The risks of untreated ulcerative colitis are significant and far-reaching, impacting every aspect of a person’s life. This condition, characterized by inflammation in the colon, can lead to a cascade of complications if left unaddressed. From digestive distress to potential long-term health concerns, understanding these risks is crucial for proactive management.
This comprehensive guide explores the various facets of untreated ulcerative colitis, detailing the immediate and long-term consequences. We will delve into the impact on the digestive system, the heightened risk of colorectal cancer, nutritional deficiencies, psychological challenges, and ultimately, strategies for long-term management.
Introduction to Ulcerative Colitis: The Risks Of Untreated Ulcerative Colitis

Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that primarily affects the colon and rectum. It’s characterized by inflammation and ulcers in the lining of the large intestine. This inflammation can range from mild to severe, impacting a patient’s overall well-being and quality of life. Understanding the stages, symptoms, and potential causes of ulcerative colitis is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.The inflammation in ulcerative colitis is continuous, affecting only the innermost lining of the colon and rectum.
Unlike Crohn’s disease, which can affect any part of the digestive tract and can involve all layers of the bowel wall, ulcerative colitis is confined to the colon and rectum. This difference in location and the way the disease presents itself makes it important to seek medical attention for any persistent digestive issues.
Stages of Ulcerative Colitis
The severity of ulcerative colitis can fluctuate, progressing through different stages. These stages are typically categorized based on the extent of the affected colon and the associated symptoms. Mild cases may only involve a small portion of the colon, while severe cases can involve the entire colon. This progression can vary significantly from person to person, highlighting the unpredictable nature of the disease.
Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis
Common symptoms of ulcerative colitis include persistent diarrhea, often with blood and mucus, abdominal cramps and pain, fever, fatigue, and weight loss. These symptoms can vary in severity depending on the stage and extent of the inflammation. In some cases, the symptoms might be mild and manageable, while in others, they can be debilitating and require immediate medical attention.
Progression of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis can progress from mild to severe. Mild cases might exhibit occasional symptoms, while severe cases can result in frequent and severe diarrhea, significant blood loss, and dehydration. The progression is not always linear, and periods of remission (where symptoms subside) can alternate with periods of exacerbation (where symptoms worsen). Factors such as stress, diet, and medications can influence the progression of the disease.
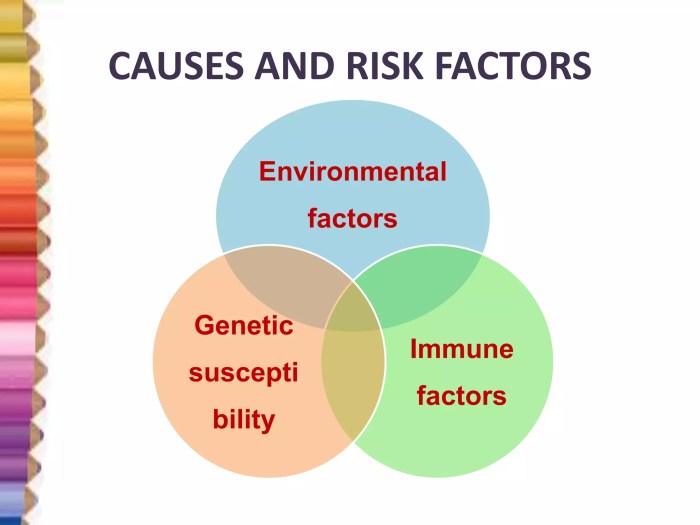
Factors Contributing to Ulcerative Colitis
The exact cause of ulcerative colitis remains unknown, but several factors are believed to play a role in its development. These include genetic predisposition, where a family history of the disease increases the risk, and environmental triggers, such as certain foods, infections, or medications. The immune system’s response to these triggers might also be a key contributor. It’s crucial to remember that while genetics and environment may increase the risk, they do not guarantee the development of the disease.
Untreated ulcerative colitis can lead to serious complications, including increased risk of colon cancer. While that’s a pretty scary thought, it’s important to remember that sometimes, seemingly unrelated symptoms like lip twitching can also be a sign of underlying health issues. If you’re experiencing lip twitching, understanding its potential causes and treatment options is crucial. For more information on lip twitching symptoms, causes, and treatment, check out this helpful resource: lip twitching symptoms causes treatment.
Ultimately, though, focusing on proper ulcerative colitis management is key to avoiding those concerning long-term health risks.
Table of Ulcerative Colitis Stages
| Stage of Ulcerative Colitis | Symptoms | Treatment Options | Potential Complications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild | Occasional diarrhea, mild abdominal pain, minimal blood in stool. | Dietary modifications, anti-inflammatory medications (e.g., corticosteroids). | Dehydration, anemia, mild malnutrition. |
| Moderate | Frequent diarrhea with blood and mucus, significant abdominal pain, fever, fatigue. | Combination of medications (e.g., corticosteroids, immunomodulators), nutritional support. | Severe dehydration, anemia, malnutrition, electrolyte imbalances. |
| Severe | Frequent, severe diarrhea with significant blood loss, severe abdominal pain, high fever, severe fatigue, and toxic megacolon. | Hospitalization, intravenous fluids, corticosteroids, immunomodulators, surgery (in some cases). | Toxic megacolon (potentially life-threatening), severe anemia, malnutrition, sepsis, and bowel perforation. |
| Fulminant | Life-threatening symptoms including severe bleeding, high fever, and severe abdominal pain. | Intensive medical care, hospitalization, and potentially surgery. | Death, bowel perforation, sepsis, severe complications from surgery. |
Health Risks of Untreated Ulcerative Colitis
Untreated ulcerative colitis can lead to a cascade of serious health complications, impacting not only the digestive system but also overall well-being. Ignoring the symptoms and delaying treatment can exacerbate the inflammation and increase the risk of severe complications, including colorectal cancer. Understanding these risks is crucial for early intervention and effective management of the condition.The consequences of untreated ulcerative colitis are multifaceted, ranging from immediate discomfort to long-term health issues.
Delayed or inadequate medical attention can significantly worsen the condition, making it more challenging to manage and leading to potentially life-altering outcomes. Proactive management, including early diagnosis and consistent medical care, is paramount in mitigating these risks.
Immediate Consequences of Untreated Ulcerative Colitis
Untreated ulcerative colitis often manifests with worsening abdominal pain, frequent diarrhea, and blood in the stool. These immediate symptoms can significantly impact daily life, causing discomfort, fatigue, and a diminished quality of life. Left unaddressed, the inflammation can escalate, leading to more severe and persistent complications.
Long-Term Consequences of Untreated Ulcerative Colitis
The long-term implications of untreated ulcerative colitis extend beyond the immediate symptoms. Prolonged inflammation can damage the colon lining, increasing the risk of serious complications, such as severe bleeding, bowel obstruction, and an increased risk of developing colorectal cancer.
Impact on the Digestive System
The digestive system is profoundly affected by untreated ulcerative colitis. Persistent inflammation can lead to a range of issues, including narrowing of the colon (strictures), which can obstruct the flow of stool. This bowel obstruction can cause significant pain, discomfort, and even require surgical intervention. In severe cases, the inflammation can cause the colon to lose its ability to absorb nutrients, leading to malnutrition and further health problems.
Severe Inflammation and its Impact on Overall Well-being
Untreated severe inflammation in ulcerative colitis can significantly affect overall well-being. The chronic inflammation can lead to anemia, malnutrition, and fatigue, making daily activities challenging. The emotional toll of managing the symptoms and potential complications can be substantial. Individuals experiencing these effects often need comprehensive support from healthcare professionals and their social network.
Increased Risk of Colorectal Cancer, The risks of untreated ulcerative colitis
A critical concern associated with untreated ulcerative colitis is the increased risk of developing colorectal cancer. Studies have shown a strong correlation between the duration and severity of inflammation and the likelihood of developing cancerous polyps in the colon. Early detection and management of the condition are essential to minimize this risk.
Table: Risks of Untreated Ulcerative Colitis
| Risk | Description | Potential Impact on Health | Prevention Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bowel Obstruction | Narrowing or blockage of the colon, hindering the passage of stool. | Severe abdominal pain, discomfort, potential need for surgery. | Regular monitoring, prompt treatment of flare-ups, and adherence to medication. |
| Severe Bleeding | Excessive bleeding from the inflamed colon. | Iron deficiency anemia, fatigue, potential need for blood transfusions. | Early diagnosis, prompt treatment of flare-ups, and monitoring for signs of bleeding. |
| Colorectal Cancer | Increased risk of developing cancerous polyps or tumors in the colon. | Potentially life-threatening, requiring extensive treatment. | Regular colonoscopies, close monitoring by healthcare professionals, and adherence to treatment plans. |
| Malnutrition | Inability of the colon to absorb nutrients due to severe inflammation. | Weakness, fatigue, deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals. | Dietary modifications, nutritional supplements, and close monitoring of nutrient intake. |
Impact on Nutrition and Metabolism
Untreated ulcerative colitis can significantly disrupt the body’s ability to absorb and utilize nutrients, leading to various nutritional deficiencies. This disruption is often a result of inflammation in the digestive tract, which interferes with the normal processes of digestion and nutrient absorption. Understanding these effects is crucial for developing effective dietary strategies to manage the condition and maintain overall health.The inflammatory process in ulcerative colitis can affect the lining of the intestines, impairing their ability to properly absorb essential vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients.
This can lead to deficiencies that require careful attention and management. The severity of these deficiencies can vary depending on the extent and duration of the disease.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Inflammation in the digestive tract can hinder the absorption of various nutrients. Malnutrition is a common concern for individuals with untreated ulcerative colitis. This can result in a wide range of deficiencies, affecting both the body’s ability to function properly and overall well-being.
- Iron Deficiency: Bleeding in the colon, a common symptom of ulcerative colitis, can lead to significant iron loss. This can cause anemia, characterized by fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. Iron is crucial for oxygen transport throughout the body.
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency: The intestines’ ability to absorb vitamin B12 can be impaired by inflammation. Vitamin B12 is essential for nerve function and red blood cell production. Symptoms of deficiency can include fatigue, neurological problems, and megaloblastic anemia.
- Calcium and Vitamin D Deficiency: Inflammation can interfere with the absorption of calcium and vitamin D, which are vital for bone health. This can increase the risk of osteoporosis and fractures, especially in the long term.
- Protein Deficiency: Inflammation and chronic diarrhea can lead to a decreased intake and absorption of protein. Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, and a deficiency can lead to muscle weakness, delayed wound healing, and impaired immune function.
- Other Deficiencies: Deficiencies in other vitamins and minerals, such as folate, zinc, and magnesium, are also possible due to impaired absorption and increased excretion. These deficiencies can affect various bodily functions and overall health.
Impact on Nutrient Absorption
The inflammatory process in the intestines can damage the intestinal villi, tiny finger-like projections that play a crucial role in nutrient absorption. Damage to these villi reduces the surface area available for absorption, impacting the body’s ability to efficiently extract essential nutrients.
Impact on Nutrient Metabolism
The disruption in nutrient absorption can further affect metabolism, the process by which the body converts food into energy. This can lead to various metabolic imbalances, further impacting health. For instance, impaired iron absorption can impact oxygen transport, while vitamin B12 deficiency can affect nerve function.
Comparison of Nutritional Requirements
| Nutrient | Individual without Ulcerative Colitis | Individual with Ulcerative Colitis |
|---|---|---|
| Iron | Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA): Varies based on age and sex | Potentially higher RDA, depending on bleeding |
| Vitamin B12 | RDA: Varies based on age and sex | Potentially higher RDA due to absorption issues |
| Calcium | RDA: Varies based on age and sex | Potentially higher RDA due to absorption issues |
| Protein | RDA: Varies based on age, sex, and activity level | Potentially higher RDA due to increased needs for tissue repair |
| Folate | RDA: Varies based on age and sex | Potentially higher RDA due to absorption issues |
Dietary Recommendations
A personalized dietary approach is essential to address the specific nutritional needs of individuals with ulcerative colitis. This includes dietary modifications to manage symptoms and prevent deficiencies.
- High-Fiber Diet: A high-fiber diet can help soothe the lining of the intestines and reduce inflammation. However, it’s important to introduce fiber gradually to avoid digestive discomfort.
- Nutrient-Rich Foods: Including nutrient-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, is crucial for replenishing essential nutrients.
- Supplements: In some cases, supplements may be necessary to address specific deficiencies. Consult a doctor or registered dietitian to determine if supplements are appropriate and to ensure they are taken correctly.
- Small, Frequent Meals: Eating smaller, more frequent meals can be helpful in managing digestive symptoms and reducing the impact on nutrient absorption.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is essential for overall health and can help manage diarrhea.
Psychological and Emotional Well-being
Living with ulcerative colitis can significantly impact an individual’s emotional and psychological well-being. The unpredictable nature of the disease, coupled with the physical discomfort and potential for debilitating symptoms, can lead to a range of emotional challenges. These challenges can manifest in various ways, impacting daily life, social interactions, and overall quality of life.The chronic nature of ulcerative colitis often results in significant stress and anxiety.
Individuals may experience fear of future flare-ups, worry about managing their condition effectively, and concerns about the potential long-term effects on their health and well-being. The unpredictable nature of symptoms can also lead to feelings of isolation and social withdrawal. Understanding these challenges and seeking appropriate support is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Emotional and Psychological Challenges
Untreated ulcerative colitis can significantly impact mental health. The constant physical discomfort, the fear of unpredictable flare-ups, and the need for frequent bathroom trips can cause significant distress. This can lead to feelings of anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem. Furthermore, social isolation can arise due to the need to limit social activities or the embarrassment associated with the condition.
These factors can significantly diminish an individual’s quality of life.
Impact on Daily Life
The physical symptoms of ulcerative colitis, such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and fatigue, can greatly impact daily life. These symptoms can disrupt work, school, social activities, and personal relationships. The unpredictable nature of the disease can also lead to missed appointments, reduced productivity, and feelings of helplessness. For example, a missed work day due to a flare-up can lead to financial stress and a loss of income.
Impact on Social Interactions
The unpredictable nature of ulcerative colitis can make social interactions challenging. Individuals may feel self-conscious about their condition, leading to avoidance of social gatherings or limitations in participation. The fear of embarrassing situations or the need for frequent bathroom breaks can also hinder social engagement. This can contribute to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
Importance of Mental Health Support
Recognizing the importance of mental health support for individuals with ulcerative colitis is paramount. Professional mental health services, such as therapy and counseling, can provide valuable tools and strategies for managing stress, anxiety, and other emotional challenges. Support groups can also offer a sense of community and understanding, fostering connections with others who share similar experiences.
Strategies for Managing Stress and Anxiety
Managing stress and anxiety related to ulcerative colitis requires a multifaceted approach. Stress-reducing techniques, such as mindfulness, yoga, and meditation, can help individuals cope with the emotional toll of the condition. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can also contribute to improved mental well-being. Open communication with healthcare providers and loved ones is essential for fostering a supportive environment.
Types of Psychological Support
| Type of Support | Description |
|---|---|
| Therapy (e.g., Cognitive Behavioral Therapy – CBT) | CBT helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors related to their condition. It equips them with coping mechanisms to manage stress and anxiety. |
| Counseling | Counseling provides a safe space for individuals to explore their emotions and concerns related to ulcerative colitis. It offers guidance on navigating the challenges of the condition and improving overall well-being. |
| Support Groups | Support groups provide a platform for individuals with ulcerative colitis to connect with others who share similar experiences. This shared understanding and support can significantly reduce feelings of isolation and provide a sense of community. |
| Mindfulness Practices | Mindfulness techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help individuals manage stress and anxiety by promoting present-moment awareness. This can help reduce the impact of physical symptoms on emotional well-being. |
Complications and Treatment Options
Untreated ulcerative colitis can lead to a range of serious complications, impacting overall health and well-being. Understanding these potential issues and the available treatment options is crucial for effective management of the condition. Early intervention and appropriate medical care are vital to prevent these complications and improve quality of life.Effective management of ulcerative colitis hinges on recognizing the complications that can arise and the range of treatments available.
Untreated ulcerative colitis can lead to some serious complications, including increased risk of colon cancer. It can also wreak havoc on your mental health, triggering anxiety and stress, which can in turn exacerbate symptoms like diarrhea. Understanding the connection between these factors is crucial; for instance, if you’re experiencing anxiety stress and diarrhea, it’s important to remember that these symptoms could be linked to ulcerative colitis.
The risks of untreated ulcerative colitis are multifaceted and significant, requiring proper medical attention. anxiety stress and diarrhea can be a symptom, but there are many others.
This section will delve into the potential complications and the various treatment approaches, including medications, surgical interventions, and lifestyle modifications. This information is designed to empower individuals with ulcerative colitis to make informed decisions about their care.
Potential Complications of Untreated Ulcerative Colitis
Untreated ulcerative colitis can lead to a cascade of complications, ranging from mild discomfort to severe, life-threatening conditions. These complications can affect various bodily systems and require immediate medical attention.The progression of untreated ulcerative colitis can lead to severe complications such as toxic megacolon, a life-threatening condition where the colon becomes dangerously dilated. This can result in significant abdominal pain, fever, and potentially, perforation of the colon.
Another significant complication is colorectal cancer, which is a substantial risk for individuals with long-standing and extensive ulcerative colitis.
Common Treatment Approaches for Ulcerative Colitis
Treatment for ulcerative colitis aims to reduce inflammation, control symptoms, and prevent complications. The most effective approach often involves a combination of strategies, tailoring treatment to individual needs and disease severity.A cornerstone of treatment is the use of medications. These can be broadly categorized into aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants. Aminosalicylates, such as mesalamine, work by reducing inflammation in the colon.
Corticosteroids, like prednisone, can be highly effective in reducing inflammation, but their long-term use is often limited due to potential side effects. Immunosuppressants, such as azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine, can be used to suppress the immune system’s response, thereby reducing inflammation.
Surgical Options for Ulcerative Colitis
Surgical interventions are sometimes necessary for severe cases of ulcerative colitis, particularly when medical management proves insufficient or complications arise.Proctocolectomy, the surgical removal of the colon and rectum, is a definitive treatment option for individuals with extensive ulcerative colitis. In some cases, a procedure known as ileal pouch-anal anastomosis (IPAA) may be performed to preserve bowel function after proctocolectomy.
Untreated ulcerative colitis can lead to serious complications, like increased risk of colon cancer. While focusing on managing such a condition, it’s also important to consider natural approaches for other health concerns. For example, exploring natural remedies for fungal nail infections, like those detailed in this helpful guide, natural remedies for fungal nail infections , can contribute to a holistic approach to health.
Ultimately, prioritizing proper medical care for ulcerative colitis remains crucial.
This creates a pouch from the small intestine and connects it to the anus.
Lifestyle Modifications in Ulcerative Colitis Management
Lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in managing ulcerative colitis symptoms and improving overall well-being. A balanced diet, stress management techniques, and regular exercise are crucial components of an effective treatment plan.Maintaining a balanced diet low in fiber and avoiding trigger foods can help manage symptoms. Dietary recommendations should be tailored to individual needs and discussed with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional.
Comparison of Treatment Options
| Treatment Option | Effectiveness | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Aminosalicylates | Generally effective in mild to moderate cases; may not be sufficient for severe disease | Mild gastrointestinal side effects, such as abdominal pain or diarrhea, are possible. |
| Corticosteroids | Highly effective in reducing inflammation but should be used cautiously due to potential side effects | Potential side effects include weight gain, mood changes, osteoporosis, and increased risk of infections. |
| Immunosuppressants | Often used for long-term management, effective in reducing inflammation and disease activity | Potential side effects include increased risk of infections, liver damage, and other serious side effects. |
| Surgery (Proctocolectomy with IPAA) | Definitive treatment for severe cases or those unresponsive to other therapies | Potential side effects include surgical complications, such as infection or bleeding, and long-term adjustments to bowel habits. |
Long-Term Management Strategies
Living with ulcerative colitis requires a proactive and comprehensive approach to long-term management. This involves not only understanding the condition but also actively participating in strategies to minimize future risks and maintain a good quality of life. The key is to develop a personalized plan with your healthcare team, tailored to your specific needs and circumstances.
Strategies for Minimizing Future Risks
Effective long-term management involves a multifaceted approach, encompassing lifestyle modifications, medication adherence, and regular monitoring. These strategies are crucial in preventing disease flares and complications. Early intervention and consistent adherence to the plan are essential for long-term well-being.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Exacerbations
A significant aspect of long-term management is implementing preventive measures to avoid exacerbations. These measures are crucial in minimizing the frequency and severity of flare-ups, which can significantly impact quality of life. Identifying triggers and adjusting lifestyle accordingly is vital.
- Dietary Modifications: A well-balanced diet can play a critical role in preventing flares. This includes avoiding foods that are known to trigger symptoms in individual patients, such as high-fiber foods, spicy foods, or processed foods. Working with a registered dietitian can be beneficial in creating a personalized dietary plan.
- Stress Management Techniques: Chronic stress can exacerbate ulcerative colitis symptoms. Incorporating stress-reducing techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature, can help manage stress levels and potentially reduce the risk of flare-ups.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can have a positive impact on both physical and mental well-being. Engaging in regular exercise, while being mindful of not overexerting, can be beneficial in managing symptoms and potentially reducing the frequency of exacerbations. However, it’s important to discuss exercise routines with your doctor, especially during flare-ups.
Importance of Regular Medical Checkups and Monitoring
Regular checkups and monitoring are essential for long-term management of ulcerative colitis. These visits allow for early detection of potential complications and adjustments to treatment plans. Proactive communication with your doctor about any changes in symptoms is critical.
- Regular Blood Tests: These tests help monitor overall health, including inflammation markers and nutrient levels. They can indicate potential complications or provide valuable information about the effectiveness of current treatment.
- Colonoscopies: Colonoscopies play a vital role in detecting any signs of disease progression or the development of complications, such as colorectal cancer. The frequency of these procedures is determined by individual risk factors and disease severity.
- Follow-up appointments: Regular follow-up appointments with your gastroenterologist are crucial to monitor the disease’s progression and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Role of Patient Education and Self-Management
Patient education and self-management are crucial components of long-term management. Understanding the disease, its triggers, and potential complications empowers patients to actively participate in their care. This empowers them to make informed decisions and better manage their condition.
- Recognizing Symptoms: Recognizing early symptoms of a flare-up is essential for prompt intervention. Knowing what to expect and how to respond can minimize the severity and duration of the flare-up.
- Medication Adherence: Adhering to prescribed medications is vital for disease control and minimizing the risk of complications. Patients should understand the importance of medication schedules and possible side effects.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Adjusting lifestyle factors such as diet, stress management, and exercise can significantly impact the long-term health outcomes for individuals with ulcerative colitis. Understanding these factors can lead to more effective management.
Preventive Measures and Follow-up Care
This table summarizes key preventive measures and recommended follow-up care for individuals with ulcerative colitis.
| Preventive Measure | Description | Follow-up Care |
|---|---|---|
| Dietary Modifications | Avoid trigger foods, maintain a balanced diet, and consult a registered dietitian. | Regular dietary assessment with healthcare provider. |
| Stress Management | Practice stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature. | Monitor stress levels and discuss coping strategies with a therapist or counselor. |
| Regular Exercise | Engage in moderate physical activity, while avoiding overexertion. | Consult with a physician about exercise routines, especially during flare-ups. |
| Regular Checkups | Attend scheduled appointments for blood tests, colonoscopies, and follow-up visits. | Report any changes in symptoms to healthcare provider. |
| Medication Adherence | Take medications as prescribed and understand potential side effects. | Report any medication side effects to healthcare provider. |
Epilogue
In conclusion, untreated ulcerative colitis presents a complex web of risks that demand immediate attention and proactive management. Understanding the multifaceted nature of these risks, from digestive complications to psychological well-being, is essential for those affected. Early intervention and a collaborative approach between patients and healthcare professionals are key to mitigating these risks and ensuring a better quality of life.




