long-term management.
Actionable Steps for Preventing Cortisone Flare-Ups
| Category | Actionable Steps |
|---|---|
| Diet |
|
| Exercise |
|
| Stress Management |
|
| Sleep Hygiene |
|
| Medication Adherence |
|
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, cortisone flares can be a complex and challenging health experience. Understanding the different factors that contribute to these episodes, from underlying medical conditions to lifestyle triggers, is crucial for effective management. By recognizing the symptoms, exploring treatment options, and adopting proactive long-term strategies, individuals can significantly improve their quality of life. Remember, early intervention and a strong support system play a vital role in navigating these flares successfully.
The information provided in this guide should not replace professional medical advice; always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized care.




