Tips to prevent infections are crucial for maintaining good health. This guide delves into various strategies, from meticulous hygiene practices to vaccination strategies and environmental considerations. We’ll explore how to protect yourself and others from infection, covering everything from handwashing techniques to the importance of stress management and travel precautions. Get ready to learn actionable steps to safeguard your well-being!
This comprehensive guide to infection prevention covers a wide range of essential topics. From the importance of hand hygiene and vaccinations to environmental factors and personal protective measures, we’ll provide practical advice and valuable insights. We’ll also explore the vital role of nutrition, stress management, and travel precautions in preventing infections. Let’s dive into the details and uncover the secrets to staying healthy!
Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good hygiene is crucial in preventing the spread of infections. By following consistent and effective practices, we can significantly reduce our risk of contracting illnesses and protecting those around us. Simple habits, like thorough handwashing and surface disinfection, can make a substantial difference in overall health.Effective hygiene goes beyond just feeling clean; it’s about actively preventing the transmission of pathogens.
This involves understanding the mechanisms of infection and employing proven methods to disrupt their spread. Cleanliness is a cornerstone of preventative healthcare, and by adopting these practices, we build a strong defense against infections.
Handwashing Techniques
Thorough handwashing is the cornerstone of hygiene. It involves more than just a quick rinse; a proper technique is essential for effectiveness. Wet your hands with clean, running water, apply soap, and lather for at least 20 seconds. This allows the soap to emulsify and break down the germs. Focus on all surfaces, including the backs of your hands, between your fingers, and under your nails.
Rinse thoroughly with clean water and dry your hands with a clean towel or air dryer. The 20-second duration is critical, allowing sufficient contact time for the soap to effectively remove germs.
Disinfecting Frequently Touched Surfaces
Many surfaces in our daily lives harbor germs. Regular disinfection is essential to minimize the risk of infection. Use a disinfectant solution appropriate for the material of the surface. For example, diluted bleach solutions are effective on hard, non-porous surfaces like countertops and sinks, but avoid using bleach on wooden surfaces. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully, paying attention to the appropriate dilution and contact time.
Comparison of Hand Sanitizers
Hand sanitizers are a convenient alternative to handwashing, particularly in situations where water and soap are unavailable. However, different types offer varying levels of effectiveness. Alcohol-based sanitizers are generally more effective than non-alcohol-based ones, as alcohol has strong germ-killing properties. Ensure the sanitizer contains at least 60% alcohol for optimal germ reduction. Excessive use of hand sanitizer can also disrupt the skin’s natural protective barrier.
Therefore, use hand sanitizer judiciously and wash hands with soap and water whenever possible.
Frequency of Handwashing
| Scenario | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Before eating | Essential |
| After using the restroom | Essential |
| After handling raw meat or poultry | Essential |
| After touching pets | Essential |
| After coughing or sneezing | Essential |
| After touching public surfaces (e.g., doorknobs, handrails) | Desirable |
The table above highlights the importance of handwashing in various daily situations. Consistency in these practices significantly reduces the risk of infection.
Common Hygiene Mistakes and Consequences
Ignoring proper handwashing and surface disinfection can lead to the spread of infections. A frequent mistake is insufficient handwashing duration, failing to reach all areas of the hands. This can lead to the persistence of germs on the hands, increasing the risk of spreading them to others or oneself. Another mistake is the use of inadequate disinfectants or neglecting to follow the instructions.
This may lead to ineffective disinfection and a continued presence of germs. For example, using a disinfectant solution that is too weak may not kill all germs, and failing to maintain a proper contact time may result in incomplete disinfection.
Germs and Cleaning Solutions
| Germ | Appropriate Cleaning Solution |
|---|---|
| Norovirus | Bleach solution (1:10 dilution) |
| Salmonella | Bleach solution (1:10 dilution) |
| Staphylococcus aureus | Bleach solution (1:10 dilution) or other disinfectants |
| Influenza virus | Alcohol-based disinfectant or wipes |
Different germs require specific cleaning solutions. The table above provides examples of common germs and suitable cleaning solutions. Always consult the product label for appropriate usage and safety precautions.
Vaccination Strategies
Vaccinations are a cornerstone of preventing infectious diseases. They work by introducing a controlled dose of a weakened or inactive form of a pathogen into the body, stimulating the immune system to develop antibodies against it. This creates immunity without the risk of contracting the full-blown illness. This proactive approach is crucial in protecting individuals and communities from the devastating effects of infectious diseases.Vaccination significantly reduces the burden of preventable illnesses, improving public health outcomes.
By creating a robust immune response, vaccinations equip the body to effectively combat future exposures to the targeted pathogens.
Importance of Vaccination
Vaccination is vital for individual and community health. It protects individuals from contracting serious illnesses and prevents the spread of infectious diseases within communities. This protection extends beyond the individual, as vaccinated individuals are less likely to transmit the infection to others, especially those who are vulnerable or cannot be vaccinated.
Recommended Vaccinations by Age Group
Vaccination schedules are tailored to different age groups, reflecting the evolving needs and vulnerabilities of individuals at various stages of life. The recommended vaccines are designed to address specific pathogens that pose the greatest threat at each developmental phase.
- Infancy and Early Childhood: Vaccinations during infancy and early childhood are crucial for establishing a strong foundation of immunity against common childhood illnesses like measles, mumps, rubella (MMR), polio, diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (DTaP), and hepatitis B. These vaccinations help prevent serious complications and long-term health issues.
- Adolescence and Young Adulthood: During adolescence and young adulthood, vaccines are crucial to protect against diseases like HPV (human papillomavirus), meningococcal disease, and influenza. These vaccines are particularly important for preventing long-term health consequences and complications associated with these diseases. For example, HPV vaccination can help prevent cervical cancer.
- Adults and Seniors: Adults and seniors benefit from vaccinations against diseases like influenza, pneumonia, shingles, and COVID-19. These vaccines are vital for mitigating the risk of severe illness and complications, especially for those with pre-existing conditions. For example, pneumonia vaccination can help prevent serious respiratory infections in seniors.
Vaccination Process
Vaccination involves administering a vaccine, typically by injection, into the body. The injection site may experience mild discomfort, redness, or swelling. The process is generally safe and well-tolerated. A healthcare professional will provide guidance on the specific process.
- Potential Side Effects: Common side effects include soreness, redness, and swelling at the injection site. Fever, fatigue, or mild headache may also occur. These side effects are usually temporary and resolve within a few days. Serious side effects are rare.
- Precautions: Individuals with certain medical conditions or allergies may require specific precautions or modifications to the vaccination schedule. Always consult a healthcare professional before receiving any vaccination. Some individuals may experience a more pronounced reaction, requiring close monitoring. This may involve a consultation with a physician, who will determine the most appropriate course of action.
Herd Immunity
Herd immunity occurs when a large portion of a community is immune to a disease, making the spread of that disease less likely. This protection extends to those who cannot be vaccinated, such as infants or individuals with compromised immune systems. The concept of herd immunity highlights the collective benefit of vaccination. For example, a high vaccination rate for measles has significantly reduced the incidence of outbreaks.
Common Misconceptions
Numerous misconceptions surround vaccination. These misconceptions are often fueled by misinformation or lack of understanding of the science behind vaccines. Accurate information and open dialogue can dispel these misconceptions and promote informed decision-making.
- Vaccines cause autism: Extensive scientific research has shown no link between vaccines and autism. The widely publicized claims of such a link have been thoroughly debunked by numerous studies.
- Vaccines contain harmful chemicals: Vaccines contain ingredients that are essential for their safety and effectiveness, such as preservatives and stabilizers. These ingredients are present in extremely small amounts and are rigorously tested for safety. Vaccines are subjected to strict regulatory oversight.
Types of Vaccines and Mechanisms of Action
Different types of vaccines utilize various approaches to stimulate an immune response. Each type has its unique characteristics and applications.
- Inactivated Vaccines: These vaccines use inactivated versions of the virus. They cannot replicate and cause disease but still stimulate an immune response. Examples include influenza vaccines.
- Live-attenuated Vaccines: These vaccines use weakened versions of the virus. They can replicate in the body, leading to a more robust immune response. Examples include measles and MMR vaccines.
- mRNA Vaccines: These vaccines use messenger RNA (mRNA) to instruct cells to produce a specific viral protein. This stimulates an immune response without the risk of infection. Examples include COVID-19 vaccines.
Environmental Factors

Our surroundings play a significant role in the spread of infections. Understanding and mitigating environmental risks is crucial in preventing disease outbreaks. From the air we breathe to the water we drink, environmental factors influence our susceptibility to various pathogens. Proper sanitation and environmental hygiene are vital tools in the fight against infectious diseases.Environmental factors exert a powerful influence on infection transmission.
The presence of contaminated water, poor waste disposal, and inadequate ventilation can all contribute to the spread of pathogens. By recognizing these connections and implementing appropriate measures, we can create a healthier environment for everyone.
Impact of Environmental Factors on Infection Transmission
Environmental factors significantly influence the transmission of infections. Contaminated water sources, improper waste disposal, and inadequate ventilation create environments conducive to pathogen proliferation and transmission. These factors increase the risk of infection, particularly for vulnerable populations. For instance, a lack of access to clean water in a community can lead to the rapid spread of waterborne diseases.
Importance of Proper Ventilation and Air Quality
Proper ventilation and air quality are paramount in preventing the spread of airborne infections. Adequate airflow helps dilute and disperse airborne pathogens, reducing the risk of inhalation and transmission. Poor ventilation, particularly in crowded or enclosed spaces, can lead to the accumulation of pathogens in the air, increasing the likelihood of infection. Consider a classroom or office setting – poor ventilation can lead to more respiratory illnesses.
Significance of Proper Waste Disposal and Sanitation
Proper waste disposal and sanitation are essential for maintaining a healthy environment and preventing the spread of infections. Improper waste management can lead to the contamination of soil and water sources, facilitating the growth and transmission of pathogens. For instance, improper sewage disposal can contaminate water supplies, leading to outbreaks of waterborne illnesses. Effective sanitation practices, including proper waste segregation and disposal, are critical in minimizing these risks.
Comparison of Different Air Purifiers and Their Effectiveness
Air purifiers employ various technologies to remove airborne pathogens. High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters are effective at capturing fine particles, including viruses and bacteria. Ultraviolet (UV) germicidal lamps emit UV light that inactivates airborne pathogens. Ionizers release ions into the air that can neutralize pathogens. The effectiveness of an air purifier depends on the specific technology used, the size of the room, and the level of contamination.
For example, HEPA filters are commonly used in hospitals to remove airborne particles. Choosing the right air purifier for a specific need requires careful consideration of the type of pollutants and the size of the space.
Environmental Factors Increasing Infection Risk and Mitigation Strategies
Several environmental factors can elevate the risk of infection. These include:
- Contaminated water sources: Improper water treatment and inadequate sanitation can lead to the contamination of water supplies, posing a significant risk of waterborne diseases. Safeguarding water sources through proper treatment and sanitation is essential to mitigate this risk.
- Poor waste disposal: Improper waste disposal can contaminate soil and water sources, fostering the growth of pathogens. Implementing effective waste management strategies, including segregation and proper disposal methods, can significantly reduce this risk.
- Inadequate ventilation: Poor ventilation in enclosed spaces allows the accumulation of airborne pathogens, increasing the risk of respiratory illnesses. Improving ventilation systems, ensuring sufficient airflow, and using air purifiers can mitigate this risk.
- Overcrowding: Crowded living conditions and workplaces facilitate the rapid transmission of infectious agents. Maintaining appropriate spacing and implementing hygiene measures can help reduce this risk.
Significance of Clean Water Access in Preventing Waterborne Diseases
Clean water access is crucial for preventing waterborne diseases. Contaminated water serves as a breeding ground for pathogens, leading to various illnesses. Access to clean, potable water significantly reduces the risk of infection and enhances overall public health. Ensuring clean water supplies is a vital public health measure.
Personal Protective Measures
Protecting ourselves and others from infections requires proactive measures beyond basic hygiene. Personal protective measures play a crucial role in preventing the spread of infectious diseases, especially those transmitted through airborne particles. Understanding and correctly applying these measures significantly reduces the risk of infection.
Masks and Their Use in Preventing Airborne Infections
Masks act as a physical barrier, intercepting airborne droplets that may carry pathogens. Their effectiveness depends largely on proper use and selection. By creating a physical barrier, masks can significantly reduce the spread of airborne infections.
Correct Procedures for Wearing and Removing Masks
Proper mask use is essential for its effectiveness. Before putting on a mask, thoroughly wash your hands with soap and water or use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer. Place the mask over your nose and mouth, ensuring a snug fit without gaps. Avoid touching the mask’s surface while wearing it. To remove the mask, grasp the ear loops or head straps and carefully remove it without touching the front of the mask.
Immediately wash your hands after removing the mask.
Different Types of Masks and Their Protective Qualities
Various types of masks offer varying levels of protection. Surgical masks are designed to prevent the wearer from spreading respiratory droplets and are often used in healthcare settings. N95 respirators offer a higher level of filtration, blocking a significant percentage of airborne particles. Cloth masks, while less protective than N95s, can still offer some protection, particularly when used in combination with other preventive measures.
Understanding the specific protective qualities of different masks is crucial for selecting the appropriate type for the situation.
Comparison of Hand Sanitizers and Masks
Hand sanitizers and masks serve different but complementary roles in infection prevention. Hand sanitizers primarily target pathogens on the hands, while masks focus on airborne transmission. A combination of both strategies provides a more comprehensive approach to infection control.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) and Their Applications
Different scenarios require different PPE. The table below Artikels various PPE and their suitable applications.
| PPE | Application |
|---|---|
| Surgical Masks | Healthcare settings, public transportation during outbreaks, crowded environments |
| N95 Respirators | Healthcare settings, close contact with individuals with respiratory illnesses, high-risk settings |
| Gloves | Handling potentially contaminated surfaces, performing medical procedures |
| Eye Protection (Goggles/Face Shields) | Procedures generating splashes or sprays of bodily fluids, protection against airborne droplets |
Proper Disposal of Used PPE
Proper disposal of used PPE is crucial to prevent contamination. Used masks and other disposable PPE should be discarded in designated waste bins, following proper waste management protocols. For reusable PPE, follow manufacturer guidelines for cleaning and disinfecting before reuse. Proper disposal methods are essential for preventing further spread of infection.
Staying healthy is key, and preventing infections is crucial. Washing your hands frequently is a simple yet effective tip, and maintaining a strong immune system through a balanced diet and exercise is equally important. Knowing how kidney stones can affect your body, like whether they cause gastrointestinal issues, is also a vital part of overall health management. For example, understanding if kidney stones can cause gastrointestinal problems is helpful in developing preventive measures.
To learn more, check out this helpful resource on can kidney stones cause gastrointestinal problems. Ultimately, a holistic approach to health, encompassing good hygiene and a deep understanding of potential health concerns, leads to better overall well-being and reduces the risk of infection.
Nutritional Considerations
A strong immune system is intricately linked to a healthy diet. Proper nutrition provides the building blocks for immune cells and supports their functions. This crucial aspect of infection prevention deserves careful consideration. Nourishing your body with the right nutrients empowers it to fight off pathogens effectively.A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants is essential for immune function.
Essential nutrients act as fuel for the body’s defense mechanisms, supporting the development and activity of immune cells. This, in turn, enhances the body’s capacity to ward off infections. The impact of nutrition on immunity is undeniable.
Boosting your immune system is key to preventing infections. Washing your hands frequently and getting enough sleep are obvious, but did you know that a diet rich in magnesium can also play a vital role? Eating foods high in magnesium, like spinach and almonds, foods high in magnesium , can support your immune function, making it easier to fight off those pesky germs.
So, prioritize a healthy diet and you’ll be well on your way to a stronger immune system and fewer infections.
The Role of Nutrition in Boosting the Immune System
A well-nourished body is better equipped to defend itself against infections. Nutrients provide the raw materials for immune cells, antibodies, and other components of the immune response. Adequate intake of vitamins and minerals fuels the production of these crucial elements, fortifying the body’s natural defenses.
Foods Rich in Vitamins and Minerals for Immune Function
A wide variety of foods contribute to a robust immune system. These include foods rich in vitamins A, C, D, E, and various minerals like zinc, selenium, and iron.
- Citrus fruits (oranges, lemons, grapefruits) are excellent sources of vitamin C, which is vital for immune cell function.
- Dark leafy greens (spinach, kale, collard greens) offer vitamins A, C, and K, along with essential minerals.
- Berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries) are packed with antioxidants and vitamin C, supporting overall immune health.
- Fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel) provide vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids, which are important for immune function.
- Legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas) are rich in protein and fiber, supporting immune cell development.
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, walnuts, pumpkin seeds) provide healthy fats, vitamin E, and essential minerals.
- Eggs are a complete protein source, providing essential amino acids that support immune function.
Importance of Hydration and Its Impact
Staying adequately hydrated is crucial for overall health, including immune function. Water helps transport nutrients to cells and remove waste products. Dehydration can compromise the immune system’s ability to respond effectively to infections.
Staying healthy is all about preventative measures, like washing your hands frequently and getting enough sleep. But did you know that timing your supplements can also play a role in overall well-being? For example, knowing the best time to take creatine can enhance its effectiveness, just like practicing good hygiene is crucial to preventing infections. Focus on a balanced approach, and you’ll be well on your way to fighting off those pesky bugs! For more insights on when to take creatine, check out this helpful guide: best time to take creatine.
Ultimately, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a strong immune system, is key to preventing infections.
- Adequate water intake is essential for maintaining optimal immune function.
- Sufficient hydration helps the body transport nutrients and remove waste, supporting immune responses.
- Dehydration weakens the immune system’s defenses, making the body more susceptible to infections.
Effects of Poor Nutrition on the Immune System and Susceptibility to Infections
Malnutrition significantly weakens the immune system. A diet deficient in essential nutrients can impair the production and function of immune cells, leaving the body vulnerable to infections. This can lead to more frequent and severe illnesses.
- Poor nutrition can hinder the production and function of immune cells.
- A diet lacking in essential nutrients can make the body more susceptible to infections.
- Malnutrition can increase the severity and duration of illnesses.
Tips on Building a Healthy Diet to Prevent Infections
Developing a healthy diet to prevent infections requires mindful choices and a balanced approach.
- Consume a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Prioritize lean protein sources, including fish, poultry, beans, and lentils.
- Include healthy fats from nuts, seeds, and avocados.
- Maintain adequate hydration by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
Nutritional Content of Beneficial Foods
The table below highlights the nutritional content of some foods beneficial for a healthy immune system.
| Food | Vitamin C (mg) | Vitamin D (mcg) | Zinc (mg) | Selenium (mcg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orange | 50-70 | 0-0.1 | 0.05 | 0.3-0.7 |
| Spinach | 25-35 | 0-0.2 | 0.5-1 | 1-2 |
| Salmon | 0-10 | 1.5-4 | 0.5-1 | 1-3 |
| Almonds | 0-5 | 0.1-0.2 | 0.3-0.7 | 1-2 |
Stress Management: Tips To Prevent Infections
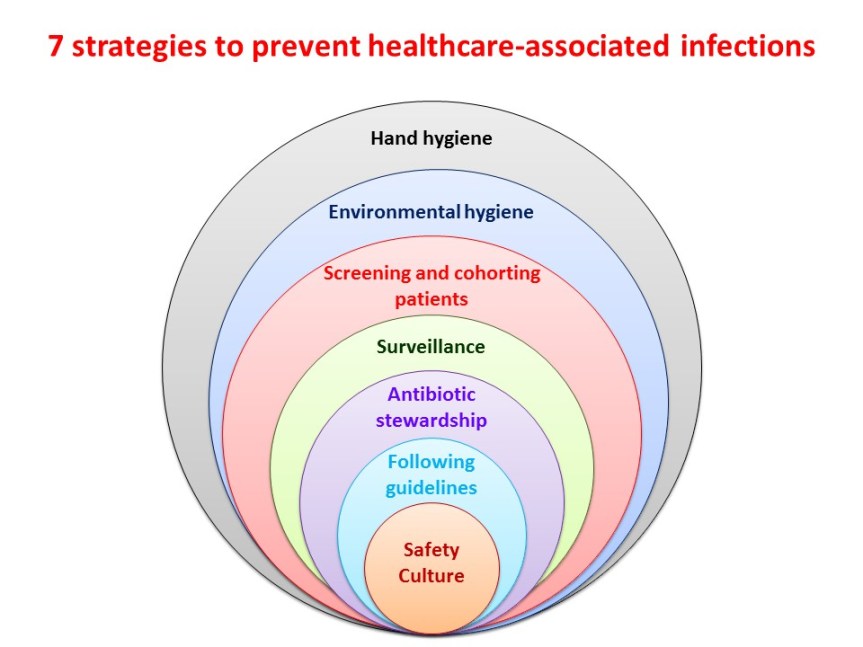
Stress, a ubiquitous part of modern life, significantly impacts our overall well-being, including our susceptibility to infections. Understanding the intricate link between stress and the immune system is crucial for proactively protecting our health. Chronic stress, in particular, can disrupt the delicate balance of our immune response, leaving us more vulnerable to various illnesses.The relationship between stress and infections is multifaceted.
High levels of stress hormones, such as cortisol, can suppress the activity of immune cells, making it harder for the body to fight off pathogens. This weakening of the immune system can manifest in a higher risk of contracting infections, as well as a slower recovery time. Furthermore, chronic stress can compromise the body’s ability to heal, potentially impacting the effectiveness of other preventative measures.
The Impact of Chronic Stress on the Immune System
Chronic stress, sustained over extended periods, exerts a detrimental effect on the immune system. The constant release of stress hormones can suppress the production of white blood cells, crucial components of the immune response. This suppression weakens the body’s defenses against invading microorganisms, increasing the risk of infections. Moreover, chronic stress can impair the function of the immune system’s regulatory mechanisms, leading to an imbalanced response.
Stress Management Techniques
Effective stress management is crucial for bolstering the immune system and preventing infections. A variety of techniques can help manage stress and promote overall well-being. Consistent exercise, for instance, can release endorphins, which have mood-boosting and stress-reducing properties. Mindfulness practices, like meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help regulate the body’s stress response. Relaxation techniques, such as progressive muscle relaxation, can also effectively alleviate tension and promote a sense of calm.
Prioritizing sufficient sleep is essential for immune function and helps the body recover from daily stressors.
Sleep and Immune Function
Adequate sleep is vital for maintaining a healthy immune system. During sleep, the body repairs and regenerates, including immune cells. Sleep deprivation weakens the immune response, making individuals more susceptible to infections. The impact of sleep on the immune system is substantial, as insufficient sleep can negatively affect the production and function of antibodies and other immune components.
Aiming for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night is generally recommended for optimal immune function.
Recognizing Stress Symptoms and Implementing Strategies
Recognizing stress symptoms is the first step in developing effective coping mechanisms. Symptoms can vary from individual to individual, but common indicators include persistent fatigue, difficulty concentrating, irritability, changes in appetite, and sleep disturbances. Once stress symptoms are identified, implementing appropriate stress-reducing strategies is crucial. This may involve incorporating regular exercise, scheduling relaxation time, seeking support from friends or family, and engaging in hobbies or activities that promote relaxation and well-being.
Stress Management Techniques and Potential Benefits, Tips to prevent infections
| Stress Management Technique | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|
| Regular Exercise | Reduces stress hormones, boosts mood, improves sleep quality |
| Meditation | Reduces anxiety, promotes relaxation, improves focus |
| Deep Breathing Exercises | Calms the nervous system, lowers heart rate, reduces stress |
| Progressive Muscle Relaxation | Reduces muscle tension, promotes relaxation, lowers stress levels |
| Sufficient Sleep | Improves immune function, promotes physical and mental recovery, reduces stress |
| Spending Time in Nature | Reduces stress, improves mood, promotes relaxation |
| Social Support | Provides emotional comfort, reduces feelings of isolation, helps manage stress |
Travel Precautions
Traveling opens up a world of experiences, but it also exposes you to new health risks. Understanding the specific infections prevalent in different destinations and taking proactive steps to protect yourself are crucial for a safe and enjoyable trip. This section delves into vital precautions for travelers to mitigate infection risks before, during, and after their journey.Traveling to new environments can expose you to various pathogens and infectious agents that may not be present in your home region.
This includes bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi. The prevalence and types of infections vary significantly depending on geographical location, climate, and local sanitation practices.
Preventive Measures for Travelers
Understanding the potential health risks in different regions is paramount. A proactive approach to infection prevention is essential, especially when traveling. These preventive measures are tailored to various environments.
- Environmental Awareness: Research the prevalence of infectious diseases in your destination. Look for information on water quality, sanitation, and local health guidelines. This allows you to anticipate potential risks and adjust your behavior accordingly.
- Vaccination Recommendations: Consult your healthcare provider for recommended vaccinations based on your destination and personal health history. Certain areas might require vaccinations against diseases like yellow fever, typhoid, or hepatitis. Vaccines can significantly reduce your risk of acquiring infections.
- Personal Protective Measures: Employ basic hygiene practices, such as frequent handwashing with soap and water or hand sanitizer, especially in public areas. Avoid contact with animals, particularly in regions with known zoonotic diseases. Wear appropriate clothing to protect against insects and ticks.
Prevalence of Infections in Different Regions
Different regions have varying rates of specific infectious diseases. Understanding these patterns can help travelers make informed choices.
- Tropical Regions: Areas with tropical climates often experience higher rates of mosquito-borne illnesses like malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus. Consult your doctor about preventative measures like mosquito repellent and potential medication.
- Developing Countries: Certain developing countries may have higher incidences of waterborne illnesses due to inadequate sanitation infrastructure. This necessitates extra caution about food and water safety.
- Areas with High Population Density: Cities and crowded areas may have higher rates of respiratory infections like influenza or common colds. Focus on maintaining good respiratory hygiene, such as covering coughs and sneezes.
Importance of Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Professional medical advice is critical before any travel. A healthcare provider can assess your individual risk factors and provide personalized guidance.
- Pre-Travel Consultation: Discuss your travel plans with your doctor well in advance. This includes your destination, duration, and any underlying health conditions. Your physician can recommend specific preventive measures and vaccinations.
- Personalized Advice: Your healthcare provider can tailor advice to your specific needs, considering your medical history, allergies, and any medications you’re taking. This is crucial for optimizing your health protection during travel.
- Potential Medication Adjustments: Your doctor can advise on any necessary adjustments to your medications before, during, and after your trip, ensuring you maintain appropriate health while traveling.
Precautions During and After Travel
Post-travel precautions are just as important as pre-travel measures.
- Hygiene Practices: Continue practicing good hygiene, such as handwashing and avoiding contact with potentially contaminated surfaces. Stay vigilant about food and water safety during and after your trip.
- Monitoring for Symptoms: Be mindful of any unusual symptoms, such as fever, nausea, or diarrhea, and consult a doctor immediately if they occur. Early intervention is key for managing potential infections.
- Reporting Travel History: Inform your healthcare provider of your travel history if you experience any illness after returning home. This will help your doctor assess the potential cause of your symptoms.
Essential Medications and Supplies for Travel
Packing the right medications and supplies can ensure you’re prepared for any eventuality.
- Prescriptions: Pack a sufficient supply of any prescribed medications, including dosage and instructions. Ensure you have enough medication for the entire duration of your trip.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Pack common over-the-counter medications like pain relievers, anti-diarrheal medication, and anti-allergic medications. These are often essential for addressing minor ailments.
- First-Aid Kit: Assemble a comprehensive first-aid kit with bandages, antiseptic wipes, pain relievers, and any other necessary supplies. A well-stocked first-aid kit can aid in managing minor injuries and illnesses.
Comparing Risks of Infection in Different Destinations
Risk assessment for infection is dependent on the specific location. Consider factors such as local sanitation, hygiene practices, and disease prevalence.
| Destination | Potential Infections | Precautions |
|---|---|---|
| Tropical Countries | Malaria, Dengue Fever, Zika Virus | Mosquito repellent, vaccinations |
| Developing Countries | Waterborne Diseases, Typhoid | Boiled/purified water, careful food handling |
| Crowded Cities | Respiratory Infections, Common Cold | Hand hygiene, covering coughs/sneezes |
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, preventing infections requires a multi-faceted approach. By incorporating these tips into your daily routine, you can significantly reduce your risk of infection. From practicing meticulous hygiene to prioritizing stress management and getting vaccinated, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge and tools to protect your health. Remember, proactive measures are key to staying healthy and preventing the spread of illness.
By understanding the various aspects discussed in this guide, you’re empowered to take control of your health and well-being.




