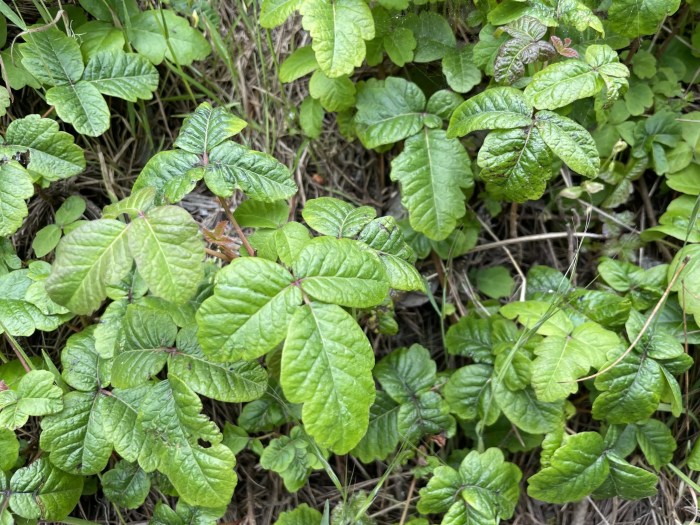
Plants that cause rashes are a common problem, affecting people worldwide. From the itchy welts of poison ivy to the stinging sensation of nettles, understanding these plants is crucial for preventing skin reactions. This guide delves into the various types of plants that trigger rashes, detailing their characteristics, geographic distribution, and how to prevent and treat the resulting skin irritations.
We’ll also explore the symptoms, severity, and necessary precautions to take.
This comprehensive guide explores the different types of rashes caused by plants, their causes, and treatments. It provides a list of the top 10 plants globally known to cause skin reactions, along with details on the specific parts of these plants that trigger allergic reactions. We will explore common names and scientific names, and compare the symptoms of reactions caused by different plants in a detailed table.
The guide also covers prevention and treatment strategies, including home remedies and when professional medical attention is needed. Learn how to identify plants that can cause rashes in your region and how to safely handle them.
Identifying Plants Causing Rashes
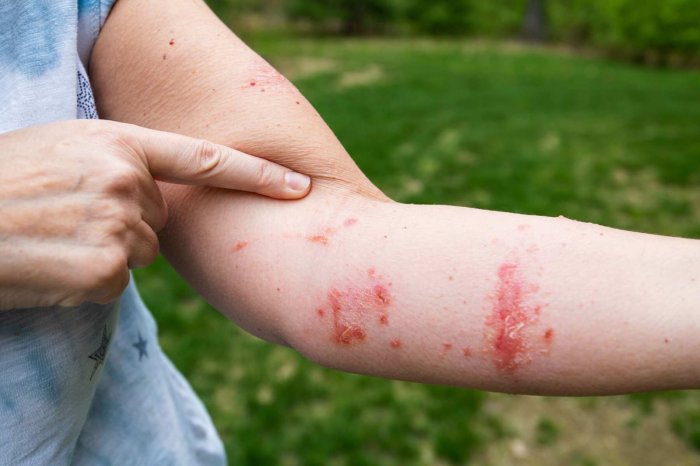
Knowing which plants can trigger skin reactions is crucial for avoiding unpleasant and sometimes painful experiences. Many plants, from the familiar to the exotic, possess compounds that can cause allergic contact dermatitis, leading to itching, redness, and blisters. This knowledge empowers you to appreciate the natural world while protecting yourself from potential harm.
Top 10 Plants Known to Cause Skin Reactions
Understanding the potential dangers of certain plants allows for better precautions and informed choices when interacting with the natural world. The following plants are globally recognized for their ability to induce skin reactions.
- Poison Ivy (Toxicodendron radicans): This vine is notorious for its urushiol oil, a potent allergen. Contact with even a small amount can lead to a severe rash. The entire plant, including stems, leaves, and roots, contains this oil.
- Poison Oak (Toxicodendron diversilobum): Similar to poison ivy, poison oak also produces urushiol. The appearance of poison oak varies depending on the location, but it generally features three-lobed leaves. The oil in the leaves, stems, and roots is the culprit.
- Poison Sumac (Toxicodendron vernix): This shrub or small tree is characterized by its clusters of smooth, greenish-white berries and often, its reddish stems. Urushiol is also present in this plant, primarily in the stems, leaves, and berries.
- Giant Hogweed (Heracleum mantegazzianum): This invasive plant is particularly dangerous due to its potent phototoxic sap. Contact with the sap followed by exposure to sunlight can cause severe blistering and scarring. The sap is found throughout the plant, including the stems and leaves.
- Oleander (Nerium oleander): All parts of the oleander plant contain cardiac glycosides, which can be toxic if ingested. However, contact with the plant’s sap or leaves can also cause skin irritation, redness, and blistering. All parts of the plant should be handled with caution.
- Prickly Ash (Xanthoceras sorbifolia): The sap and thorns of this plant can cause skin irritation, leading to allergic reactions. The plant’s sap is highly allergenic, and contact can lead to an itchy rash.
- Stinging Nettle (Urtica dioica): The stinging nettle is well-known for its tiny hairs that inject a histamine-containing irritant into the skin upon contact. This leads to intense itching, burning, and redness. The hairs are distributed across the plant’s stems and leaves.
- Giant Knotweed (Fallopia japonica): This invasive plant contains compounds that can cause skin irritation upon contact. The plant’s sap, stems, and leaves are all potential sources of irritation.
- Bamboo (Bambusoideae): Certain species of bamboo contain irritant substances that can cause contact dermatitis. Contact with the sap or stems of some bamboo varieties may lead to itching, redness, and skin inflammation.
- Lantana (Lantana camara): The sap from some lantana species is known to cause skin irritation and allergic reactions. Contact with the leaves, stems, or flowers can trigger a rash in sensitive individuals.
Comparing Symptoms of Plant-Induced Rashes
A table showcasing the varied symptoms of skin reactions caused by different plants provides a valuable reference for identifying potential triggers.
| Plant Name | Symptoms | Affected Areas | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Poison Ivy | Itching, redness, blisters, swelling | Anywhere contacted; often linear | Moderate to severe |
| Poison Oak | Itching, redness, blisters, swelling | Anywhere contacted; often in patches | Moderate to severe |
| Poison Sumac | Severe itching, blisters, swelling | Anywhere contacted; often in clusters | Severe |
| Giant Hogweed | Severe blistering, burning, scarring, swelling | Anywhere contacted; often worsened by sunlight | Severe |
| Oleander | Skin irritation, redness, blistering | Anywhere contacted | Moderate to severe |
| Prickly Ash | Itching, redness, swelling | Areas contacted; often localized | Moderate |
| Stinging Nettle | Itching, burning, redness | Areas contacted; often localized | Moderate |
| Giant Knotweed | Skin irritation, redness, swelling | Areas contacted; often localized | Moderate |
| Bamboo | Skin irritation, redness, swelling | Areas contacted; often localized | Moderate |
| Lantana | Skin irritation, redness, swelling | Areas contacted; often localized | Moderate |
Types of Rashes and Reactions
Plant-induced skin reactions can manifest in various ways, ranging from mild irritation to severe allergic responses. Understanding the different types of rashes and their symptoms is crucial for prompt identification and appropriate treatment. Early recognition can prevent complications and ensure effective management.Identifying the specific type of rash helps in determining the appropriate course of action, whether it’s home remedies or professional medical attention.
Knowing the potential triggers allows for better prevention strategies in the future.
Common Types of Plant Rashes
Plant contact can lead to a spectrum of skin reactions. These reactions can vary in their appearance and severity, depending on the plant’s toxin and the individual’s sensitivity.
- Contact Dermatitis: This is a common type of skin rash characterized by redness, itching, and sometimes blistering. It occurs when the skin comes into direct contact with an irritant, such as plant oils. Examples include poison ivy, oak, and sumac. The reaction typically appears within hours to a few days after contact.
- Allergic Contact Dermatitis: A more severe reaction than simple contact dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis is an immune response to a specific plant allergen. The rash may be more intense and persistent, often with significant swelling and blistering. It is triggered by an allergic reaction to plant compounds. Similar to poison ivy, oak, and sumac, this type of reaction can occur from touching certain plants.
- Phytophotodermatitis: This reaction is caused by a combination of plant chemicals and sunlight exposure. The plant’s sap interacts with UV radiation, causing a skin inflammation. The rash typically appears in areas exposed to the sun and may be accompanied by pain or burning sensations. Examples include certain citrus fruits and some weeds.
- Urticaria (Hives): These are characterized by raised, itchy welts on the skin. While not always plant-related, they can sometimes be triggered by plant contact. The welts can vary in size and shape and often appear and disappear over time. Plant-related urticaria may be a result of allergic reaction to plant extracts.
Symptoms of Plant-Induced Rashes
Recognizing the symptoms of a plant-induced rash is essential for timely treatment. The severity of symptoms can vary greatly.
- Redness and Swelling: The affected area becomes red and inflamed, often accompanied by swelling.
- Itching and Burning: A persistent itching or burning sensation is a common symptom, varying in intensity.
- Blisters and Oozing: In more severe cases, blisters filled with fluid may develop, potentially oozing or weeping.
- Pain: The affected area might experience pain, especially with blisters or intense inflammation.
- Skin Peeling: After the rash subsides, some skin areas may peel or flake off.
Summary Table of Common Plant-Induced Rashes
This table summarizes the common types of plant-induced rashes, their causes, symptoms, and potential treatments.
| Rash Type | Cause | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contact Dermatitis | Direct contact with plant irritant (e.g., sap) | Redness, itching, mild swelling | Cool compresses, topical hydrocortisone, antihistamines |
| Allergic Contact Dermatitis | Immune response to plant allergen (e.g., certain oils) | Intense itching, blisters, swelling | Corticosteroids, antihistamines, oral steroids (in severe cases) |
| Phytophotodermatitis | Plant chemicals + sunlight exposure | Redness, blisters, burning sensation in sun-exposed areas | Cool compresses, topical corticosteroids, pain relievers |
| Urticaria | Allergic reaction to plant extracts or oils | Raised itchy welts, varying in size and shape | Antihistamines, cool compresses, avoidance of triggers |
Geographic Distribution of Problem Plants: Plants That Cause Rashes
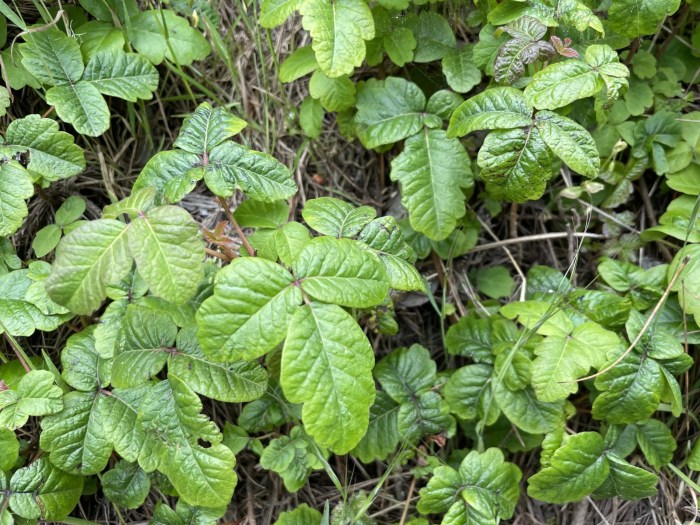

Plants causing skin irritation aren’t evenly distributed across the globe. Their prevalence is heavily influenced by climate, soil type, and human activity. Understanding these patterns helps in developing preventative measures and identifying areas where awareness campaigns might be most effective. This knowledge is critical for individuals traveling to new regions and for local communities needing to recognize and avoid these problematic plants.The geographic distribution of plants causing skin irritation is complex, influenced by a variety of factors including climate, soil conditions, and human activities.
Understanding this distribution is crucial for preventing and managing skin reactions, particularly in regions where these plants are prevalent. It allows for targeted educational efforts and development of preventative measures specific to the local flora.
Global Distribution of Irritant Plants
The global distribution of plants causing skin irritation is not uniformly spread. Some regions, characterized by specific climates and ecological conditions, harbor a higher concentration of these plants. Factors such as rainfall, temperature, and soil composition significantly impact plant growth and distribution. This in turn influences the presence and abundance of species that cause skin reactions.
Regional Variations in Problem Plants
| Region | Common Plants | Reaction Types |
|---|---|---|
| Southeast Asia | Toxicodendron species (poison ivy, poison oak, poison sumac), certain species of Dendrocnide (tree nettles) | Contact dermatitis, allergic reactions |
| North America | Toxicodendron species (poison ivy, poison oak, poison sumac), Primula (some varieties), Plantago (some species) | Contact dermatitis, allergic reactions |
| Australia | Dendrocnide species (tree nettles), certain species of Urtica (nettles), Acacia species (some varieties) | Contact dermatitis, skin blistering, and severe reactions |
| Mediterranean Region | Certain species of Euphorbia (spurges), Oleander | Contact dermatitis, skin irritation, potential ingestion issues |
| South America | Various species of Urtica (nettles), Acalypha species (some varieties), certain species of Euphorbia (spurges) | Contact dermatitis, skin inflammation, itching |
This table highlights some of the commonly encountered plants in different regions that can cause skin irritation. Note that this is not an exhaustive list and many other species contribute to these reactions. The specific plant species and reaction severity can vary significantly based on local conditions.
Problematic Plants in Specific Regions
In Southeast Asia, the Toxicodendron species and Dendrocnide are particularly problematic, with documented cases of severe contact dermatitis. In Australia, Dendrocnide species are notorious for causing intense skin reactions. Certain Acacia species, while not always causing skin reactions, have been implicated in localized dermatitis in some areas. In the Mediterranean region, Euphorbia and Oleander pose risks due to their irritant saps.
Prevalence of Rash-Causing Plants
The prevalence of skin irritation caused by various plants differs considerably between regions. In North America, Toxicodendron species are widely distributed and responsible for a substantial number of skin reactions. Similar patterns are observed in other regions, with the severity and frequency of reactions linked to plant abundance and local environmental conditions. For example, increased rainfall and humidity can increase the likelihood of skin contact and resultant reactions.
Prevention and Treatment Strategies
Plant-induced rashes, while often irritating and uncomfortable, can be effectively managed with appropriate prevention and treatment strategies. Understanding the triggers and knowing how to respond promptly can significantly reduce the severity and duration of the reaction. This section will detail various methods to prevent contact and effective approaches to treating the rashes, including the use of home remedies and when professional medical attention is crucial.
Preventing Plant-Induced Rashes
Preventing contact with problematic plants is the most effective way to avoid rashes. This involves careful awareness of the plants in your environment and taking precautions when venturing outdoors.
- Identification and Avoidance: Thoroughly learn to identify plants known to cause rashes in your region. Carry a field guide or use online resources to help with identification. Avoid contact with any suspected plant by keeping a safe distance and using protective clothing, such as long sleeves and pants, when in potential contact areas.
- Protective Clothing: Wear long sleeves, pants, and closed-toe shoes when gardening, hiking, or spending time outdoors, particularly in areas known to have problematic plants. Using gloves when handling plants can provide additional protection.
- Protective Barriers: Use barriers like garden gloves, aprons, and barrier creams to prevent direct contact with plants. For instance, applying a barrier cream to exposed skin before going into an area with known problematic plants can act as a physical barrier.
- Cleaning Equipment and Clothing: Thoroughly wash gardening tools, clothing, and equipment after contact with plants to remove any lingering plant particles that may cause a reaction.
Treating Plant-Induced Rashes
Effective treatment of plant-induced rashes depends on the severity of the reaction. Mild reactions can often be managed with home remedies, while more severe cases may require professional medical attention.
- Mild Reactions: For mild rashes, cool compresses, oatmeal baths, and over-the-counter anti-itch creams can provide relief. Apply a thin layer of hydrocortisone cream to the affected area to reduce inflammation and itching.
- Moderate Reactions: If the rash is more widespread or intense, consider using oral antihistamines to help reduce itching and swelling. Calamine lotion can also help soothe the skin.
- Severe Reactions: If the rash is accompanied by difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or other systemic symptoms, seek immediate medical attention. These reactions require immediate medical intervention to prevent serious complications.
Home Remedies for Mild Rashes
Home remedies can offer relief for mild plant-induced rashes. Natural ingredients and readily available household items can provide soothing and anti-inflammatory benefits.
- Cool Compresses: Applying cool, wet cloths to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and itching.
- Oatmeal Baths: Adding colloidal oatmeal to a bath can soothe irritated skin and reduce itching. The gentle abrasiveness of the oatmeal helps reduce the irritation and inflammation.
- Baking Soda Paste: A paste made from baking soda and water can help draw out moisture and reduce itching.
- Aloe Vera Gel: Applying aloe vera gel directly to the rash can provide cooling and soothing relief. The gel has known anti-inflammatory properties.
Treatment Options Comparison
The following table provides a comparative overview of treatment options based on rash severity. It is crucial to remember that this is a general guide, and individual responses may vary.
Ever wondered what plants are notorious for causing skin rashes? Knowing which ones to avoid can save a lot of discomfort. To delve deeper into the potential health risks and get the specific details on identifying these plants, you could check out how to access the medical information bureau. how to access the medical information bureau This will give you valuable insights into reliable resources for plant identification and potential allergic reactions, helping you avoid unpleasant encounters with these troublesome botanicals.
| Severity | Treatment Options | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Mild | Cool compresses, oatmeal baths, over-the-counter anti-itch creams, calamine lotion | Generally effective for localized, mild reactions |
| Moderate | Oral antihistamines, calamine lotion, cool compresses | May provide significant relief, but may not address the root cause |
| Severe | Professional medical attention (corticosteroids, antihistamines, etc.) | Essential for managing potentially life-threatening reactions |
When to Seek Professional Medical Attention
Professional medical attention is necessary for severe reactions or if symptoms worsen. Early intervention can prevent complications.
- Difficulty Breathing: If the rash is accompanied by difficulty breathing or wheezing, immediate medical attention is crucial.
- Significant Swelling: Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat requires immediate medical attention.
- High Fever: A high fever associated with a rash warrants immediate medical evaluation.
- Systemic Symptoms: Symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or dizziness should prompt a visit to a healthcare professional.
Plant Identification and Safety Precautions
Knowing which plants can cause skin reactions is crucial for safe outdoor activities. Identifying these plants accurately is paramount to avoiding exposure and subsequent discomfort. Incorrect identification can lead to serious health consequences, ranging from mild irritation to severe allergic reactions. This section provides a guide to identifying potentially problematic plants, emphasizing safe handling practices and the importance of protective measures.Proper plant identification is essential for preventing skin irritation.
Many plants, while beautiful and harmless to some, can trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Mistaking one plant for another can have serious consequences. This section focuses on practical steps to ensure safe interactions with the natural world.
Ever wondered about plants that cause skin irritation? Certain plants, like poison ivy and oak, are notorious for their rash-inducing properties. It’s important to be cautious when handling these plants, and always wear protective gear. Interestingly, similar care is needed with the use of CBD oil, which sometimes interferes with drug tests, potentially leading to false positives or issues if you’re trying to avoid a negative outcome.
CBD oil and failing drug tests can be a tricky area, so it’s essential to be aware of the potential complications. Luckily, knowledge of plants that trigger skin reactions can help you avoid similar pitfalls with potentially hazardous encounters with other flora.
Identifying Plants Causing Rashes in Your Region
A thorough understanding of the flora in your local area is vital. Local botanical gardens, libraries, and online resources (like regional plant identification apps) can provide valuable information about common plants, including those that may cause skin irritation. Carefully studying pictures and descriptions, paying attention to leaf shapes, stem characteristics, and flower structures, can help in accurate identification.
Ever wondered about those pesky plants that make your skin itch? Knowing which plants cause rashes is crucial for avoiding them. Luckily, if you do get a rash from one of these culprits, there are 22 effective ways to treat hives, like cool compresses and antihistamines, detailed in this helpful resource: 22 effective ways to treat hives.
Learning about these remedies can be a real lifesaver when dealing with plant-related skin reactions.
Remember that some plants have similar appearances, requiring careful observation to avoid misidentification. Also, be aware of seasonal variations in plant characteristics.
Importance of Proper Plant Identification
Incorrect plant identification can lead to accidental exposure to toxic or irritating plants. For example, mistakenly handling poison ivy can result in a rash, while a similar-looking plant might be harmless. Precise identification prevents unnecessary contact and minimizes the risk of skin irritation.
Detailed Procedure for Handling Suspected Poisonous Plants
When encountering a plant you suspect may be poisonous, adopt a cautious approach. First, try to identify the plant using reliable resources, focusing on details like leaf shape, stem characteristics, and flower structure. If uncertain, avoid contact altogether. If you must approach the plant, wear protective clothing and gloves. Avoid touching your face or eyes after potential exposure.
If you experience a rash, seek medical attention immediately.
Safe Handling Practices to Avoid Contact, Plants that cause rashes
Always maintain a safe distance from plants known to cause rashes. Do not touch any part of the plant if you suspect it may be poisonous. Use long sleeves, pants, and gloves when gardening or hiking in areas with known problematic plants. If you must handle a suspected poisonous plant, use tools or protective equipment.
Importance of Wearing Protective Clothing and Gear
Wearing protective clothing and gear is a critical safety measure. Long sleeves, long pants, closed-toe shoes, and gloves offer a physical barrier against potential contact with irritant plants. Wear sturdy footwear to protect your feet from thorns or sharp objects. Appropriate eyewear can protect your eyes from accidental contact with plant materials. Remember to thoroughly wash your hands and exposed skin after handling any plants, even those deemed harmless.
A simple handwashing routine is crucial for preventing the spread of plant irritants.
Specific Plant Examples
Unveiling the culprits behind itchy skin reactions, we delve into the characteristics, toxicity, and allergenic properties of some notorious plant offenders. Understanding these plants’ behaviors helps us identify, prevent, and treat potential contact dermatitis. Knowing the specific features and distribution of each plant species empowers us to make informed decisions about our outdoor activities.
Poison Ivy
Poison ivy, a notorious plant culprit, is easily identified by its characteristic three-leafleted structure. Each leaf typically has a smooth, pointed edge and a slightly glossy surface. The leaves are often arranged alternately along the stem. The color varies depending on the season, ranging from a vibrant green in spring and summer to a fiery orange or red in autumn.
Poison ivy often grows as a vine, scrambling up trees and other structures, or as a low-lying shrub. Contact with its urushiol oil, a potent allergen, causes an itchy, red rash. The rash typically appears within a few hours to a few days after contact, peaking in intensity and spreading over the affected area. Blisters may also form on the skin.
Stinging Nettles
Stinging nettles, despite their prickly appearance, are not necessarily a plant to be feared. Their stinging ability stems from specialized cells containing histamine and other irritants. The plant is characterized by its distinctive, often reddish-green, lance-shaped leaves. These leaves, which often grow in dense clusters, are covered with fine, stinging hairs. Contact with these hairs results in an immediate, burning sensation followed by a red rash.
The rash is often accompanied by itching and sometimes swelling. Stinging nettles are known for their high levels of toxicity. The stinging hairs inject histamine and other irritants into the skin, leading to a localized inflammatory response. The allergenicity is high, with some people experiencing more severe reactions. This reaction is due to the plant’s unique ability to inject irritant substances.
Oak Trees
Various oak species are known to cause contact dermatitis. These rashes typically manifest as an itchy, red rash, often with blisters, at the site of contact. The rash develops within a few hours to a few days after contact with the plant’s oil, a potent allergen. Oak trees vary in their appearance, but many have distinctive lobed leaves.
The leaves’ shape, size, and arrangement can be used for identification. The severity of the rash depends on the individual’s sensitivity and the amount of contact with the plant’s oil.
Other Plants Causing Contact Dermatitis
Numerous other plants can cause contact dermatitis, often due to the presence of irritant or allergenic compounds in their sap, resins, or oils. These compounds, when contacted by the skin, can trigger an inflammatory response, leading to a rash. The specific symptoms and appearance of the rash can vary depending on the plant and the individual’s sensitivity.
- Privet: Privet plants, characterized by their glossy leaves and clusters of small, fragrant flowers, are known for causing allergic reactions in some individuals. The symptoms often include an itchy, red rash, which may spread or become more intense over time.
- Sumac: Similar to poison ivy, poison sumac has a characteristic appearance with three to seven leaflets per leaf. Contact with the plant’s oils can lead to a severe rash, which often features blisters and intense itching. Sumac plants are known for their varying growth habits and preferences for specific environments.
- Oleander: Oleander plants are beautiful but potentially dangerous. The sap of this plant contains toxins that can cause skin irritation, digestive problems, and other symptoms when ingested or touched. It is essential to be aware of the potential risks of contact with this plant.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, understanding plants that cause rashes is essential for personal safety and well-being. By learning to identify these plants, practicing preventative measures, and knowing how to treat reactions, you can minimize the risk of discomfort and ensure a more enjoyable experience in nature. The information provided in this guide serves as a valuable resource for anyone seeking to navigate the world of potentially problematic plants safely.

