Nsaids non steroidal anti inflammatories and ibd – NSAIDs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and IBD, inflammatory bowel disease, are intricately linked. This exploration delves into the complex relationship between NSAIDs and IBD, examining potential mechanisms, clinical implications, and alternative treatment approaches. Understanding the interplay of these factors is crucial for effective patient management.
NSAIDs are widely used to relieve pain and inflammation, but their use in IBD patients requires careful consideration. Different types of NSAIDs have varying effects on the gastrointestinal tract, impacting the already compromised intestinal lining in IBD. This detailed overview examines the potential risks and benefits of NSAID use in IBD patients, providing a comprehensive understanding of this critical area of medical concern.
Introduction to NSAIDs and IBD: Nsaids Non Steroidal Anti Inflammatories And Ibd
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a class of medications commonly used to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation. They’re widely available over-the-counter and by prescription, making them a crucial part of many people’s healthcare routines. However, their use can be complicated by potential side effects, especially concerning the gastrointestinal system. This discussion delves into the relationship between NSAIDs and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD).NSAIDs work by inhibiting cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, primarily COX-1 and COX-2.
These enzymes play a vital role in producing prostaglandins, which are crucial for various bodily functions, including protecting the stomach lining. The inhibition of prostaglandin production can lead to gastrointestinal issues, including ulcers and bleeding. The impact of NSAIDs on individuals with IBD is particularly important to understand due to the inflammatory nature of these conditions.
Common Types of NSAIDs
Several types of NSAIDs are available, each with slightly different mechanisms and potential side effects. Common over-the-counter NSAIDs include ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve). Prescription NSAIDs, often used for more severe pain or inflammation, include diclofenac, celecoxib, and others. The selection of an NSAID depends on the individual’s needs and medical history.
Mechanisms of Action of NSAIDs
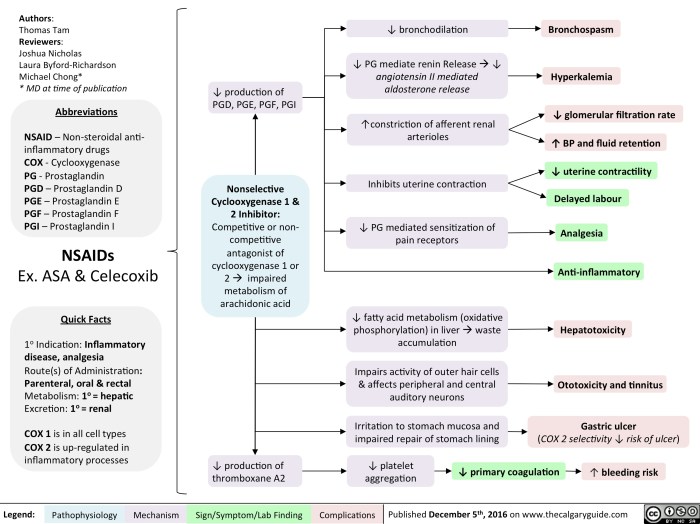
NSAIDs primarily work by blocking the action of cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes. COX enzymes are crucial for the production of prostaglandins, which are involved in pain, fever, and inflammation. By inhibiting COX, NSAIDs reduce the production of these inflammatory mediators, leading to a decrease in pain and swelling. However, this inhibition also affects prostaglandins vital for protecting the stomach lining, potentially increasing the risk of gastrointestinal issues.
Effects of NSAIDs on the Gastrointestinal Tract
The inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis by NSAIDs can significantly impact the gastrointestinal tract. Prostaglandins are essential for maintaining the health of the stomach lining. Their reduction can lead to gastric irritation, ulcers, and even bleeding. This effect is a significant concern, particularly for individuals prone to gastrointestinal issues or those with pre-existing conditions like ulcers or inflammatory bowel disease.
NSAIDs, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can sometimes play a role in managing inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). However, it’s crucial to remember that IBD isn’t always easily diagnosed, and understanding what other potential symptoms might look like is vital. For example, knowing what gonorrhea might present as can help distinguish it from IBD symptoms, which can be a tricky process.
What does gonorrhea look like ? This can help in a proper diagnosis and treatment plan, leading to better management of IBD symptoms. Ultimately, proper medical guidance from a qualified professional is essential for any health concern, including IBD.
Role of NSAIDs in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD)
Individuals with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, face a heightened risk of gastrointestinal complications when using NSAIDs. The existing inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract makes them more susceptible to the ulcerogenic effects of NSAIDs. This can exacerbate existing symptoms, leading to increased pain, bleeding, and potentially more severe complications.
Comparison of NSAIDs and Potential Gastrointestinal Risks
| NSAID | Potential Gastrointestinal Risks |
|---|---|
| Ibuprofen | Generally considered to have a moderate risk of gastrointestinal side effects. |
| Naproxen | Potentially carries a slightly higher risk of gastrointestinal side effects compared to ibuprofen. |
| Diclofenac | Known to have a higher risk of gastrointestinal complications, including ulcers and bleeding, compared to ibuprofen or naproxen. |
| Celecoxib | Generally associated with a lower risk of gastrointestinal issues compared to traditional NSAIDs, but still poses some risk. |
This table provides a general overview of the potential gastrointestinal risks associated with different NSAIDs. Individual responses can vary. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any NSAID therapy, especially for individuals with a history of gastrointestinal problems or IBD.
NSAIDs and IBD: Specific Mechanisms
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to relieve pain and inflammation, but their use can sometimes exacerbate inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Understanding the specific mechanisms by which NSAIDs interact with IBD is crucial for managing patients effectively and minimizing potential complications. This section delves into the potential pathways through which NSAIDs influence IBD development and progression.NSAIDs exert their effects primarily by inhibiting cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, which are crucial for the production of prostaglandins.
Prostaglandins play a complex role in regulating various bodily functions, including the inflammatory response. By inhibiting prostaglandin production, NSAIDs can effectively reduce inflammation in some conditions. However, this effect can be problematic in individuals with IBD, where the delicate balance of intestinal inflammation is already disrupted.
Potential Interactions between NSAID Use and IBD Development
NSAIDs can potentially trigger or worsen IBD symptoms in susceptible individuals. This interaction is not fully understood, but several factors likely contribute. One possibility involves the disruption of the protective mucous layer lining the intestines. NSAIDs can impair the production of protective prostaglandins, thereby reducing the integrity of this crucial barrier.
NSAIDs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can sometimes trigger IBD (inflammatory bowel disease) symptoms in some people. It’s a tricky connection, and sometimes the culprit isn’t the NSAIDs themselves, but rather hidden sensitivities to certain foods or even plants that cause rashes. For example, if you’re struggling to pinpoint a rash-causing culprit, checking out this guide on plants that cause rashes might help.
Ultimately, figuring out what’s behind your IBD flare-ups is key to finding the right treatment and avoiding future issues with NSAIDs.
Potential Effects of NSAIDs on the Intestinal Lining
The intestinal lining is a complex and dynamic structure, essential for nutrient absorption and defense against harmful substances. NSAIDs, by inhibiting prostaglandin production, can disrupt the balance of this lining, potentially leading to increased permeability and inflammation. This can exacerbate existing IBD-related damage and potentially contribute to the development of new complications. Specifically, reduced prostaglandin production can lead to ulceration and erosion of the intestinal mucosa, further compromising its protective function.
Detailed Description of How NSAIDs May Influence the Immune Response in IBD
The immune system plays a critical role in IBD, and NSAIDs can influence this response in various ways. By impacting prostaglandin levels, NSAIDs may alter the balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, further contributing to the chronic inflammatory state characteristic of IBD. This imbalance can lead to an exaggerated immune response in the gut, making the inflammation more severe and persistent.
This effect is likely mediated through a complex interplay of inflammatory pathways and immune cell activation.
Comparison of Effects of Different NSAIDs on Inflammatory Processes in IBD
Different NSAIDs exhibit varying degrees of COX inhibition, which can impact their effects on IBD. For example, selective COX-2 inhibitors may have a lower risk of gastrointestinal side effects compared to non-selective COX inhibitors. However, the influence on the complex inflammatory response in IBD is still not fully understood for different NSAID types. Further research is needed to fully delineate the impact of specific NSAID structures on the inflammatory processes in IBD.
Role of COX-2 Inhibition in the Context of NSAIDs and IBD
COX-2 is a specific isoform of cyclooxygenase, and its inhibition is a key mechanism of action for some NSAIDs. COX-2 is primarily involved in the production of prostaglandins associated with inflammation. In IBD, selective COX-2 inhibitors may have a lower risk of gastrointestinal complications compared to non-selective COX inhibitors. However, this does not negate the potential for these drugs to affect the immune response in the gut and exacerbate IBD symptoms in susceptible individuals.
Table Summarizing Potential Inflammatory Pathways Affected by NSAIDs in IBD
| Inflammatory Pathway | Potential NSAID Effect | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Prostaglandin Production | Inhibition | Reduces protective prostaglandins, increasing intestinal permeability and mucosal damage. |
| Cytokine Balance | Disruption | Alters the ratio of pro-inflammatory to anti-inflammatory cytokines, potentially exacerbating inflammation. |
| Immune Cell Activation | Modulation | Affects immune cell function and response, contributing to the chronic inflammatory state. |
| Mucous Layer Integrity | Compromise | Reduces the protective mucous layer, increasing susceptibility to inflammation and damage. |
NSAIDs and IBD: Clinical Implications
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are frequently used for pain relief and inflammation management. However, for individuals with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), NSAID use can present unique challenges. This section delves into the clinical implications of NSAID use in IBD patients, exploring potential complications, management strategies, and the importance of careful monitoring.Understanding the clinical presentation of IBD patients using NSAIDs is crucial.
IBD, encompassing Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, involves chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. This inflammation can be exacerbated by NSAIDs, leading to various symptoms. The interplay between IBD and NSAID use requires careful consideration of individual patient needs and potential risks.
Clinical Presentation of IBD Patients Using NSAIDs
IBD patients using NSAIDs may experience a range of symptoms, including worsening abdominal pain, cramping, diarrhea, and bleeding. These symptoms can often mimic or exacerbate existing IBD symptoms, making diagnosis and management more complex. In some cases, patients may experience acute exacerbations of their IBD, requiring immediate medical intervention. The severity of these symptoms can vary significantly between individuals.
Common Side Effects of NSAID Use in IBD Patients
The use of NSAIDs in IBD patients can lead to a variety of side effects. These effects are often related to the direct impact of NSAIDs on the gastrointestinal tract, which is already inflamed in IBD. Gastrointestinal bleeding, ulcers, and perforation are significant concerns. Furthermore, NSAIDs can potentially worsen existing IBD symptoms, leading to a vicious cycle of inflammation and discomfort.
- Gastrointestinal bleeding: This is a serious concern, potentially requiring hospitalization and transfusions. A patient with Crohn’s disease experiencing significant bleeding while taking ibuprofen may need urgent intervention.
- Ulcers and erosions: NSAIDs can induce or worsen ulcers and erosions in the gastrointestinal tract, especially in individuals with existing IBD. This can result in significant pain and discomfort.
- Bowel perforation: In severe cases, NSAID use may lead to bowel perforation, requiring surgical intervention. This is a rare but life-threatening complication.
- Exacerbation of IBD symptoms: NSAIDs can exacerbate existing IBD symptoms, making them more frequent and severe. This can lead to a decline in the patient’s overall health and quality of life.
Management Strategies for NSAID-Related Complications in IBD
Effective management of NSAID-related complications in IBD patients requires a multi-faceted approach. Careful monitoring, prompt diagnosis, and appropriate treatment are essential. The strategy must prioritize the patient’s specific needs and the severity of their condition.
NSAIDs, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can sometimes be a tricky issue for people with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Understanding how your body responds to these medications is key. Finding the right balance, for instance, involves considering factors like the number of steps you take in a day, which can influence how your body processes these drugs. Knowing that a mile is roughly 2000 steps can help you understand how much activity you get throughout the day, potentially impacting your IBD management.
For a detailed calculation, check out this resource on how many steps in one mile. Ultimately, though, proper IBD management requires consulting with a doctor to determine the best course of action for your individual needs.
- Alternative pain management strategies: For patients experiencing IBD symptoms while using NSAIDs, alternative pain management strategies should be explored, such as acetaminophen or opioids, with careful consideration of potential side effects.
- Careful monitoring of IBD symptoms: Close monitoring of IBD symptoms is crucial to detect early signs of NSAID-related complications. This includes regular blood tests and endoscopic evaluations to track inflammation levels.
- Dietary modifications: Dietary changes may be beneficial in managing symptoms and preventing complications, especially in patients with ulcerative colitis.
- Medication adjustments: In some cases, reducing or discontinuing NSAID use may be necessary to prevent further complications. This should be done under the supervision of a gastroenterologist.
Importance of Careful Monitoring of IBD Patients Using NSAIDs
Close monitoring of IBD patients using NSAIDs is essential to detect and manage potential complications early. This involves regular check-ups, symptom assessments, and laboratory tests. Early intervention can significantly improve patient outcomes and prevent serious consequences.
Potential Risks Associated with Long-Term NSAID Use in IBD
Long-term NSAID use in IBD patients can pose significant risks. The continuous use of NSAIDs can contribute to the development of chronic complications and long-term gastrointestinal damage. It can also impact the overall health and well-being of the patient.
Summary Table: Common NSAID-Related Side Effects in IBD Patients
| Side Effect | Description | Potential Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal Bleeding | Internal bleeding from the GI tract | High |
| Ulcers and Erosions | Damage to the lining of the GI tract | Moderate to High |
| Bowel Perforation | Hole in the bowel wall | Critical |
| Exacerbation of IBD Symptoms | Increased inflammation and pain | Moderate to High |
Alternative Treatment Approaches
Navigating Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) often requires a multifaceted approach beyond NSAIDs. While NSAIDs can offer symptom relief, their potential side effects and limited long-term effectiveness necessitate exploration of alternative treatments. These alternative approaches can complement or even replace NSAIDs in managing IBD, tailoring treatment to individual needs and minimizing adverse reactions.Alternative therapies aim to reduce inflammation, improve gut health, and manage symptoms associated with IBD.
These therapies may be more suitable for some individuals, especially those with a history of NSAID intolerance or severe side effects. It’s crucial to remember that these therapies are not a replacement for conventional medical care and should always be discussed with a gastroenterologist or other qualified healthcare provider.
Dietary Modifications
Dietary modifications play a crucial role in managing IBD symptoms and potentially reducing the need for NSAIDs. A well-balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can support gut health. Avoiding trigger foods, such as processed foods, red meat, and dairy products, can also be beneficial. Specific dietary approaches, such as the low-FODMAP diet, may help reduce symptoms for some individuals.
However, it’s essential to consult with a registered dietitian to tailor a diet that meets individual needs and nutritional requirements.
Biologic Therapies
Biologic therapies represent a significant advancement in IBD treatment. These therapies target specific inflammatory pathways, offering more targeted and often more effective management of inflammation than NSAIDs. Examples include anti-TNF agents (such as infliximab and adalimumab), which reduce the production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, a key inflammatory mediator. These medications may be particularly beneficial for individuals with moderate to severe IBD who do not respond adequately to conventional treatments, including NSAIDs.The effectiveness of biologic therapies varies among individuals, and some may experience side effects.
Careful monitoring and potential adjustments to the treatment regimen are necessary.
Immunomodulators
Immunomodulators work by suppressing the immune system’s overactive response that contributes to inflammation in IBD. Examples include azathioprine and 6-mercaptopurine. These medications can be effective in managing IBD symptoms and potentially reducing reliance on NSAIDs. However, they may take several weeks or months to show their full effect, and long-term use is often necessary.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Complementary and alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, yoga, and meditation, may offer additional support for managing IBD symptoms. While not a substitute for conventional medical care, these therapies can contribute to stress reduction and overall well-being. However, it is crucial to emphasize that these therapies should be integrated into a comprehensive treatment plan and should not replace medical advice.
Personalized Treatment Strategies
The effectiveness of any treatment, including alternative therapies, can vary significantly among individuals with IBD. A personalized treatment strategy considers individual factors such as disease severity, location of the inflammation, and patient preferences. This approach involves close collaboration between the patient and their healthcare team to optimize treatment outcomes. The treatment plan should be regularly evaluated and adjusted as needed.
Dietary Modifications and NSAID Use, Nsaids non steroidal anti inflammatories and ibd
Dietary modifications can significantly impact the need for NSAIDs in IBD management. A well-balanced diet, rich in nutrients and low in potential triggers, can potentially reduce inflammation and minimize symptoms, potentially reducing the dosage or frequency of NSAID use. Conversely, a diet high in inflammatory foods could exacerbate symptoms and increase the need for NSAIDs.
Table Comparing NSAIDs and Alternative Treatments
| Treatment Approach | Effectiveness in IBD | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| NSAIDs | Variable, often short-term relief; can be effective for mild symptoms | Gastrointestinal ulcers, bleeding, kidney problems, cardiovascular risks |
| Biologic Therapies | Often more effective for moderate to severe IBD | Infection risk, allergic reactions, other immune-related side effects |
| Immunomodulators | Effective in some cases, but takes time to show effect | Immune suppression, potential liver problems |
| Dietary Modifications | Reduces symptoms and potentially reduces need for NSAIDs in some cases | Requires careful planning and adherence to a specific diet |
| Complementary/Alternative Therapies | May offer symptom relief and stress reduction | Limited scientific evidence for effectiveness; potential interactions with medications |
Future Research Directions
Unraveling the intricate relationship between non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) necessitates further investigation into the underlying mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies. Current knowledge, while substantial, still leaves gaps in our understanding, particularly regarding the specific pathways involved in NSAID-induced inflammation and the development of tailored treatment approaches. This exploration into future research directions aims to address these knowledge gaps.
Specific Mechanisms of NSAID-Induced Inflammation in IBD
A deeper understanding of the precise mechanisms by which NSAIDs trigger or exacerbate inflammation in IBD patients is crucial. Further research should focus on identifying the specific cellular and molecular pathways involved in this process. For example, studies should investigate the interaction of NSAIDs with various immune cells, such as macrophages and T cells, within the gut mucosa.
Investigating the role of oxidative stress and inflammation mediators like cytokines in the NSAID-IBD connection is also critical. Understanding how NSAID use impacts the gut microbiome composition and its subsequent influence on inflammation is another area demanding attention.
Novel Therapeutic Strategies to Mitigate Negative Effects
Developing novel therapeutic strategies to minimize the detrimental effects of NSAIDs on IBD is paramount. One potential area of investigation is the identification of specific biomarkers that can predict individual susceptibility to NSAID-induced IBD exacerbation. This predictive capability could allow for the tailoring of NSAID prescriptions to minimize risks. Exploring the potential of targeted therapies that modulate specific inflammatory pathways or counteract NSAIDs’ detrimental effects on the gut microbiome is also warranted.
Patient-Centered Research
Patient-centered research is essential to guide the development of effective and safe NSAID-related treatment strategies. This includes incorporating patient preferences and experiences into research protocols and clinical trials. Understanding the impact of NSAID use on patient quality of life and their daily activities is critical. Patients’ perspectives on the severity and frequency of side effects should be actively collected and analyzed.
This information can guide the development of more personalized treatment approaches and improve patient outcomes.
Key Research Questions and Areas Requiring Further Investigation
| Research Question | Specific Area of Investigation |
|---|---|
| What specific molecular pathways mediate NSAID-induced inflammation in IBD patients with different genetic backgrounds? | Investigating gene expression profiles and genetic variations associated with NSAID-induced inflammation in IBD subtypes. |
| How does NSAID use affect the gut microbiome composition and its interplay with the host immune response in IBD? | Utilizing advanced microbiome sequencing techniques to assess the impact of NSAIDs on the gut microbial community and its role in inflammation. |
| Can biomarkers be identified to predict individual susceptibility to NSAID-induced IBD exacerbation? | Developing and validating blood or stool-based biomarkers to identify patients at high risk of adverse events. |
| What are the optimal strategies to mitigate the detrimental effects of NSAIDs on IBD-related symptoms, such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fatigue? | Developing and evaluating the efficacy of novel therapies targeting inflammation mediators, intestinal barrier integrity, and gut microbiome dysbiosis. |
| How can patient-reported outcomes be incorporated into clinical trials to better understand the real-world impact of NSAIDs on IBD patients? | Designing clinical trials that actively solicit and incorporate patient perspectives on treatment efficacy and side effects. |
Case Studies and Illustrations
Understanding the complex interplay between non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) requires a nuanced approach, moving beyond theoretical discussions to examine real-world scenarios. This section delves into case studies, diagnostic procedures, management strategies, and visual representations to illuminate the relationship between NSAIDs and IBD.The following examples illustrate the potential for NSAIDs to exacerbate or trigger IBD symptoms, highlighting the importance of careful consideration and individualized treatment plans.
We will explore the diagnostic process, management strategies, and the impact on the gut visualized through imaging studies and biopsy analysis.
Illustrative Case Study of NSAID-Induced IBD Flare
A 45-year-old female with a history of ulcerative colitis (UC) presented with worsening abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, and fever. She had been taking ibuprofen for chronic back pain for the past six months. Her UC was well-controlled with mesalamine. The patient’s symptoms escalated rapidly, prompting a visit to the emergency room. The rapid onset of symptoms, coupled with her known history of UC and recent NSAID use, strongly suggested an NSAID-induced exacerbation.
The diagnosis was confirmed through a combination of clinical assessment, imaging, and biopsy analysis, which revealed increased inflammation in the colon.
Diagnostic Process for NSAID-IBD Interactions
The diagnosis of NSAID-induced IBD exacerbation relies on a combination of factors. A detailed medical history, including current medications, previous diagnoses, and symptom onset patterns, is crucial. Physical examination and laboratory tests (e.g., complete blood count, inflammatory markers) aid in assessing the patient’s overall health status and the severity of inflammation. Colonoscopy with biopsies is essential to visualize the colon’s lining and identify inflammatory changes.
Histological analysis of the biopsy specimens is vital to distinguish between NSAID-induced colitis and spontaneous IBD flares.
Management Flowchart for NSAID-IBD Patients
- Initial Assessment: Gather complete patient history, including NSAID use, IBD diagnosis, and current symptoms. Conduct physical examination and relevant laboratory tests.
- Diagnostic Procedures: Perform colonoscopy with biopsies for visual inspection and histological analysis. Consider imaging studies like CT scans or MRI for evaluating the extent of inflammation.
- Treatment Plan: Discontinue or carefully evaluate NSAID use, considering the severity of the IBD flare and the patient’s overall health. Initiate appropriate IBD treatment based on the severity of the flare, which may include corticosteroids, immunomodulators, or biologics.
- Monitoring and Follow-up: Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to assess treatment effectiveness, monitor for complications, and adjust the treatment plan as needed. Close monitoring of inflammatory markers, symptoms, and imaging results is essential.
Imaging Studies for Visualizing Gut Effects
Imaging plays a significant role in evaluating the extent and severity of inflammation in the gut. Colonoscopy, a direct visualization technique, allows for assessment of the colon’s lining and identification of mucosal lesions, ulcers, and inflammatory changes. CT scans and MRI provide cross-sectional views of the abdomen, aiding in assessing the extent of inflammation, the presence of abscesses, or complications like bowel wall thickening.
These imaging modalities can be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment over time.
Significance of Illustrative Examples
These case studies and diagnostic procedures emphasize the importance of recognizing the potential for NSAID-induced IBD flares. A thorough understanding of the diagnostic process and appropriate management strategies is crucial to prevent further complications and ensure optimal patient outcomes. The significance lies in preventing misdiagnosis and providing tailored treatment plans to avoid exacerbating existing IBD.
Inflammatory Processes in Colon Biopsies
Microscopic analysis of colon biopsies provides valuable insights into the inflammatory processes occurring within the gut. In patients with IBD, biopsies show characteristic features like crypt abscesses, inflammation of the lamina propria, and inflammatory cell infiltration. In cases where NSAIDs trigger an exacerbation, the inflammatory changes are often more pronounced and potentially widespread, as seen in increased crypt damage and cellular infiltration.
The intensity and distribution of these inflammatory processes can be observed and compared between biopsies taken with and without NSAID use, to determine the potential role of NSAIDs in the progression of IBD. This visual comparison provides strong evidence of the inflammatory effects of NSAIDs on the gut.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, the interaction between NSAIDs and IBD is multifaceted and complex. Careful monitoring and personalized treatment strategies are essential for managing IBD patients who require NSAIDs. Alternative treatments and ongoing research offer promising avenues for improving outcomes. Ultimately, a comprehensive understanding of this intricate relationship is paramount to optimizing patient care and improving quality of life.




