Pineapple benefits and nutrition are a fascinating subject. This comprehensive exploration delves into the rich nutritional profile of pineapples, examining vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients. We’ll uncover the potential health advantages, from boosting immunity to aiding digestion and even supporting skin health. Learn about pineapple’s role in different cuisines and how to maximize its nutritional value in your meals.
We’ll also explore the potential risks and considerations, like allergies and pregnancy, providing a well-rounded view of this tropical fruit.
Beyond its delicious taste, pineapples pack a surprising punch of nutrients. This detailed analysis will help you understand the multifaceted benefits of incorporating this fruit into your diet. From its unique enzymes to its antioxidant properties, we’ll uncover the science behind pineapple’s potential impact on your well-being.
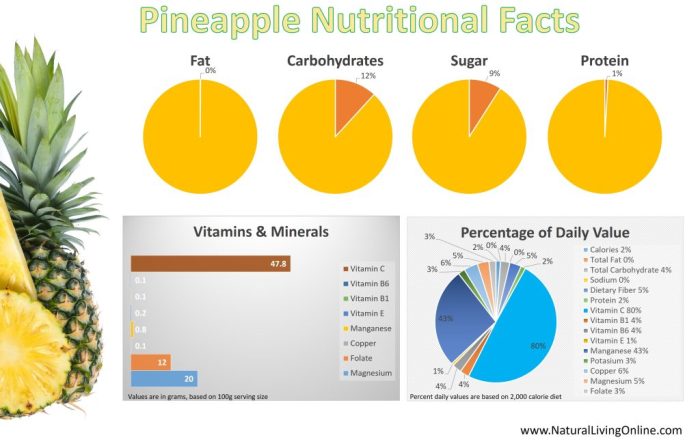
Nutritional Profile

Pineapples, a tropical delight, offer a wealth of nutrients beyond their juicy sweetness. Their vibrant yellow flesh and sweet taste mask a powerful nutritional punch, making them a valuable addition to a balanced diet. Understanding their nutritional profile can help you appreciate the many health benefits they provide.Pineapples are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, contributing to overall well-being.
This section delves into the detailed nutritional composition of pineapples, exploring their vitamins, minerals, macronutrients, fiber content, and calorie count across various preparations.
Vitamins and Minerals
Pineapples are a good source of several essential vitamins and minerals. These nutrients play critical roles in various bodily functions, from supporting immune health to promoting energy production.
Pineapple is packed with vitamin C and bromelain, great for digestion and overall health. While exploring the nutritional wonders of different plants, it’s interesting to consider alternative remedies like mugwort, which has a range of potential benefits but also potential side effects. Learning about the proper dosage and interactions of mugwort is crucial for safe use, as detailed in this comprehensive guide: mugwort benefits side effects dosage and interactions.
Ultimately, understanding the nutritional value of pineapple, and how it contributes to a balanced diet, is key to overall wellness.
- Vitamin C: Pineapples are rich in vitamin C, a potent antioxidant that supports immune function and collagen production. A single cup of diced pineapple provides a significant portion of the recommended daily intake of vitamin C.
- Vitamin B6: Vitamin B6 is essential for brain function, red blood cell production, and the metabolism of amino acids. Pineapples provide a moderate amount of vitamin B6, contributing to overall metabolic health.
- Manganese: Pineapples contain manganese, a trace mineral vital for bone health, wound healing, and carbohydrate metabolism. Adequate manganese intake supports various bodily processes.
- Potassium: Pineapples offer a moderate amount of potassium, an electrolyte essential for maintaining healthy blood pressure and nerve function. Including pineapples in your diet can contribute to maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system.
Macronutrient Composition
The macronutrient composition of pineapples consists primarily of carbohydrates, with a smaller amount of protein and negligible fat. This balanced composition makes them a suitable option for various dietary needs.
- Carbohydrates: Pineapples are predominantly composed of carbohydrates, primarily in the form of natural sugars. The carbohydrate content varies based on the preparation, from fresh pineapple chunks to pineapple juice.
- Protein: Pineapples contain a moderate amount of protein, essential for building and repairing tissues. The protein content is relatively lower compared to other protein-rich foods.
- Fat: Pineapples have a very low fat content, making them a suitable choice for those following a low-fat diet.
Fiber Content and Health Benefits
Pineapple’s fiber content contributes to digestive health and satiety. Dietary fiber aids in promoting regular bowel movements and contributes to a feeling of fullness, which can be beneficial for weight management.
- Digestive Health: The fiber in pineapple aids in promoting regular bowel movements, contributing to digestive health. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with digestive issues.
- Satiety: The fiber content of pineapple contributes to a feeling of fullness, which can help with managing appetite and weight.
Calorie Count per Serving Size
The calorie count of pineapples varies depending on the serving size and preparation method. Fresh pineapple chunks contain fewer calories than processed pineapple products like juice or canned pineapple.
| Nutrient | Amount | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fresh Pineapple (1 cup, diced) | 50 | Calories |
| Canned Pineapple (1 cup, drained) | 70 | Calories |
| Pineapple Juice (1 cup) | 100 | Calories |
Note: Calorie counts may vary based on specific preparation methods and serving sizes.
Health Benefits
Pineapples, a tropical delight, offer more than just a sweet taste. Their nutritional profile is packed with vitamins, minerals, and compounds that contribute to overall well-being. Beyond their deliciousness, pineapples show potential benefits for various aspects of health, from boosting the immune system to aiding digestion and potentially supporting heart health. Let’s explore the remarkable health advantages associated with consuming this juicy fruit.
Immune System Support
Pineapples are rich in vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant known for its role in supporting the immune system. Vitamin C helps stimulate the production of white blood cells, which are crucial for fighting off infections. This contribution to immune function makes pineapples a valuable addition to a healthy diet.
Digestive Health Benefits
The presence of bromelain, a proteolytic enzyme, in pineapples contributes to digestive health. Bromelain helps break down proteins, aiding in digestion and potentially reducing bloating and discomfort. Consumption of pineapples may ease digestion and reduce inflammation in the digestive tract.
Cardiovascular Health Potential
Pineapples contain antioxidants that can potentially protect against cellular damage. These antioxidants may play a role in maintaining healthy blood vessels and supporting heart health. However, further research is needed to definitively establish the extent of these benefits. A balanced diet and regular exercise are crucial for maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system.
Weight Management Support
The low calorie and high fiber content of pineapples can contribute to feelings of fullness, potentially supporting weight management efforts. The combination of fiber and water content helps regulate appetite and provides sustained energy. However, a balanced diet and exercise regimen remain essential for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
Pineapples are packed with vitamin C and bromelain, great for digestion. But did you know that incorporating some brisk walking into your routine can help you burn calories and boost your overall health? Knowing how many calories you burn while walking can help you tailor your exercise plan and make the most of your workouts. For example, check out this resource to see how many calories a specific walking routine might burn: how many calories does walking burn.
Regardless of your calorie burn, pineapples still provide a healthy and delicious way to support your well-being.
Anti-inflammatory Properties
Bromelain, the enzyme found in pineapples, possesses anti-inflammatory properties. It may help reduce inflammation in the body, potentially contributing to overall well-being. However, the effectiveness of bromelain in reducing inflammation in various conditions needs further investigation.
Comprehensive List of Potential Health Advantages
- Supports immune function through vitamin C.
- Aids digestion with bromelain’s protein-digesting properties.
- May promote heart health through antioxidant content.
- Potentially contributes to weight management by promoting fullness.
- May reduce inflammation due to bromelain’s anti-inflammatory effects.
Summary Table of Health Benefits
| Health Benefit | Supporting Evidence |
|---|---|
| Immune Support | Rich in vitamin C, which stimulates white blood cell production. |
| Digestive Health | Bromelain aids in protein breakdown, easing digestion. |
| Cardiovascular Health | Antioxidants may protect against cellular damage and support blood vessel health. |
| Weight Management | Low calorie and high fiber content contribute to feelings of fullness. |
| Anti-inflammatory Effects | Bromelain possesses anti-inflammatory properties. |
Culinary Applications
Pineapples, with their vibrant flavor and juicy texture, are a versatile addition to a wide range of cuisines. Beyond their refreshing nature as a standalone fruit, pineapples excel in sweet and savory dishes, adding a unique zing to various culinary creations. Their delicate sweetness complements savory elements, while their acidity provides a delightful balance.Optimal cooking methods play a crucial role in preserving the pineapple’s nutritional value.
Understanding these techniques allows you to enjoy the fruit’s rich nutrients while maximizing its flavor. Choosing the right method for your recipe ensures you retain the most beneficial compounds present in the pineapple.
Cooking Methods for Preserving Nutritional Value
Different cooking methods affect the retention of vitamins and minerals. Steaming and microwaving, for example, are gentler methods, minimizing nutrient loss compared to frying or roasting. Roasting or frying, while allowing for caramelization, can lead to a reduction in certain vitamins and minerals. Boiling, while straightforward, also results in some loss of water-soluble vitamins. Thus, careful consideration of the method is key to maintaining the pineapple’s nutritional integrity.
Pineapple in Various Cuisines
Pineapple’s adaptability extends across diverse culinary traditions. From the tropical flavors of Southeast Asia to the vibrant dishes of Latin America, pineapple finds a place in numerous cuisines. Its tangy and sweet profile seamlessly blends with ingredients in both sweet and savory preparations.
Pineapple-Based Recipes by Cuisine
| Cuisine | Recipe | Flavor Profile | Nutritional Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Southeast Asian | Pineapple Fried Rice | Sweet, savory, with a hint of spice | Rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber |
| Latin American | Pineapple Salsa | Tangy, sweet, and slightly spicy | Excellent source of vitamin C |
| Caribbean | Pineapple Chicken Skewers | Sweet and savory, with a hint of Caribbean spice | Provides a good balance of protein and vitamins |
| Hawaiian | Pineapple Upside-Down Cake | Sweet, moist, and with a caramelized pineapple topping | Good source of fiber and vitamins |
| Asian Fusion | Pineapple-Ginger Stir-fry | Savory, with a touch of ginger and garlic | A blend of flavors and vitamins, particularly vitamin C |
Examples of Dishes Featuring Pineapple
- Pineapple Salsa with Grilled Chicken: The tangy salsa provides a delightful contrast to the savory grilled chicken. This combination highlights the versatility of pineapple in both sweet and savory dishes.
- Pineapple and Shrimp Stir-fry: This dish combines the sweetness of pineapple with the protein-rich shrimp. The addition of soy sauce and ginger creates a flavorful stir-fry that is both delicious and nutritious.
- Pineapple Upside-Down Cake: A classic dessert that showcases the fruit’s natural sweetness. The caramelized pineapple creates a delightful contrast in texture and flavor.
Optimal Cooking Methods for Different Applications
- Fresh Salads: Fresh pineapple slices add a burst of tropical flavor and a vibrant touch. Minimal cooking is ideal to preserve its texture and nutrients.
- Sauces and Chutneys: Pineapple can be cooked gently to create delicious sauces and chutneys. Steaming or microwaving are preferred methods.
- Main Courses: In stir-fries or curries, the pineapple is usually added toward the end of cooking to prevent it from becoming mushy.
- Desserts: For desserts, cooking methods like baking or roasting can be used to create a range of textures and flavors.
Pineapple and Digestive Health: Pineapple Benefits And Nutrition
Pineapple, a tropical delight, offers more than just a sweet taste. Its unique composition plays a significant role in digestive processes. This exploration delves into the mechanisms by which pineapple aids digestion, its potential impact on gut health, and its comparative benefits against other fruits. We’ll also examine potential risks and present research findings to provide a comprehensive understanding of this fruit’s influence on digestive well-being.Pineapple’s digestive benefits are primarily attributed to its bromelain content.
Bromelain is a complex mixture of proteolytic enzymes, which play a crucial role in breaking down proteins. This enzymatic action facilitates the digestion of proteins in the stomach and intestines, potentially alleviating digestive discomfort associated with protein-rich meals.
Pineapple Enzymes and Protein Digestion
Pineapple’s bromelain enzymes have demonstrated the ability to break down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids. This enhanced breakdown improves the efficiency of protein absorption in the digestive tract. The increased bioavailability of amino acids supports various bodily functions, including muscle repair and growth. The presence of bromelain can thus be beneficial for individuals consuming substantial amounts of protein in their diet.
Potential Effects of Pineapple on Gut Health
The impact of pineapple on gut health is multifaceted. While not a direct probiotic or prebiotic, the digestive aid provided by bromelain can indirectly contribute to a healthier gut environment. By improving protein digestion, bromelain may potentially reduce strain on the digestive system, leading to reduced discomfort and improved overall digestive health. Further research is needed to fully understand the intricate interplay between pineapple consumption and gut microbiome composition.
Comparing Pineapple’s Digestive Benefits to Other Fruits
Various fruits offer digestive support, each with its unique properties. While pineapple excels in protein digestion due to bromelain, other fruits offer distinct advantages. For instance, apples and pears are rich in fiber, promoting regularity and gut health. Bananas contain potassium and fiber, which contribute to overall digestive function. A balanced diet including a variety of fruits and vegetables is crucial for optimal digestive health.
Potential Risks of Excessive Pineapple Consumption
While pineapple offers numerous digestive benefits, consuming excessive amounts may lead to potential side effects. Bromelain, while generally safe, can potentially cause stomach upset, nausea, or diarrhea in some individuals, particularly those with pre-existing digestive conditions. Moderation is key to reaping the benefits of pineapple without experiencing adverse effects.
Research Findings on Pineapple’s Role in Digestive Processes, Pineapple benefits and nutrition
Several studies have investigated pineapple’s role in digestive processes. Some research suggests that bromelain can aid in reducing inflammation associated with digestive issues. However, more rigorous and extensive research is required to fully establish the efficacy and long-term effects of pineapple consumption on various digestive conditions. A controlled clinical trial may provide further insights.
Table Comparing Pineapple to Other Fruits for Digestive Support
| Fruit | Key Digestive Benefit |
|---|---|
| Pineapple | High bromelain content aids protein digestion |
| Apples | Rich in fiber, promotes regularity |
| Bananas | Potassium and fiber support overall digestive function |
| Pears | Fiber content promotes healthy bowel movements |
Pineapple and Skin Health
Pineapples, a tropical delight, offer more than just a sweet taste. Their nutritional profile suggests a potential role in supporting healthy skin. This juicy fruit, packed with vitamins and antioxidants, may contribute to collagen production, reduce inflammation, and ultimately, promote a radiant complexion. Let’s delve deeper into how pineapples might benefit your skin.Pineapple’s potent enzymes, primarily bromelain, have garnered attention for their potential impact on skin health.
These enzymes are believed to play a crucial role in breaking down proteins, which could have implications for skin rejuvenation and inflammation reduction. This section explores the specifics of how pineapple’s constituents may contribute to healthy skin.
Potential Role of Pineapple in Skin Health
Pineapples contain a unique blend of nutrients, including vitamin C, vitamin A, and various minerals, all vital for skin health. Vitamin C, a potent antioxidant, helps protect skin cells from damage caused by free radicals. Vitamin A is crucial for cell turnover and maintaining skin elasticity. These elements contribute to the overall well-being of the skin.
Effects of Pineapple on Collagen Production
Bromelain, the key enzyme found in pineapple, is believed to influence collagen production. Collagen is a structural protein essential for skin firmness and elasticity. While further research is needed to fully understand the precise mechanism, some studies suggest bromelain may promote collagen synthesis, potentially contributing to a more youthful and supple complexion.
Pineapple’s Impact on Skin Inflammation
Inflammation can lead to various skin concerns, including redness, irritation, and breakouts. Bromelain, with its anti-inflammatory properties, may help alleviate these issues. By reducing inflammation, pineapple could contribute to a healthier and smoother skin tone. This aligns with its potential role in supporting skin healing and reducing discomfort.
Research Findings on Pineapple’s Impact on Skin Health
While conclusive studies on pineapple’s direct impact on human skin are limited, research on bromelain’s anti-inflammatory and collagen-boosting effects in other contexts suggests a promising potential. More clinical trials are necessary to establish a definitive link between pineapple consumption and specific skin benefits in humans.
Comparison of Pineapple’s Skin Benefits to Other Fruits
Many fruits contribute to healthy skin. Berries, rich in antioxidants, are well-known for their potential protective effects. Citrus fruits, particularly oranges and lemons, are excellent sources of vitamin C, essential for collagen production. Comparing pineapple’s benefits to others highlights the multifaceted approach to maintaining skin health through a balanced diet. The unique blend of bromelain and other nutrients in pineapple could provide a distinct advantage.
Vitamins and Minerals Supporting Skin Health in Pineapple
The table below Artikels the vitamins and minerals found in pineapple that may contribute to skin health. These nutrients play vital roles in maintaining skin elasticity, promoting cell regeneration, and protecting against damage.
| Nutrient | Potential Benefit to Skin |
|---|---|
| Vitamin C | Antioxidant, collagen synthesis, wound healing |
| Vitamin A | Cell turnover, skin elasticity, protection against damage |
| Bromelain | Anti-inflammatory, collagen production, potential skin healing |
| Potassium | Hydration, skin health |
| Manganese | Collagen synthesis, antioxidant |
Pineapple and Antioxidants
Pineapples are a tropical delight that offer more than just a sweet taste. Their vibrant yellow flesh and juicy texture hide a wealth of beneficial nutrients, including potent antioxidants. These compounds play a crucial role in protecting our bodies from damage and promoting overall health. This section delves into the antioxidant content of pineapples, exploring their role in combating free radicals, and examining their potential benefits for cellular health.
Antioxidants in Pineapple
Pineapples are rich in various antioxidants, primarily due to the presence of vitamin C and compounds like phenolic acids and carotenoids. These antioxidants act as scavengers, neutralizing harmful free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to aging and various health issues. Vitamin C, a well-known antioxidant, plays a critical role in neutralizing these harmful agents.
It’s crucial to maintain a balance between free radicals and antioxidants to prevent cellular damage.
Role of Antioxidants in Combating Free Radicals
Antioxidants effectively neutralize free radicals by donating electrons to these unstable molecules. This process prevents the chain reaction of oxidative damage, which can lead to cellular dysfunction. The presence of antioxidants in the body can help prevent damage to cells and tissues, thereby contributing to overall well-being.
Potential Benefits of Antioxidants for Overall Health
The antioxidant capacity of pineapple, and other foods rich in antioxidants, is linked to a variety of potential health benefits. These benefits include a reduced risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and certain types of cancer. Antioxidants are also vital for maintaining healthy immune function and supporting overall cellular health.
Research on Antioxidant Content of Pineapple
Studies have shown that pineapple contains significant levels of antioxidants. While the exact levels can vary based on factors like ripeness and growing conditions, pineapple consistently demonstrates a positive antioxidant capacity. This makes it a valuable addition to a diet aimed at promoting overall health. Scientific research is ongoing to further elucidate the specific mechanisms and full range of benefits associated with pineapple antioxidants.
How Antioxidants Contribute to Cellular Health
Antioxidants help protect cells from damage by neutralizing free radicals. This cellular protection is crucial for maintaining optimal function and preventing premature aging. By reducing oxidative stress, antioxidants support the overall health of cells, contributing to their longevity and proper functioning.
Foods High in Antioxidants (Compared to Pineapple)
Many fruits and vegetables are excellent sources of antioxidants. Comparing the antioxidant content between various foods can be complex, as different methods exist for measuring antioxidant capacity. However, a general comparison can offer a valuable perspective.
| Food | Antioxidant Content (General Estimate) |
|---|---|
| Blueberries | Very High |
| Spinach | High |
| Pineapple | Moderate |
| Strawberries | High |
| Artichokes | High |
Note: The table provides a general comparison. Specific values can differ based on various factors, including ripeness and growing conditions. It is essential to maintain a balanced and varied diet to reap the benefits of various antioxidants.
Pineapple and Allergies
Pineapple, a tropical fruit enjoyed worldwide, is generally considered safe to consume. However, like many foods, it can trigger allergic reactions in susceptible individuals. Understanding the potential for allergic reactions, symptoms, and management strategies is crucial for those who consume pineapple or work with it.
Pineapples are packed with vitamins and minerals, great for overall health. Did you know that some of these nutrients might help manage blood pressure? Knowing the facts about high blood pressure is crucial for good health, and understanding the role of healthy foods like pineapple is key. high blood pressure facts Incorporating pineapples into your diet, rich in bromelain and vitamin C, could be a delicious way to support healthy blood pressure levels.
Their nutritional punch makes them a worthwhile addition to a balanced diet.
Potential for Allergic Reactions
Pineapple allergies, though less common than other food allergies, can manifest in various ways. The proteins present in pineapple, like those found in other fruits and vegetables, can potentially elicit an immune response in predisposed individuals. This immune response, characterized by the release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators, leads to the allergic symptoms. The severity of reactions can range from mild discomfort to life-threatening anaphylaxis.
Symptoms of Pineapple Allergies
Allergic reactions to pineapple can present with a variety of symptoms, impacting different body systems. Early recognition of these symptoms is essential for appropriate management.
- Skin reactions, such as hives, itching, and skin rashes, are common symptoms.
- Gastrointestinal distress, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, can occur.
- Respiratory issues, like sneezing, coughing, and difficulty breathing, might be experienced.
- Anaphylaxis, a severe and potentially life-threatening reaction, involves a rapid onset of symptoms affecting multiple systems, including difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat and tongue, and low blood pressure.
Identifying and Managing Pineapple Allergies
Proper identification and management of pineapple allergies are crucial for preventing severe reactions. A detailed understanding of the symptoms and triggers is key to effective management.
- Careful observation of symptoms following pineapple consumption is essential.
- If symptoms appear, immediate medical attention should be sought, especially if symptoms are severe or involve difficulty breathing.
- Keeping a detailed food diary can help identify potential triggers and patterns associated with reactions.
- Working with an allergist can provide personalized strategies for managing pineapple allergies and other potential food sensitivities.
Cross-Reactivity with Other Foods
Cross-reactivity between pineapple and other foods is a possibility, especially among individuals with pre-existing sensitivities or allergies. Similar protein structures in different foods can lead to allergic reactions.
| Food Allergy | Potential Cross-reactivity with Pineapple |
|---|---|
| Latex Allergy | Possible, though less commonly reported. |
| Peach Allergy | Moderate possibility, due to shared proteins. |
| Other Tropical Fruits | High possibility, especially within the same family of plants, like other members of the Bromeliaceae family. |
| Birch pollen allergy | Moderate possibility, as cross-reactivity is often observed with similar plant families. |
Prevalence of Pineapple Allergies
The prevalence of pineapple allergies is relatively low compared to other common food allergies. Precise figures are challenging to obtain, as many cases may be misdiagnosed or go unreported. However, the potential for allergic reactions exists, emphasizing the importance of awareness and careful monitoring.
Pineapple and Pregnancy
Pineapples, a tropical delight known for their sweet and tangy flavor, are a popular fruit enjoyed worldwide. However, when it comes to pregnancy, certain considerations regarding their consumption need attention. This section explores the potential benefits and risks of incorporating pineapples into a pregnant woman’s diet, emphasizing the importance of professional guidance.
Potential Benefits of Pineapple During Pregnancy
Pineapples contain bromelain, an enzyme with potential digestive benefits. Some studies suggest bromelain may aid in reducing inflammation and potentially ease nausea or discomfort associated with morning sickness. Furthermore, pineapples are a good source of vitamin C, a vital nutrient for immune function and collagen production, both crucial during pregnancy.
Potential Risks of Pineapple Consumption During Pregnancy
While pineapples offer potential benefits, they also pose certain risks. Raw pineapple, particularly the core and skin, can contain high levels of bromelain. Unripe pineapples might cause gastrointestinal upset in some individuals. Excessive bromelain consumption could potentially affect blood clotting, which is a concern during pregnancy. There is also the possibility of allergic reactions, although this is less common.
Importance of Consulting with a Healthcare Professional
Given the potential benefits and risks, consulting a healthcare professional is paramount. A doctor can assess an individual’s unique circumstances, including pre-existing conditions and dietary needs, and provide personalized recommendations regarding pineapple consumption during pregnancy. This personalized approach ensures that the benefits of pineapple are maximized while minimizing any potential risks.
Impact of Pineapple Consumption on Fetal Development
There’s currently limited conclusive evidence on the direct impact of pineapple consumption on fetal development. While the presence of essential nutrients in pineapples is beneficial, the potential effects of high bromelain levels on a developing fetus need further investigation. It’s crucial to prioritize balanced nutrition and follow the advice of healthcare providers to ensure optimal fetal growth.
Safe and Recommended Consumption Guidelines for Pregnant Women
For pregnant women considering pineapple consumption, moderation is key. Cooked or lightly processed pineapple is generally safer than raw pineapple. Start with small portions and monitor any reactions. If any digestive issues or discomfort arise, discontinue consumption and consult a healthcare professional. Avoid consuming pineapple during the third trimester, as there’s concern about the potential impact on uterine contractions.
Fruits Generally Safe During Pregnancy, Contrasting Profiles to Pineapple
Numerous fruits are generally considered safe and beneficial during pregnancy. These include bananas, apples, oranges, berries, and pears. These fruits offer various nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and fiber without the potential digestive or blood-clotting concerns associated with high bromelain content in pineapples. The differing nutrient profiles and potential impacts on pregnancy highlight the need for a balanced and varied diet that incorporates fruits carefully selected in consultation with a healthcare provider.
Last Point
In conclusion, pineapple offers a diverse range of potential benefits, from supporting digestion and immunity to promoting skin health. Its nutritional profile, rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber, makes it a valuable addition to a balanced diet. While enjoying the delicious taste of pineapple, remember to consider potential risks, such as allergies or excessive consumption. By understanding the various aspects of pineapple’s benefits and nutrition, you can make informed decisions about incorporating this tropical treasure into your lifestyle.




