What are face mites? These microscopic creatures, part of the Demodex genus, live on human skin, often in the face and scalp. They’re tiny, and while usually harmless, some people experience discomfort from their presence. Understanding these tiny inhabitants and their impact on our health is key to managing any potential issues.
This comprehensive guide explores everything from their anatomy and lifestyle to the potential symptoms of an infestation, diagnostic methods, and effective treatments. We’ll also look at how to prevent these tiny pests from settling in and impacting your well-being.
Introduction to Face Mites
Face mites, tiny creatures often invisible to the naked eye, are a fascinating aspect of human biology. These microscopic arthropods, belonging to the order Prostigmata, are part of the larger class of arachnids, which also includes spiders and scorpions. Their presence on human skin, though generally harmless, can be a source of concern for some individuals. Understanding these mites, their characteristics, and their habitat can help in managing any potential discomfort or concerns.
Common Types of Face Mites
Face mites are predominantly found in the genus
- Demodex*. Two common species are
- Demodex folliculorum* and
- Demodex brevis*. These mites are distinguished by their specific location and behavior on the skin.
- Demodex folliculorum* reside primarily in hair follicles, while
- Demodex brevis* are found in sebaceous glands. This difference in location impacts their interaction with the host.
Size and Appearance
Face mites are extremely small, typically ranging from 0.3 to 0.4 mm in length. They have an elongated, worm-like body shape, with a pair of legs on each segment. Their bodies are typically translucent or yellowish-white in color, allowing for observation under a microscope. Visualizing these mites requires magnification. Imagine tiny, translucent worms, slightly elongated, nestled within the skin’s follicles and glands.
Their appearance is characteristic of microscopic arthropods.
Common Environments
Face mites are typically found on the skin of humans and other mammals. They are most commonly located on the face, particularly around the nose and cheeks. Their presence in these areas is correlated with the concentration of sebaceous glands, providing a suitable environment for their sustenance. The warm, moist conditions of these regions on the face create an ideal environment for these mites to thrive.
Comparison of Face Mite Types
| Characteristic | Demodex folliculorum | Demodex brevis |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Habitat | Hair follicles | Sebaceous glands |
| Size (approximate) | 0.3-0.4 mm | 0.3-0.4 mm |
| Appearance | Elongated, translucent/yellowish-white | Elongated, translucent/yellowish-white |
| Feeding Habits | Feed on sebum and skin cells | Feed on sebum and skin cells |
The table above provides a succinct comparison of the two most common types of face mites. These differences in their preferred environments and location within the skin’s structure help in understanding their ecological role. While the size and appearance are similar, their specific location within the skin’s ecosystem differentiates them.
Symptoms and Signs of Face Mite Infestation: What Are Face Mites
Identifying face mite infestations can be challenging, as the symptoms can mimic other skin conditions. A thorough understanding of the common signs and potential variations is crucial for accurate diagnosis. The symptoms are often subtle, and their severity can depend on several factors, including the individual’s immune response and the duration of the infestation.Understanding these symptoms empowers individuals to seek professional help and manage any potential discomfort effectively.
Common Symptoms
Symptoms of face mite infestations often present as mild skin irritations initially, which can progress if left untreated. Common symptoms include persistent itching, particularly at night, and skin irritation. These symptoms frequently manifest in areas of the face, such as the cheeks, forehead, or around the eyes, often appearing as tiny bumps or pimples.
Skin Reactions
Various skin reactions can accompany face mite infestations. These reactions are primarily caused by the mites’ presence and their waste products triggering an inflammatory response in the skin. Redness, inflammation, and a general feeling of skin discomfort are frequently reported. These reactions may vary in intensity and location depending on the individual’s sensitivity. Some individuals might experience mild redness, while others might develop more significant areas of inflammation and itching.
Individual Variations
The symptoms of face mite infestations can vary significantly between individuals. Some people may experience only mild itching and redness, while others may experience more severe reactions. This variation depends on factors such as the individual’s immune system response and the extent of the infestation. Age, pre-existing skin conditions, and other health factors also play a role in symptom severity.
For example, a person with a compromised immune system might experience more severe symptoms compared to someone with a healthy immune system. Similarly, someone with eczema or rosacea might experience more pronounced skin reactions.
Relationship with Other Skin Conditions
Face mites can sometimes be confused with other skin conditions due to overlapping symptoms. The itching and redness associated with face mites can be similar to those seen in eczema, rosacea, or even fungal infections. Proper diagnosis requires a thorough evaluation by a dermatologist, who can distinguish between different skin conditions based on the patient’s medical history and physical examination.
Careful consideration of the patient’s medical history is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Symptom Severity Table
| Symptom | Description | Potential Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Itching | Persistent, often worse at night | Mild to severe, depending on individual sensitivity and infestation level |
| Redness | Inflammation of the skin | Mild redness to significant inflammation |
| Inflammation | Swelling and irritation | Localized to widespread, potentially causing discomfort |
| Bumps/Pimples | Small raised areas on the skin | Can range from barely noticeable to noticeable, often clustered |
| Dryness | Dehydration of the skin | Mild to severe, potentially leading to scaling |
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors behind face mite infestations is crucial for effective prevention and management. While often linked to poor hygiene, the reality is more nuanced, involving a complex interplay of factors. These factors influence the environment conducive to face mite proliferation and the susceptibility of individuals.
Typical Causes of Face Mite Infestations, What are face mites
Face mites, scientifically known as
- Demodex folliculorum* and
- Demodex brevis*, are microscopic organisms that reside in the hair follicles and sebaceous glands of the skin. Their presence is generally considered normal, but an overpopulation can lead to irritation and inflammation. This overpopulation is not always directly tied to poor hygiene. Instead, various factors can create a favorable environment for them to thrive.
Role of Hygiene and Lifestyle Factors
Maintaining good hygiene practices is important for overall skin health and can influence face mite populations. However, excessive washing or harsh scrubbing can disrupt the skin’s natural oils, potentially creating an environment where face mites feel more comfortable. Lifestyle factors like stress, poor diet, and insufficient sleep can also play a role. For example, individuals experiencing chronic stress often have weakened immune systems, which might contribute to the overgrowth of face mites.
Similarly, a diet lacking essential nutrients can impact skin health, making it more susceptible to infestations.
Potential Contributing Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can increase the risk of face mite infestations. Conditions such as eczema, rosacea, or seborrheic dermatitis can create an environment where mites proliferate. These conditions often involve skin inflammation and changes in skin oil production, making the skin more susceptible to mite growth.
Potential Triggers Exacerbating Face Mite Infestations
Several factors can exacerbate existing face mite infestations. These include environmental irritants like harsh soaps, cosmetics, and pollutants. Additionally, stress and changes in hormone levels, such as during pregnancy or menopause, can also contribute to increased mite activity. For example, a sudden change in hormones can lead to fluctuations in sebum production, which can create a more favorable environment for the mites.
Potential Risk Factors
- Poor Hygiene Practices: While not always the sole cause, neglecting regular cleansing and skin care can contribute to a more hospitable environment for face mites.
- Skin Conditions: Pre-existing skin conditions such as eczema, rosacea, or seborrheic dermatitis can create an environment conducive to mite proliferation.
- Lifestyle Factors: Stress, poor diet, and lack of sleep can weaken the immune system and potentially contribute to an overgrowth of face mites.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, can influence sebum production, potentially impacting mite populations.
- Environmental Irritants: Exposure to harsh chemicals, soaps, cosmetics, and pollutants can disrupt the skin’s natural barrier and increase susceptibility to mite infestations.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as weakened immune systems, can make individuals more vulnerable to mite overgrowth.
Diagnosis and Treatment
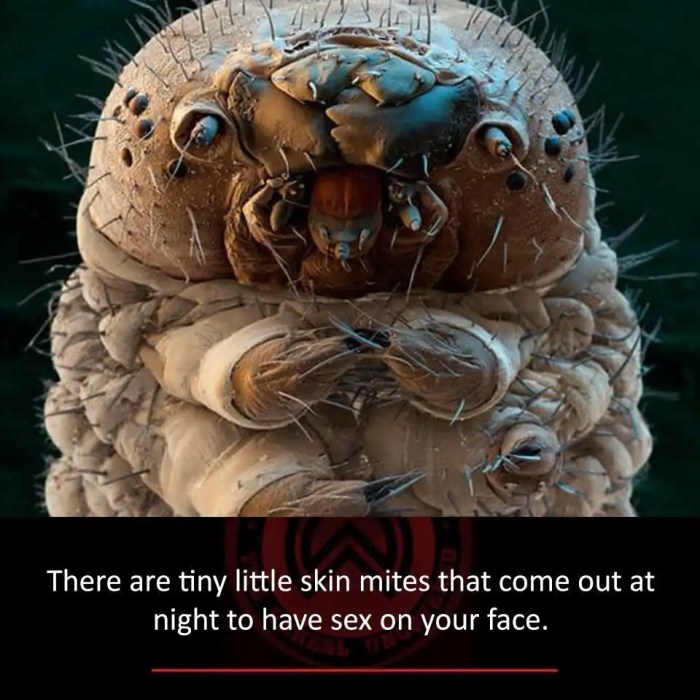
Figuring out if you have face mites and then getting rid of them can feel like a detective story. Luckily, there are reliable methods for diagnosis and effective treatments available. This section will Artikel the common approaches used to identify and address face mite infestations.
Common Methods for Diagnosing Face Mite Infestations
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for successful treatment. Misdiagnosis can lead to ineffective treatments and unnecessary frustration. Several methods are used to confirm the presence of face mites, ranging from visual examination to microscopic analysis.
Skin Examination
A visual inspection of the skin, particularly affected areas, is the first step in the diagnostic process. A dermatologist or a healthcare professional trained in skin conditions can assess the skin for characteristic symptoms, like tiny bumps, redness, or intense itching. The location and appearance of the symptoms can provide valuable clues. For instance, a concentrated rash around the nose or forehead might suggest a face mite infestation.
Microscopy
Microscopy plays a critical role in confirming the presence of face mites. A skin scraping from the affected area is examined under a microscope. This allows for the direct visualization of the mites and their eggs. The presence of these microscopic organisms provides definitive proof of infestation.
Confirming a Face Mite Infestation
Combining skin examination and microscopy provides the most reliable confirmation of a face mite infestation. A positive result from either method, particularly when both confirm the presence of mites, strongly suggests the infestation. The absence of mites through both methods, however, doesn’t definitively rule out the possibility of an alternative condition. It is important to discuss findings with a healthcare professional to ensure an accurate diagnosis.
Ever wondered about those tiny creatures called face mites? They’re microscopic, and while they’re pretty common, they usually don’t cause any problems. However, fluctuating hormones during menopause can sometimes affect mood in significant ways, impacting a person’s overall well-being. Learning to cope with these shifts can be incredibly helpful, and resources like menopause mood swings causes and coping offer practical strategies.
Ultimately, understanding the factors influencing your emotional state, including the presence of face mites, is key to feeling your best.
Common Treatments for Face Mites
Effective treatment for face mites typically involves a combination of topical medications and meticulous hygiene practices. Addressing both the mites and the environmental factors that support their growth is essential for long-term relief.
Topical Medications
Topical medications, often prescribed by a dermatologist, are commonly used to kill face mites. These medications are formulated to target and eliminate the mites. Examples include certain types of creams or lotions. Proper application and adherence to the prescribed dosage are vital for effectiveness.
Ever wondered what those tiny critters crawling on your face might be? They’re called face mites, and while they’re harmless, they’re certainly fascinating. But, while these microscopic creatures aren’t directly linked to health problems like, say, ovarian cancer causes risk factors , it’s still good to understand their presence and how to maintain healthy skin habits.
Ultimately, understanding face mites is all about good hygiene and a healthy lifestyle.
Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good hygiene is equally crucial in managing face mite infestations. Regular and thorough cleaning of the affected areas, combined with proper skincare practices, can help to reduce the mite population and prevent reinfestation. This includes using gentle cleansers and avoiding harsh scrubbing. Changing bedding and towels regularly can also help.
Comparison of Treatment Options
| Treatment Option | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topical Medications | Creams or lotions applied directly to the skin | Directly targets mites, often effective | May have side effects, requires consistent application |
| Hygiene Practices | Regular cleaning, proper skincare, and environmental control | Helps reduce mite population, preventative | May not eliminate mites immediately, needs consistent effort |
Prevention and Management
Preventing face mite infestations hinges on meticulous hygiene and lifestyle adjustments. Understanding the environmental factors that contribute to their proliferation is crucial for effective prevention. By adopting proactive measures, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing a face mite infestation.Maintaining a clean environment, coupled with consistent hygiene practices, is paramount in preventing face mite infestations. This proactive approach is not just about physical cleanliness, but also about recognizing and addressing potential contributing factors to a hospitable environment for these microscopic creatures.
Hygiene Practices for Prevention
Proper hygiene plays a vital role in minimizing the risk of face mite infestations. Maintaining a clean environment and consistent personal hygiene habits are essential to disrupt the life cycle of these mites.
- Regular Cleansing: Washing the face with gentle cleansers twice daily is crucial. This removes dead skin cells, oil, and debris that can provide a breeding ground for face mites. Choose cleansers specifically formulated for sensitive skin to avoid irritation. Avoid harsh scrubbing, as this can damage the skin barrier, making it more susceptible to infestation.
- Clean Bedding and Linens: Face mites can thrive in bedding and linens. Regularly washing bedding, pillowcases, and towels in hot water (at least 130°F or 54°C) can kill face mites and their eggs, preventing re-infestation. This practice should be part of a weekly or bi-weekly cleaning routine. Ensure that these items are thoroughly dried to prevent moisture buildup.
- Regular Vacuuming: Regular vacuuming of surfaces, especially those in the bedroom and areas where you spend a lot of time, can help remove dust mites and other allergens that can contribute to a favorable environment for face mites. This can reduce the overall environmental load of potential allergens.
- Proper Handwashing: Frequent handwashing, particularly before touching the face, is essential. This prevents the transfer of face mites from hands to the face, a common mode of transmission. Use soap and water for at least 20 seconds to effectively remove any potential mites or eggs from the hands.
Lifestyle Changes for Prevention
Implementing lifestyle changes can significantly contribute to preventing or managing face mite infestations. These adjustments encompass a holistic approach to well-being, recognizing the interconnectedness of physical health, environmental factors, and personal habits.
- Stress Management: Stress can weaken the immune system, potentially making individuals more susceptible to face mite infestations. Stress reduction techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature, can help improve overall well-being and create a more resilient environment for the body.
- Balanced Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports overall health and a strong immune system. A diet lacking in essential nutrients can compromise the body’s ability to fight off infections, including those potentially associated with face mites.
- Adequate Sleep: Getting sufficient sleep is essential for the body’s natural healing processes. Adequate sleep allows the body to repair and regenerate, strengthening the immune system and potentially reducing susceptibility to infestations.
Preventative Measures
A proactive approach to preventing face mite infestations involves a combination of environmental and personal hygiene practices.
- Regularly clean and wash all bed linens, pillowcases, and towels in hot water to eliminate mites and eggs.
- Use gentle cleansers to wash the face twice daily, focusing on thorough cleansing.
- Maintain a clean and dust-free environment to reduce the presence of allergens.
- Practice proper hand hygiene, especially before touching the face.
- Manage stress effectively through relaxation techniques to bolster the immune system.
Impact on Health and Well-being
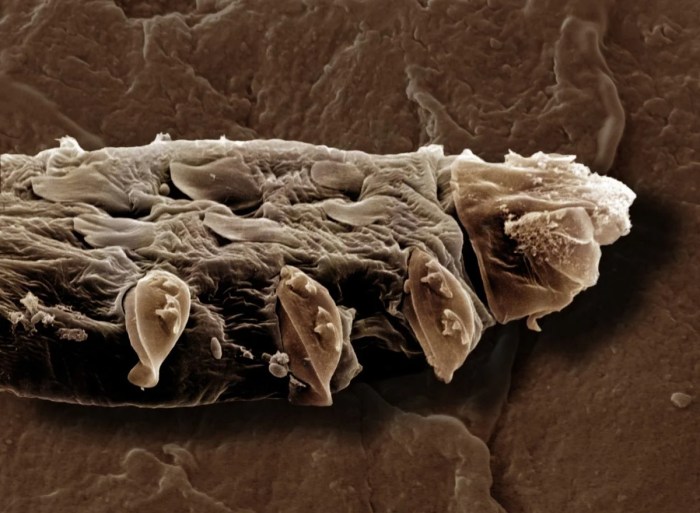
Face mites, while often not a serious health concern, can significantly impact an individual’s overall well-being. These microscopic creatures, present in many individuals, rarely cause severe problems. However, their presence can lead to discomfort, affecting self-esteem and social interactions. Understanding the potential impact is crucial for addressing any associated concerns effectively.The presence of face mites can trigger a variety of reactions, including itching, redness, and inflammation of the skin.
These physical symptoms can disrupt sleep, leading to fatigue and impacting daily functioning. The constant irritation can be distracting and unpleasant, affecting an individual’s ability to focus and engage in activities they enjoy.
Impact on Self-Esteem and Confidence
Face mite infestations, although not a reflection of personal hygiene, can negatively impact self-perception. The visible symptoms, such as redness and itching, can be a source of embarrassment and self-consciousness. Individuals may feel self-conscious about their appearance, affecting their confidence in social settings. This can lead to avoidance of social situations, further impacting their well-being. For example, someone might hesitate to participate in group activities or events because of their perceived appearance.
Psychological Impact
Dealing with a face mite infestation can trigger a range of psychological reactions. The constant itching and discomfort can lead to anxiety and stress. The fear of social judgment or the feeling of being different can contribute to feelings of isolation and depression. It is important to acknowledge that these reactions are normal responses to a perceived issue.
Ever wondered what those tiny critters crawling on your face might be? They’re called face mites, and while they’re generally harmless, understanding your overall health is key. Monitoring blood sugar levels with a1c home test kits can provide valuable insights, and this can indirectly affect your skin’s health. So, while face mites themselves aren’t directly related to diabetes, a healthy lifestyle and good blood sugar control can contribute to better skin health, reducing the potential for skin problems.
In the end, knowing what face mites are and keeping your body healthy are both important.
Seeking appropriate information and support can help alleviate these psychological impacts.
Impact on Social Interactions
The physical symptoms associated with face mite infestations can influence social interactions. Constant itching and skin irritation can lead to discomfort, making it challenging to engage fully in conversations or activities. The feeling of embarrassment or self-consciousness may discourage individuals from interacting with others, potentially leading to feelings of social isolation. For instance, an individual might avoid close-contact activities or situations where their skin is exposed.
Impact on Quality of Life
Face mite infestations can significantly reduce quality of life. The persistent itching and discomfort can disrupt sleep, leading to fatigue and affecting daily activities. Individuals may experience difficulty concentrating at work or school, and find it challenging to enjoy leisure activities. Furthermore, the emotional distress associated with the infestation can impact relationships and overall well-being. For example, someone might find it difficult to relax and enjoy social gatherings or family events due to the constant worry and discomfort.
Illustrative Information
Understanding face mites requires a look at their physical characteristics, microscopic structure, the skin’s response to their presence, and the common methods used to address them. This section provides detailed descriptions for illustrative purposes, aiding in visualization and comprehension.
Physical Characteristics of Face Mites
Face mites, scientifically known as
- Demodex folliculorum* and
- Demodex brevis*, are microscopic arachnids, meaning they are related to spiders and ticks. They are tiny, roughly 0.3 to 0.4 millimeters in length. Their bodies are elongated and slightly curved, with a segmented appearance. The appearance of the mites is translucent, and their color ranges from a light yellowish-white to a light brownish-red, depending on the individual mite and its stage of development.
Microscopic Structure of Face Mites
Face mites have a simple, yet intricate, microscopic structure. Their bodies are composed of a cephalothorax (fused head and thorax) and an abdomen. They have eight legs, adapted for gripping and moving around within hair follicles. Their mouthparts are adapted for feeding on skin cells and oils. The structure of the mite’s mouthparts and claws are important for their ability to penetrate the skin and consume the sebum and cellular debris in hair follicles.
The presence of specialized sensory structures, such as hairs or bristles, allows the mites to detect their environment and navigate within the hair follicles.
Skin Affected by Face Mites
Skin affected by face mite infestation often displays a range of symptoms. Initially, the skin might appear red or irritated. A subtle rash or inflammation might develop in areas where mites are concentrated. As the infestation progresses, the skin might become flaky, dry, or itchy. The skin may also develop small, red bumps or papules, particularly around the nose and cheeks.
These areas might appear slightly raised and rough in texture. In severe cases, the skin can become inflamed, leading to more pronounced redness and irritation.
Common Treatment Methods
Several treatment options are available for face mite infestations. These methods vary in their effectiveness and application, and should be discussed with a dermatologist for personalized recommendations. Topical medications, such as creams or lotions containing benzoyl peroxide or other anti-inflammatory agents, can help reduce inflammation and irritation. Some treatments use topical sulfur-based preparations, known for their anti-microbial properties.
Oral medications are sometimes prescribed for severe cases. These methods target the mites directly, disrupting their life cycle or killing them. The chosen method should be carefully considered in conjunction with the patient’s overall health and any other existing conditions.
Illustrative Image Descriptions
| Image Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | A high-resolution microscopic image of aDemodex* mite, highlighting its segmented body and eight legs. The image shows the mite in its natural environment, within a hair follicle. The image will be detailed enough to show the delicate structures of the mite’s body, mouthparts, and legs. |
| 2 | A close-up view of skin affected by face mites, showcasing the redness, inflammation, and potential presence of small bumps. The illustration should clearly depict the difference between normal skin and skin with a face mite infestation. |
| 3 | A diagram illustrating the life cycle ofDemodex* mites, highlighting the different stages of development. The diagram should show the progression from egg to adult and explain the importance of each stage in the mite’s life cycle. |
| 4 | A side-by-side comparison of normal skin and skin affected by a face mite infestation, clearly demonstrating the redness and inflammation associated with the condition. The illustration should provide a clear visual contrast. |
| 5 | A depiction of different topical treatments, such as benzoyl peroxide cream, sulfur-based lotion, and other related medications. The illustration will highlight the different forms these medications can take, including ointments, creams, and lotions. |
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, understanding what are face mites, their potential impact, and effective management strategies is crucial for maintaining healthy skin. While usually not a serious health concern, a proper understanding of these tiny creatures can empower you to address any discomfort they might cause. We’ve explored their biology, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatments, prevention, and impact on overall well-being, offering a complete picture of this common skin issue.
Armed with this knowledge, you can confidently approach any concerns you may have about face mites.




