Trapezius muscle pain massage technique is a powerful approach to alleviate discomfort and restore function. This comprehensive guide delves into the anatomy, causes, and various massage techniques for targeting trapezius pain. We’ll explore everything from understanding the muscle itself to identifying trigger points, and even incorporating self-massage techniques for long-term relief.
From identifying the root causes of your pain to learning effective massage techniques, this guide empowers you with the knowledge and tools to manage trapezius pain effectively. We’ll provide clear instructions, detailed explanations, and illustrative examples to ensure a deep understanding of the process.
Understanding Trapezius Muscle Pain
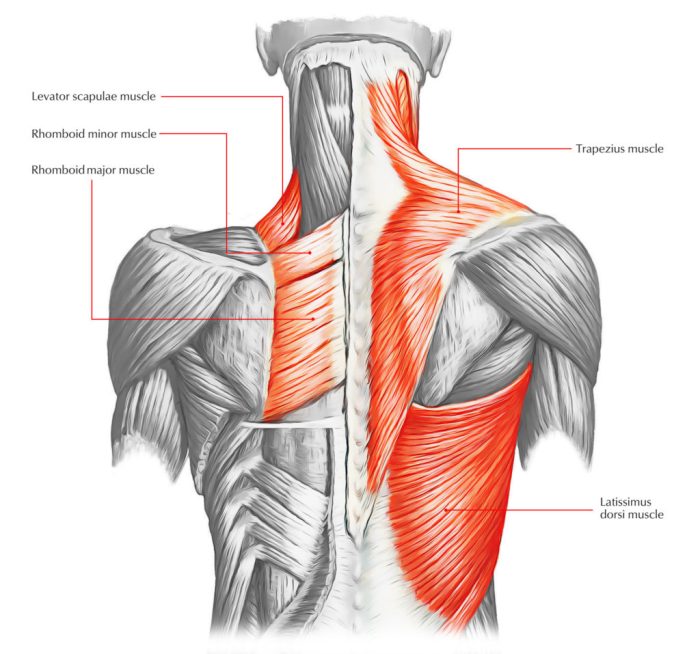
The trapezius muscle, a large, trapezoid-shaped muscle in the upper back and neck, plays a crucial role in supporting the shoulders and head. Understanding its anatomy, common pain triggers, and potential risk factors is vital for effective management and prevention. This exploration will delve into the intricacies of trapezius pain, offering a comprehensive overview.
Anatomical Description of the Trapezius Muscle
The trapezius muscle is a superficial muscle of the back, extending from the base of the skull to the mid-back and shoulders. It has three distinct parts, each originating from different areas of the back and neck:
- Upper Trapezius: Originating from the occipital bone and superior nuchal line of the skull, it ascends superiorly.
- Middle Trapezius: Originating from the spinous processes of the thoracic vertebrae, it runs horizontally.
- Lower Trapezius: Originating from the spinous processes of the thoracic and lumbar vertebrae, it descends inferiorly.
These three sections converge to insert on the scapula (shoulder blade), specifically the lateral third of the clavicle (collarbone), the acromion, and the spine of the scapula. The muscle’s diverse attachments allow for a wide range of movements, including elevation, depression, retraction, and rotation of the scapula.
Common Causes of Trapezius Muscle Pain
Trapezius pain can stem from various factors. Muscle strains are a frequent culprit, often resulting from overuse, poor posture, or sudden forceful movements. Repetitive lifting, prolonged periods of sitting with poor posture, or forceful neck movements can all contribute to muscle strains. Overuse injuries are another significant cause, particularly in individuals with jobs requiring extended periods of lifting, reaching, or straining the neck and shoulders.
Inadequate warm-up before strenuous activities can also predispose individuals to trapezius strains.
- Posture Issues: Poor posture, such as hunching over a computer or desk, can lead to chronic muscle strain in the trapezius, causing persistent pain and discomfort.
- Other Related Conditions: Conditions like arthritis, fibromyalgia, and neurological disorders can sometimes manifest as trapezius pain. These conditions can affect the nerves and muscles around the trapezius, contributing to pain and other symptoms.
Comparing Types of Trapezius Pain
| Type of Pain | Potential Causes |
|---|---|
| Sharp, Stabbing Pain | Muscle strain, sudden trauma, or referred pain from a different area (e.g., cervical spine). |
| Dull, Aching Pain | Chronic muscle tension, overuse, poor posture, or underlying conditions. |
| Burning Pain | Nerve impingement, inflammation, or conditions affecting the surrounding nerves. |
Risk Factors for Developing Trapezius Pain
Several factors can increase an individual’s susceptibility to trapezius pain.
- Age: Older individuals may experience degeneration or wear and tear in the neck and shoulder region, potentially contributing to muscle pain.
- Occupation: Jobs demanding repetitive movements or heavy lifting, such as construction workers or delivery drivers, pose a significant risk.
- Previous Injuries: Individuals with a history of neck or shoulder injuries may be more prone to developing trapezius pain, as the muscles and supporting structures may be weakened.
- Stress and Anxiety: Chronic stress and anxiety can contribute to muscle tension and pain in the trapezius region.
- Poor Posture: Sustained poor posture habits, particularly while working at a desk or using electronic devices, can lead to long-term muscle strain and pain.
Massage Techniques for Trapezius Pain Relief

Targeting the trapezius muscle, a crucial component of the upper back and neck, requires specific massage techniques for effective pain relief. These techniques, when performed correctly, can alleviate muscle tension, improve blood flow, and promote relaxation, leading to reduced pain and discomfort. Understanding the proper application of these techniques is essential to avoid potential injury and maximize therapeutic benefits.Effective massage therapy for trapezius pain involves a range of techniques that address different aspects of muscle tension and discomfort.
These techniques, when combined and strategically applied, can yield significant results in alleviating pain and restoring function.
Effleurage
Effleurage, a gentle stroking technique, is an excellent starting point for any massage session targeting the trapezius. It promotes relaxation and prepares the muscles for deeper work. The strokes should be long, smooth, and continuous, moving in the direction of lymphatic drainage. Apply light to moderate pressure, and maintain consistent contact with the skin. This technique improves blood circulation and reduces muscle tension, making it ideal for initial treatment.
Petrissage
Petrissage involves kneading and lifting the muscle tissue. This technique improves circulation and helps break down adhesions, promoting muscle flexibility and reducing pain. Use a cupping or kneading motion, applying moderate pressure. The stroke direction should follow the muscle fibers. Be mindful to avoid over-pressing, which could lead to discomfort or injury.
Friction
Friction involves applying firm, sustained pressure to specific points within the trapezius muscle. This technique is effective for releasing knots and adhesions, targeting areas of chronic pain. The pressure should be firm but not painful. The stroke direction should be along the muscle fibers. It’s essential to focus on specific trigger points, avoiding unnecessary pressure on surrounding tissues.
Tapotement
Tapotement involves rhythmic tapping, percussion, or slapping movements. This technique stimulates blood circulation, and helps to release muscle tension. The movements should be light and focused, avoiding excessive force. This technique is typically used in combination with other techniques to enhance their effectiveness. Avoid using this technique if the client reports any pain or discomfort.
Gradual Pressure Increase
A critical aspect of any massage, especially for sensitive areas like the trapezius, is the gradual increase in pressure. Starting with light pressure and progressively increasing it allows the client to adjust and communicate discomfort. This method prevents injury and ensures the massage remains a therapeutic experience. It allows for personalized adjustments to accommodate individual sensitivities.
Massage Technique Comparison
| Technique | Description | Pressure | Stroke Direction | Illustration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effleurage | Gentle stroking | Light to Moderate | Along lymphatic drainage | Imagine a smooth, continuous gliding motion over the muscle, similar to the way a painter would apply a stroke of paint. |
| Petrissage | Kneading and lifting | Moderate | Along muscle fibers | Visualize the motion of kneading dough, but on the muscle tissue. |
| Friction | Firm, sustained pressure | Firm, but not painful | Along muscle fibers | Imagine applying focused pressure with a firm, but gentle hand, targeting specific points. |
| Tapotement | Rhythmic tapping | Light | Along muscle fibers | Visualize light, rhythmic tapping on the muscle, similar to a gentle percussion instrument. |
Identifying Trigger Points and Myofascial Release
Understanding trigger points and myofascial release is crucial for effectively addressing trapezius pain. These techniques go beyond superficial massage, delving into the underlying causes of the discomfort by targeting specific areas of tension and restriction. By identifying and releasing these trigger points, we can significantly improve circulation, reduce muscle spasms, and alleviate pain, ultimately restoring optimal function to the trapezius muscle.Trigger points are hyperirritable spots within a tight band of muscle fibers.
These knots, often accompanied by referred pain, can be the source of chronic neck, shoulder, and back pain. The pain from a trigger point isn’t always felt directly over the affected muscle. Instead, it can radiate to other areas, making diagnosis and treatment challenging.
Identifying Trigger Points Through Palpation, Trapezius muscle pain massage technique
Precise palpation is key to identifying trigger points. A trigger point will feel like a hard, tender nodule within the muscle. It’s often described as a knot or a tight band. Pay close attention to the surrounding tissue. If the muscle feels excessively tight or tense, it’s a good indication that trigger points might be present.
Careful palpation allows you to pinpoint the exact location of the trigger point and its surrounding area, guiding subsequent treatment.
Techniques for Releasing Trigger Points
Various techniques can be used to release trigger points, from manual therapy to self-release methods.
Dealing with that nagging trapezius muscle pain? A gentle massage technique can really help. Focusing on the upper back and neck muscles, you can find relief from stiffness and tension. While we’re on the topic of pain relief, have you ever struggled with stubborn nail glue stuck to your skin? If so, check out this helpful guide on how to get nail glue off skin for some effective removal tips.
Once you’ve tackled that, you can get back to those soothing trapezius muscle massage techniques to further enhance your relaxation.
- Manual Release: A trained professional can effectively identify and release trigger points using specialized massage techniques. These techniques involve applying pressure and sustained pressure to the affected area. This can involve a variety of techniques, from deep tissue massage to myofascial release techniques, aiming to restore the muscle’s normal length and flexibility. Proper application is essential to avoid injury or further aggravation of the pain.
- Self-Release Using Tools: Tools like massage balls, foam rollers, or lacrosse balls can be used for self-treatment. Roll or press the tool over the trigger point, maintaining a consistent, firm pressure. It’s crucial to use the appropriate amount of pressure and avoid any pain that’s too intense. For example, a foam roller can be used to apply gentle, sustained pressure to the affected muscle group, which can help alleviate muscle tension and promote relaxation.
- Foam Rolling: Foam rolling is a self-myofascial release technique. It involves using a foam roller to apply pressure to the muscle tissue, effectively releasing the tension and knots. The pressure can be varied based on individual tolerance. The rolling action helps to lengthen the muscle fibers, reducing tightness and improving range of motion. A good example is rolling out the upper trapezius muscle by applying pressure to the affected area with the foam roller and gently moving the roller along the muscle.
Myofascial Release Techniques
Myofascial release addresses restrictions in the surrounding tissues. These tissues, including fascia, tendons, and ligaments, often become intertwined with the trigger points, further contributing to the pain. Myofascial release techniques aim to loosen these restrictions, improving the muscle’s flexibility and reducing pain. The therapist will apply sustained pressure to the surrounding tissues, gently stretching and releasing the tension.
The myofascial release technique can involve applying direct pressure, using specific stretches, and incorporating different types of movements to improve flexibility and range of motion.
Posture and Movement Considerations
Poor posture is a significant contributor to trapezius pain. Sustained slouching, hunching, or improper positioning during work or daily activities can strain the trapezius muscle, leading to chronic pain and discomfort. Addressing these postural issues is crucial for long-term relief and preventing future pain episodes. Understanding the specific postural problems affecting the trapezius, along with the exercises to correct them, will empower you to take control of your pain management.
Common Posture Issues Affecting the Trapezius
Poor posture, especially prolonged sitting, can strain the trapezius muscles. Various posture problems impact the trapezius, leading to pain and discomfort.
| Posture Issue | Description | Impact on Trapezius |
|---|---|---|
| Forward Head Posture | The head is positioned forward of the shoulders, creating an anterior tilt. | Increased tension and strain on the upper trapezius, leading to pain and tightness. |
| Rounded Shoulders | The shoulders are rounded forward, often accompanied by a forward head posture. | Strain on the middle and lower trapezius, potentially leading to pain and discomfort. |
| Kyphosis (Hunchback) | An excessive outward curvature of the thoracic spine. | Strain on the middle and lower trapezius, possibly leading to postural imbalances and pain. |
| Lordosis (Swayback) | An excessive inward curvature of the lumbar spine. | While not directly impacting the trapezius as much as other postures, it can indirectly contribute to imbalances and strain. |
Exercises to Improve Posture and Reduce Trapezius Strain
Regular exercise is vital to maintain good posture and alleviate trapezius pain. Exercises targeting the back, neck, and shoulders can strengthen the supporting muscles, promoting better posture and reducing strain on the trapezius.
- Neck Stretches: Gentle neck stretches help alleviate stiffness and tension in the neck muscles, which can reduce stress on the trapezius. Examples include chin tucks, side neck stretches, and rotation exercises.
- Shoulder Blade Retractions: These exercises strengthen the muscles that pull the shoulder blades together, improving posture and reducing pressure on the trapezius. Simple exercises include scapular retractions, where you squeeze your shoulder blades together, and rows.
- Thoracic Spine Mobilization: Improving the mobility of the thoracic spine can improve posture and reduce the strain on the trapezius. This can be achieved through gentle stretches and rotations, targeting the mid-back area.
- Core Strengthening: A strong core provides stability and support for the entire spine. Exercises like planks, bridges, and crunches can improve core strength, contributing to better posture and reduced stress on the trapezius.
Ergonomic Adjustments for a Pain-Free Workstation
Proper workstation ergonomics is crucial for preventing trapezius pain. Adjustments to your workspace can significantly reduce stress on the trapezius, minimizing pain and discomfort.
- Chair Adjustments: Ensure your chair provides adequate lower back support and allows for proper spinal alignment. Adjust the seat height so your feet are flat on the floor and your knees are at a 90-degree angle.
- Monitor Placement: Position your monitor at arm’s length and slightly below eye level to avoid straining your neck and shoulders.
- Keyboard and Mouse Placement: Position your keyboard and mouse close to your body to avoid reaching and straining your arms and shoulders.
- Regular Breaks: Get up and move around every 30-60 minutes to alleviate muscle tension and improve circulation.
Self-Massage Techniques for Trapezius Pain: Trapezius Muscle Pain Massage Technique
Taking control of your trapezius pain is achievable with targeted self-massage techniques. These techniques can help alleviate muscle tension, reduce pain, and improve range of motion. By incorporating these strategies into your routine, you can significantly enhance your overall well-being and reduce reliance on external therapies.Effective self-massage is crucial for managing trapezius pain. Understanding the specific trigger points and applying appropriate pressure and movement is key to achieving optimal relief.
Consistent self-massage can lead to long-term improvements in muscle health and function, enhancing your ability to perform daily activities without discomfort.
Foam Roller Techniques
Foam rolling is an excellent tool for targeting the trapezius muscle. It provides deep pressure, aiding in the release of knots and tension. The consistent rolling motion helps improve blood flow to the area, facilitating recovery and reducing pain.
- Position: Lie on your back with the foam roller placed under the middle portion of your trapezius muscle. Ensure the roller is positioned comfortably and aligned with the targeted area.
- Rolling Technique: Slowly roll back and forth, applying moderate pressure. Maintain a controlled motion, avoiding any sudden movements that could cause pain. Focus on areas where you feel tightness or knots.
Maintain contact for 30-60 seconds per area.
- Important Considerations: Be mindful of your body’s signals. If you experience sharp pain, stop immediately and adjust the pressure or position. Gradually increase the duration of each rolling session as you get accustomed to the technique.
Tennis Ball Techniques
Tennis balls offer a highly effective way to target specific trigger points within the trapezius muscle. The focused pressure of a tennis ball can effectively break down these knots and alleviate pain.
- Position: Place the tennis ball on the floor or a firm surface. Lie on your back, positioning the tennis ball directly on the affected area of the trapezius muscle. You can also place the ball against a wall or other stable surface for a variation.
- Trigger Point Release: Gently press into the trigger point, maintaining a firm but not painful pressure.
So, I’ve been exploring trapezius muscle pain massage techniques lately, and it’s been surprisingly helpful. While I’m focusing on relieving those nagging aches, I’ve also been reading up on natural remedies for fatty liver prevention, which is something I’m quite keen to learn more about. Natural remedies for fatty liver prevention seem to involve a lot of healthy lifestyle choices, and I’m thinking I might need to adjust my diet and exercise routine.
Ultimately, the focus is still on that trapezius muscle pain, but knowing I’m taking steps for better overall health is a nice bonus!
Move the tennis ball in small circular motions. The pressure should be firm enough to feel the release of the muscle fibers but not cause extreme discomfort.
- Important Considerations: Maintain a consistent pressure while rolling the tennis ball to achieve targeted trigger point release. This should not be a jarring or rapid motion. Hold each position for 30-60 seconds to allow for muscle relaxation and pain relief.
Massage Stick Techniques
Massage sticks provide a versatile approach to self-massage, offering controlled pressure and targeted release. The firm but flexible nature of the stick allows for precise application, especially for the trapezius muscles.
- Position: Hold the massage stick with both hands and position it along the affected area of the trapezius muscle. Use the pressure and motion of the stick to apply firm, controlled pressure to the muscle. Use a comfortable, stable position that allows for proper control.
- Application: Use the massage stick to apply consistent pressure and movement to the area, paying close attention to trigger points.
Apply moderate pressure, focusing on the areas where you feel tightness or knots. Move the stick in a slow, steady manner.
- Important Considerations: Maintain consistent pressure and a controlled motion to target the trapezius muscle. Maintain a firm but not painful pressure. This technique may be helpful in areas where the foam roller or tennis ball is less effective.
Self-Massage Techniques Table
| Tool | Technique | Position | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Foam Roller | Rolling | Lie on back, roller under trapezius | Roll back and forth, moderate pressure |
| Tennis Ball | Trigger Point Release | Lie on back, ball on trigger point | Apply firm pressure, small circular motions |
| Massage Stick | Direct Pressure | Hold stick, apply along trapezius | Controlled pressure and movement, focus on trigger points |
Combining Massage with Other Therapies
Massage therapy, while effective on its own, often yields even better results when combined with other complementary therapies. Integrating these approaches can significantly enhance pain relief, reduce recovery time, and improve overall well-being for individuals experiencing trapezius muscle pain. This holistic approach addresses the multifaceted nature of the issue, targeting various contributing factors.By incorporating additional therapies, you can create a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs and preferences.
This tailored approach can lead to a more effective and satisfying recovery journey.
Complementary Therapies for Trapezius Pain
Integrating various therapies can amplify the benefits of massage. Different therapies target distinct aspects of pain and recovery, creating a synergistic effect.
| Therapy | Description | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Therapy | Applying heat to the affected area using methods like hot packs, warm compresses, or saunas. | Increases blood flow to the muscles, promoting relaxation, reducing muscle tension, and easing pain. |
| Cold Therapy | Applying ice or cold packs to the area. | Reduces inflammation, swelling, and pain in the short term. Effective for acute pain or post-massage soreness. |
| Physical Therapy | Exercises, stretches, and manual techniques prescribed by a physical therapist. | Strengthens supporting muscles, improves posture, enhances range of motion, and promotes long-term pain management. |
| Acupuncture | Inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. | May relieve pain and muscle tension, stimulate the body’s natural healing mechanisms, and improve circulation. |
| Chiropractic Care | Adjustments to the spine and joints to address misalignments that might be contributing to pain. | May alleviate pain and restore proper biomechanics, which can contribute to reduced trapezius pain. |
Diet and Lifestyle Modifications
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle plays a critical role in managing trapezius pain. Poor diet, lack of exercise, and stress can exacerbate pain and hinder recovery.
- Balanced Diet:
- A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins supports overall health and can help reduce inflammation.
- Hydration:
- Drinking sufficient water helps to maintain healthy tissues and facilitates recovery.
- Regular Exercise:
- Consistent physical activity, including stretching and low-impact exercises, can strengthen muscles, improve posture, and promote overall well-being. Examples include swimming, yoga, and walking.
- Stress Management:
- Chronic stress can contribute to muscle tension and pain. Incorporating stress-reducing activities such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature can be beneficial.
Comparing Pain Management Approaches
Different pain management strategies can yield varying levels of effectiveness. Factors like the severity of pain, individual response, and the presence of underlying conditions influence treatment outcomes.
Effective pain management often involves a combination of approaches rather than relying on a single method.
Massage therapy, when combined with other therapies like heat or cold, often provides a more comprehensive and lasting approach. Physical therapy can strengthen supportive muscles, addressing the root cause of pain. Individual responses to these therapies vary; therefore, a personalized approach is essential.
Safety Precautions and Contraindications
Massage therapy, while generally safe, presents potential risks for individuals with certain medical conditions. Careful consideration of these factors and adherence to safety protocols are crucial for preventing complications and ensuring a positive experience. Knowing when to seek professional medical advice is equally important for managing trapezius pain effectively.Understanding the potential risks and contraindications of massage is vital for safe and effective treatment.
This section details precautions to take and situations where a professional consultation is necessary for managing trapezius pain.
Trying to soothe that nagging trapezius muscle pain? A good massage technique can be a lifesaver. Before you embark on your healing journey, remember to carefully consider what to pack for the hospital what to pack for the hospital. Essential items like comfortable clothing and pain relief medication will contribute to your comfort, and you’ll be able to focus on the trapezius muscle pain massage technique more effectively.
Potential Risks and Contraindications
Certain medical conditions can increase the risk of complications during massage therapy. These conditions require careful consideration and possible modifications to the massage techniques.
- Osteoporosis: Individuals with osteoporosis may be more susceptible to fractures if pressure is applied to the bones, especially in areas of low bone density. Massage techniques should avoid excessive pressure or forceful movements in the affected areas. A professional massage therapist should be aware of the individual’s bone density and adjust techniques accordingly.
- Herniated Discs: Massage therapy can be risky for individuals with herniated discs. Applying pressure to the spine or surrounding muscles can potentially worsen the condition. Massage should avoid direct pressure on the affected area and focus on surrounding muscles to reduce pain and inflammation. The therapist must prioritize the patient’s comfort and avoid any actions that could exacerbate the herniated disc.
- Blood Clotting Disorders: Individuals with blood clotting disorders should avoid massage in areas where blood clots are likely to form. Massage techniques should be gentle and avoid excessive pressure on the affected area.
- Skin Conditions: Individuals with skin conditions such as open wounds, infections, or rashes should avoid massage on the affected areas. The massage may worsen the condition and lead to discomfort or pain.
- Recent Surgery or Injury: Individuals who have undergone recent surgery or have experienced a recent injury should consult with a healthcare professional before receiving massage therapy. The massage may aggravate the healing process or cause discomfort.
Warning Signs to Stop Massage Therapy
It is essential to be aware of warning signs that indicate the massage should be stopped immediately. These signs can range from mild discomfort to more serious concerns.
- Increased Pain: If the pain in the trapezius area increases significantly during the massage, the massage should be stopped immediately. This could be a sign of injury or a reaction to the massage technique.
- Muscle Spasms: Muscle spasms or involuntary muscle contractions during massage may indicate that the pressure is too intense or that the technique is inappropriate for the individual’s condition.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: If the individual experiences dizziness or lightheadedness during the massage, the massage should be stopped immediately and the individual should be assisted to a comfortable position.
- Nausea or Vomiting: Nausea or vomiting during a massage may indicate a reaction to the pressure or technique and requires immediate cessation of the massage and medical attention.
- Unusual Sensations: Any unusual sensations, such as numbness, tingling, or burning, should immediately stop the massage.
When to Seek Professional Medical Advice
Trapezius pain can stem from various causes, some requiring professional medical intervention. It’s crucial to recognize when medical advice is needed.
- Persistent Pain: If trapezius pain persists despite self-care measures or massage therapy, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional.
- Severe Pain: Intense, debilitating pain that significantly interferes with daily activities should prompt a consultation with a medical professional.
- Numbness or Tingling: Numbness or tingling in the affected area, or in surrounding areas, requires professional medical attention.
- Weakness or Loss of Movement: Any weakness or loss of movement in the affected area or surrounding areas should prompt a consultation with a healthcare professional.
- Redness, Swelling, or Heat: Redness, swelling, or heat in the area of pain can be signs of infection or inflammation and should be addressed by a medical professional.
Situations Requiring Professional Consultation
In some cases, it’s essential to seek professional medical advice before or during massage therapy. These are situations where a professional should be consulted.
- History of Medical Conditions: Individuals with a history of medical conditions, such as heart problems, cancer, or autoimmune diseases, should consult with their healthcare provider before receiving massage therapy.
- Pregnancy: Pregnant women should consult with their doctor before undergoing massage therapy. Adjustments to massage techniques may be necessary during pregnancy.
- Recent Surgery: If the individual has recently undergone surgery, massage therapy should only be performed under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- Unclear Pain Origin: If the source of the trapezius pain is unclear or if there are other accompanying symptoms, a medical professional should be consulted.
- Pain Not Responding to Treatment: If the pain doesn’t improve after several sessions of massage therapy, it is necessary to seek professional medical advice to determine the underlying cause.
Illustrative Examples of Trapezius Massage
Understanding the various massage techniques for the trapezius muscle is crucial for effective pain relief. This section provides detailed illustrations, demonstrating different massage approaches and the use of tools, to guide you through a personalized massage experience. Specific examples will highlight targeting different pain areas within the trapezius.The trapezius, a large, superficial muscle of the upper back, is often a source of pain due to its frequent involvement in posture-related issues and repetitive strain.
Effective massage techniques can help alleviate this pain, improve muscle function, and enhance overall well-being.
Applying Direct Pressure
Understanding the different pressure points and angles is key to a safe and effective trapezius massage. Direct pressure, when applied correctly, can help break down adhesions and release tension in the muscle fibers. Illustrations should show different angles of application, ranging from a more superficial approach to a deeper one. For example, a superficial massage with the thumb, applied at a slight angle, targets the upper portion of the muscle, while deeper pressure with the knuckles can be used for the middle and lower regions.
Using Massage Tools
Using massage tools like foam rollers and massage sticks can enhance the reach and effectiveness of the massage. Foam rollers can be used to target larger areas of the trapezius, while massage sticks provide more precise pressure for trigger points. Illustrations should clearly demonstrate how to position the foam roller along the trapezius muscle, either horizontally or diagonally.
The use of a massage stick should show proper hand placement and the direction of pressure for both the upper, middle, and lower trapezius regions.
Massage Sequences for Different Pain Locations
The location of pain within the trapezius often dictates the massage sequence. Illustrations should show sequences targeting specific areas of the trapezius. For instance, for pain concentrated in the upper trapezius, a sequence beginning with gentle strokes, progressing to more targeted pressure on trigger points, and finishing with stretches could be illustrated. Similarly, if the pain is primarily in the lower trapezius, the massage sequence should focus on this area, with appropriate pressure and techniques.
Illustrative Guide to a Massage Session
This visual guide will demonstrate a full massage session targeting specific pain areas within the trapezius. The sequence should include:
- Initial Assessment: The therapist should assess the patient’s pain level and areas of greatest discomfort.
- Warm-up: Gentle circular motions to prepare the muscle tissue for deeper work. Illustrations should demonstrate specific movements for different regions of the trapezius.
- Targeted Massage: Specific techniques, including trigger point therapy and myofascial release, are illustrated for the upper, middle, and lower trapezius, with varying pressure and angles. Illustrations should include different angles and depths of pressure to demonstrate the range of techniques.
- Muscle Release: Techniques like cross-fiber friction, and deep tissue massage are illustrated. Show how to use massage tools like foam rollers and massage sticks to aid in muscle release.
- Stretches: Gentle stretches targeting the trapezius, illustrated from different angles, are crucial for long-term pain relief and improved range of motion.
- Cool-down: Gentle, relaxing strokes to complete the session.
Last Word
In conclusion, addressing trapezius muscle pain requires a multifaceted approach that considers the underlying causes, effective massage techniques, and supportive therapies. This guide provides a roadmap for understanding and managing your pain through a combination of targeted massage, self-care strategies, and posture improvements. Remember, consistency and proper technique are key to achieving long-term relief. Consult with a healthcare professional if your pain persists or worsens.




