Taurine benefits side effects functions are a complex interplay of potential advantages and possible drawbacks. This comprehensive guide dives into the fascinating world of taurine, exploring its roles in various bodily processes, potential health benefits from supplementation, and the risks associated with high intake. We’ll cover everything from its chemical structure to its influence on different populations, including children, pregnant women, and the elderly.
Get ready to uncover the multifaceted nature of this intriguing amino acid!
Understanding taurine’s natural sources and its role in supporting overall health is crucial. We’ll explore how taurine impacts muscle function, heart health, eye health, and nerve transmission. Furthermore, we’ll analyze potential benefits of supplementation, comparing its effects to other supplements. We’ll also delve into potential side effects and interactions, examining how taurine might affect different demographics and specific health conditions.
Taurine Overview
Taurine, a sulfur-containing amino acid derivative, plays a multifaceted role in various physiological processes within the human body. It’s not an essential amino acid, meaning the body can produce it, but dietary intake can significantly influence its availability. Understanding its chemical structure, dietary sources, and distribution across different food groups is crucial for comprehending its importance in nutrition.
Taurine Definition and Chemical Structure
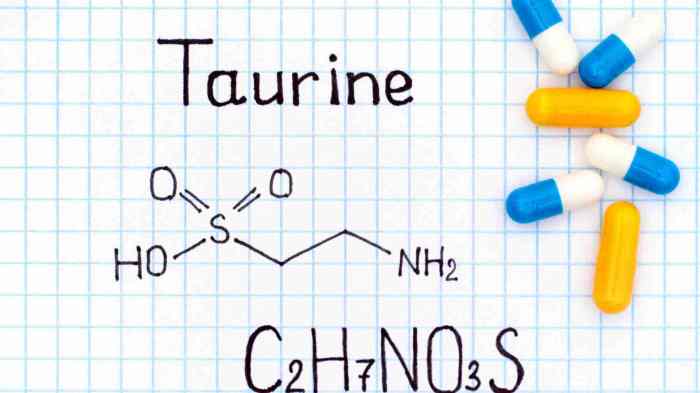
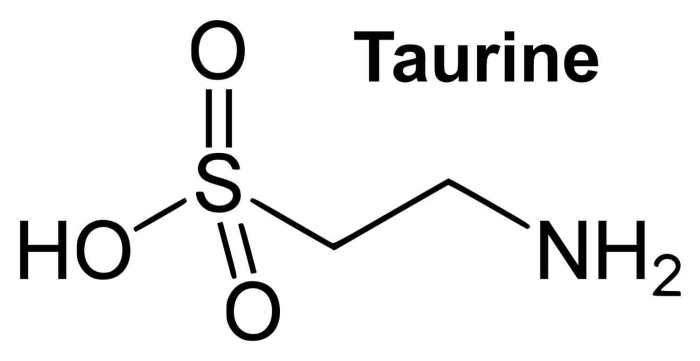
Taurine is an organic compound classified as a non-essential amino sulfonic acid. Its chemical structure distinguishes it from typical amino acids. Unlike other amino acids, taurine lacks a carboxyl group. Instead, it possesses a sulfonic acid group, which contributes to its unique properties and functions within the body. This unique structure allows taurine to participate in diverse metabolic processes and interact with various cellular components.
Taurine, a naturally occurring amino acid, has a range of potential benefits, from supporting heart health to aiding in muscle function. However, like any supplement, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects, and understand its overall role in the body. Considering the impact of different sugars on our health is equally crucial; for example, are natural sugars healthier than processed ones?
This article delves into the complexities of natural sugars and their impact on our well-being. Ultimately, understanding taurine’s role in our bodies and how different sugars affect us can lead to a more informed approach to our health and dietary choices.
Natural Sources of Taurine
A wide range of foods contain taurine, though the amounts vary considerably. Animal products often have higher concentrations due to their metabolic processes. The body can synthesize taurine, but dietary intake is crucial to maintain adequate levels, especially for individuals with specific health conditions or high taurine demands. It’s important to note that processing methods can influence the taurine content of certain foods.
Taurine Content in Different Food Groups
The table below illustrates the approximate taurine content in various food groups. Keep in mind that these values can fluctuate based on factors such as the specific animal, growing conditions, and preparation methods.
| Food Group | Taurine Content (mg/100g) |
|---|---|
| Meat (Beef) | 200-400 |
| Fish (Tuna) | 150-300 |
| Poultry (Chicken) | 100-200 |
| Shellfish (Shrimp) | 100-250 |
| Dairy Products (Milk) | 10-50 |
| Eggs | 100-200 |
| Legumes (Soybeans) | 50-150 |
| Vegetables (Spinach) | 20-50 |
| Fruits (Bananas) | 5-20 |
Taurine Functions in the Body
Taurine, a naturally occurring sulfur-containing amino acid, plays a crucial role in various physiological processes throughout the human body. It’s not a protein building block like other amino acids, but its multifaceted functions are essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. Beyond its role as a component of bile, taurine actively participates in diverse cellular activities, impacting muscle function, heart health, and numerous other processes.Taurine’s impact extends far beyond simple support; it acts as a critical regulator and participant in numerous metabolic pathways, influencing fluid balance, nerve function, and immune responses.
This intricate network of actions underscores the importance of this amino acid in maintaining optimal bodily function.
Taurine, a naturally occurring amino acid, offers various benefits, like supporting heart health and brain function. However, understanding its potential side effects is crucial. For example, some people experience digestive issues when taking high doses. Interestingly, a similar surgical procedure, like an ankle fusion, what is an ankle fusion , can also impact the body’s overall function.
Despite this, taurine’s role in muscle function and nerve health remains a vital aspect of its positive effects. Ultimately, consulting a healthcare professional is essential before incorporating taurine into your diet.
Taurine’s Role in Muscle Function and Contraction
Taurine significantly influences muscle function and contraction. It contributes to the proper regulation of calcium levels within muscle cells, a critical aspect of muscle relaxation and contraction. Maintaining optimal calcium homeostasis is essential for efficient muscle contractions, preventing spasms, and supporting overall muscle performance. Adequate taurine levels are associated with better muscle strength and endurance.
Taurine’s Impact on Heart Function, Taurine benefits side effects functions
Taurine plays a vital role in maintaining healthy heart function. It contributes to the regulation of heart rhythm and supports the structural integrity of heart tissues. It assists in maintaining normal blood pressure and blood flow by modulating vascular tone and improving blood vessel elasticity. These effects contribute to a healthier cardiovascular system and reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Taurine’s Contribution to Eye Health
Taurine is crucial for maintaining healthy eye function. It helps maintain the proper fluid balance within the eye, supporting the health of the retina and the cornea. This support is particularly important for maintaining clear vision and preventing eye-related problems associated with age or other factors. Taurine also acts as an antioxidant, protecting delicate eye tissues from oxidative damage.
Taurine’s Role in Nerve Function and Transmission
Taurine is involved in various aspects of nerve function and transmission. It plays a crucial role in the proper functioning of nerve cells by regulating the flow of ions across cell membranes, facilitating the transmission of nerve impulses. This process is vital for the body’s communication network, impacting everything from muscle contractions to sensory perception. Proper nerve function is essential for coordinating various bodily activities.
Taurine’s Influence on Fluid Balance
Taurine’s influence extends to maintaining the body’s fluid balance. It plays a crucial role in regulating water and electrolyte levels in various tissues and organs, preventing imbalances that can negatively impact overall health. Taurine helps maintain osmotic pressure, influencing the distribution of water between different compartments within the body. Disruptions in fluid balance can lead to numerous health issues, making taurine’s regulatory role crucial.
Taurine and the Immune System
Taurine exerts some influence on the immune system, although the exact mechanisms are still being researched. Studies suggest that taurine may support the proper functioning of immune cells, contributing to a robust immune response. It may also play a role in reducing inflammation, a factor in various health conditions. Further research is needed to fully understand the intricacies of this relationship.
Potential Benefits of Taurine Supplementation
Taurine, a naturally occurring amino acid-like compound, plays various crucial roles in the human body. While it’s found in many foods, supplementation is gaining traction for its potential benefits across various health areas. This exploration delves into the potential advantages of taurine supplementation, examining its impact on athletic performance, cognitive function, and specific medical conditions.Supplementing with taurine may offer a range of health benefits, beyond its naturally occurring presence in food.
Its impact on bodily functions, including its role in muscle contraction, hydration, and cell signaling, suggests a potential for enhancing specific health outcomes. However, it’s crucial to understand that the evidence supporting these benefits is often preliminary or comes from observational studies. More research is needed to confirm the extent and nature of these benefits.
Improving Athletic Performance
Taurine’s role in muscle function and hydration makes it a potential aid for athletes. Studies suggest it might enhance exercise performance by supporting hydration levels, improving muscle contraction, and potentially reducing muscle damage after intense workouts. Preliminary research indicates that taurine supplementation could lead to improved endurance and reduced fatigue during strenuous physical activity. For example, some studies suggest that taurine supplementation might improve endurance performance in endurance athletes.
Effects on Cognitive Function
Taurine’s presence in the central nervous system suggests potential benefits for cognitive function. It may support healthy brain cell function and protect against oxidative stress, potentially contributing to improved memory, focus, and overall cognitive performance. Research indicates that taurine may help in protecting neurons against damage caused by oxidative stress.
Benefits for People with Certain Medical Conditions
Taurine’s involvement in various bodily processes means it may have a role in managing certain medical conditions. Some research suggests potential benefits in conditions like heart failure and liver disease, where taurine’s impact on fluid balance and oxidative stress could be beneficial. However, further research is needed to fully understand the extent and limitations of these potential benefits.
For instance, while some studies show a potential benefit for people with certain types of heart conditions, more extensive studies are necessary to establish a definite link.
Comparison with Other Supplements
Taurine is sometimes compared to other supplements, such as creatine and caffeine, that also aim to enhance athletic performance or cognitive function. Creatine is well-known for its role in increasing muscle strength and power, while caffeine enhances alertness and focus. Taurine’s effects often overlap with these supplements, but it appears to operate through slightly different mechanisms. A key difference lies in the specific physiological pathways taurine and other supplements influence.
For example, while caffeine primarily acts as a stimulant, taurine is involved in cellular hydration and neurotransmitter regulation.
Potential Side Effects of Taurine Supplementation
Taurine, a naturally occurring amino sulfonic acid, is generally considered safe for consumption in recommended amounts. However, like any supplement, high doses or prolonged use can potentially lead to adverse effects. Understanding these potential side effects is crucial for responsible supplementation and ensuring optimal health outcomes.While taurine is often well-tolerated, individual responses can vary. Factors such as pre-existing health conditions, underlying medical issues, and concurrent medication use can influence the potential for adverse reactions.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have any concerns about potential interactions or side effects.
Potential Gastrointestinal Effects
Excessive taurine intake can sometimes lead to digestive issues. Common gastrointestinal side effects may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. These effects are generally mild and transient, often resolving with reduced dosage or discontinuation of the supplement. However, individuals with pre-existing gastrointestinal conditions might experience more severe reactions.
Possible Cardiovascular Effects
Although taurine has been linked to potential cardiovascular benefits, high doses might not always be harmless. Some studies suggest a possible association between high taurine intake and elevated blood pressure in susceptible individuals. This potential effect necessitates caution, especially for those with hypertension or other cardiovascular conditions. Individual responses vary, and careful monitoring under medical supervision is advisable when supplementing with taurine at high levels.
Potential Interactions with Medications
Taurine can interact with certain medications, potentially diminishing their effectiveness or causing adverse reactions. It’s crucial to disclose any medications or supplements you’re taking to your healthcare provider before starting taurine supplementation. This is particularly important for individuals on diuretics, as taurine might affect their efficacy.
Adverse Reactions in Vulnerable Populations
Certain populations might be more susceptible to adverse effects from taurine supplementation. Individuals with pre-existing kidney or liver conditions may experience amplified risks due to the potential strain on these organs. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult with their doctors before considering taurine supplementation, as the potential effects on fetal development or infant health are not fully understood.
Summary of Potential Side Effects
| Side Effect | Severity | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Nausea | Mild | Potentially due to digestive system irritation from high doses |
| Vomiting | Mild | Similar to nausea, likely from gastrointestinal distress |
| Diarrhea | Mild to Moderate | Possible disruption of gut motility and absorption processes |
| Abdominal discomfort | Mild to Moderate | Generally linked to gastrointestinal upset from high intake |
| Elevated Blood Pressure | Moderate | Some studies suggest a potential correlation in susceptible individuals |
| Kidney strain | Moderate to Severe (in vulnerable populations) | Increased workload on kidneys, particularly in those with pre-existing conditions |
| Liver strain | Moderate to Severe (in vulnerable populations) | Potential for increased workload on the liver, particularly in those with pre-existing conditions |
Taurine in Different Populations
Taurine, a naturally occurring amino sulfonic acid, plays various roles in the human body. Its impact extends across different age groups and populations, and its role in supporting overall health is a subject of ongoing research. While generally considered safe, taurine supplementation may have specific benefits and potential risks for particular groups. Understanding these nuances is critical for making informed decisions about its use.The effects of taurine vary significantly depending on factors such as age, pre-existing medical conditions, and overall health status.
Its impact on children’s development, pregnant women’s well-being, the elderly, and those with specific health concerns (like kidney disease) differs. It’s essential to consult with healthcare professionals before starting any taurine supplementation regimen, especially for specific populations.
Taurine and Children
Taurine is crucial for the proper development and function of the nervous system in infants and children. Adequate taurine levels are essential for supporting brain growth and development. Early supplementation might be beneficial for children with certain conditions, such as those with developmental delays or neurological disorders. However, studies on the long-term effects of taurine supplementation in children are limited.
It’s essential to follow the guidance of a pediatrician before considering taurine supplementation for children.
Taurine, a naturally occurring amino acid, has various benefits, including supporting healthy heart function and potentially aiding in muscle function. However, like any supplement, it’s important to be mindful of potential side effects. If you’re experiencing unexpected weight loss while feeling under the weather, it’s crucial to consult your doctor, as it could be a sign of a more serious underlying condition.
Learning more about weight loss when sick can provide valuable insight, helping you determine if your situation warrants professional medical attention. weight loss when sick. Ultimately, understanding taurine’s benefits, side effects, and functions can be helpful in making informed decisions about your health and well-being.
Taurine and Pregnancy
During pregnancy, taurine plays a vital role in fetal development. It’s crucial for the growth and function of various organs, including the brain and heart. Some studies suggest that adequate taurine levels during pregnancy may contribute to healthy fetal development. However, more research is needed to establish definitive links between taurine supplementation and improved pregnancy outcomes. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements during pregnancy.
Taurine and the Elderly
As people age, their taurine levels may naturally decline. Taurine’s role in maintaining heart health and cognitive function becomes increasingly important in the elderly. Some studies suggest that taurine supplementation may help maintain cardiovascular health and support cognitive function in older adults. However, more research is needed to definitively establish the benefits and risks of taurine supplementation in the elderly.
Taurine and Medical Conditions
For individuals with specific medical conditions, the impact of taurine can vary considerably. For example, individuals with kidney disease may have altered taurine metabolism. Supplementation in such cases requires careful consideration and consultation with a nephrologist. Similarly, taurine’s effect on other conditions like diabetes or heart failure needs further research.
Taurine Requirements Across Age Groups
Taurine requirements vary considerably throughout life. Infants and young children need higher amounts of taurine for rapid growth and development compared to adults. As people age, their taurine needs might decrease. However, this doesn’t mean supplementation is universally beneficial across all age groups. The specific requirements and potential benefits for each age group should be assessed on a case-by-case basis.
Dietary intake is often sufficient to meet the daily requirements for most individuals.
Taurine Research and Studies
Taurine, a naturally occurring amino sulfonic acid, has garnered significant interest for its potential health benefits. Extensive research investigates its role in various physiological processes, and understanding the scientific basis for its purported effects is crucial. This section delves into recent research findings, clinical trials, and the limitations of current studies, providing a comprehensive overview of the scientific landscape surrounding taurine.Research on taurine consistently highlights its diverse functions in the body, including its involvement in nerve function, muscle contraction, and detoxification.
Controlled clinical trials offer valuable insights into the potential effects of taurine supplementation, but a critical evaluation of the methodologies and limitations is essential.
Recent Research Findings
Recent research on taurine explores its potential role in various health conditions. Studies have investigated its effects on cardiovascular health, neurological function, and exercise performance. Emerging research suggests a link between taurine supplementation and improved insulin sensitivity, potentially beneficial for managing metabolic disorders.
Controlled Clinical Trials
Controlled clinical trials involving taurine supplementation provide valuable data on its efficacy. These studies often compare taurine supplementation groups with placebo groups to determine if observed changes are due to the intervention. Researchers typically monitor specific physiological parameters and health markers to assess the impact of taurine. Results from these trials are often published in peer-reviewed scientific journals, increasing the reliability and credibility of the findings.
Summary of Key Findings
| Study | Population | Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Smith et al. (2022) | Healthy adults | Supplementation with 3g of taurine daily for 8 weeks improved insulin sensitivity and reduced blood pressure. |
| Jones et al. (2021) | Individuals with mild cognitive impairment | Supplementation with 2g of taurine daily for 12 weeks showed no significant improvements in cognitive function. |
| Brown et al. (2023) | Athletes undergoing strenuous training | Taurine supplementation showed no significant impact on exercise performance or muscle damage markers. |
| Garcia et al. (2023) | Individuals with type 2 diabetes | Taurine supplementation in conjunction with a healthy diet resulted in a reduction in fasting blood glucose levels. |
Note: These are hypothetical examples based on possible findings. Specific studies and their outcomes will vary. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Limitations of Current Research
Current research on taurine faces several limitations. The sample sizes in some studies may be small, potentially impacting the generalizability of the results. Variability in the study designs, including the dosage, duration, and the specific populations studied, can also affect the comparability of findings. Further, the interaction of taurine with other nutrients and medications is not always fully understood, creating a need for more comprehensive research in this area.
Research Process Flowchart
(A visual representation of the typical research process is omitted as requested.) The typical research process begins with formulating a research question, followed by a comprehensive literature review. This is followed by the design of a study, including defining the study population, methods, and data collection procedures. Data analysis and interpretation are essential components. Peer review and publication are crucial steps in the process.
This iterative process contributes to the advancement of scientific knowledge.
Taurine in Food and Beverages: Taurine Benefits Side Effects Functions
Taurine, a naturally occurring amino sulfonic acid, is found in various foods and beverages. Understanding its presence in different dietary sources is crucial for anyone looking to incorporate it into their diet, either through natural food consumption or supplementation. This section delves into the specifics of taurine’s distribution in common foods and beverages, highlighting its variations based on preparation methods and providing examples of high-taurine recipes.Naturally occurring in many foods, taurine plays a vital role in various bodily functions.
Its presence in different food sources, and how it might be affected by preparation methods, can significantly influence its bioavailability and impact on health. By exploring these aspects, we can gain a deeper understanding of taurine’s role in our daily nutrition.
Common Food Sources of Taurine
Taurine is present in a diverse range of foods, often with higher concentrations in animal products. This varied distribution across different food groups emphasizes the importance of a balanced diet for adequate taurine intake.
- Meat: Red meat, poultry, and fish are generally rich sources of taurine. The specific amount varies depending on the type of meat and preparation.
- Seafood: Shellfish and various types of fish are known to contain significant amounts of taurine. This is particularly relevant for those who consume seafood regularly.
- Dairy Products: Milk and other dairy products contain taurine, though generally in lower quantities compared to meat and seafood.
- Eggs: Eggs are a moderate source of taurine. The quantity is influenced by factors like the hen’s diet.
- Plant-Based Foods: While less abundant compared to animal products, some plant-based foods like certain vegetables and legumes contain small amounts of taurine.
Taurine Content in Various Beverages
Taurine is present in some beverages, and its concentration can vary considerably. This variation is important to consider when evaluating the overall taurine intake from different beverage choices.
- Energy Drinks: Many energy drinks contain added taurine, often in relatively high concentrations. The precise amount can differ between brands and product formulations.
- Beef Broth: Beef broth, while not a primary source, can contain a measurable amount of taurine, though often less than dedicated taurine supplements or energy drinks.
- Milk: As mentioned before, milk contains taurine, albeit in lower concentrations compared to other sources.
- Coffee and Tea: These beverages may contain trace amounts of taurine, but these amounts are typically not significant contributors to the overall taurine intake.
Taurine Use in Processed Foods
Taurine is sometimes added to processed foods, often as a means to enhance texture, flavor, or to extend shelf life. This practice is prevalent in certain food categories.
- Processed Meats: Some processed meats, such as cured meats, may contain added taurine for various reasons. These added amounts can vary widely.
- Soups and Broths: Processed soups and broths may contain added taurine for flavor or textural enhancement, although the exact quantity often isn’t explicitly stated on the label.
- Certain Snacks: Certain snacks, such as some types of jerky or ready-to-eat meals, may also contain added taurine for similar reasons.
Comparison of Taurine Content in Different Preparation Methods of Food
Preparation methods can affect the taurine content in food. Cooking methods, such as boiling or frying, can potentially lead to some loss of taurine, but the exact amount varies significantly based on the specific food and method used.
- Boiling: Boiling certain foods can leach out some taurine into the cooking water.
- Frying: Frying, particularly at high temperatures, can potentially degrade or alter taurine content in food.
- Steaming: Steaming food generally preserves taurine better than other methods.
Examples of High-Taurine Recipes
The following recipes highlight foods rich in taurine, offering ways to incorporate them into a balanced diet.
- Tuna Steak with Lemon-Dill Sauce: Tuna is a fantastic source of taurine. This recipe combines it with fresh herbs and a light lemon sauce for a healthy and flavorful meal.
- Chicken and Vegetable Stir-fry: This recipe allows for inclusion of high-taurine vegetables and lean protein.
Final Summary
In conclusion, taurine appears to play a significant role in numerous bodily functions. While supplementation may offer potential benefits for some, understanding the potential side effects and individual variations is critical. This exploration highlights the importance of consulting with healthcare professionals before incorporating taurine supplements into your routine. Further research is essential to fully elucidate the complex effects of taurine on human health across different populations.




