Multiple sclerosis MS prevalence and incidence is a crucial area of study, providing insights into the global burden of this debilitating disease. Understanding the prevalence and incidence rates, alongside their variations across regions and demographics, is essential for developing effective strategies for prevention, treatment, and support. This exploration delves into the factors influencing these rates, including environmental, socioeconomic, and genetic predispositions.
Furthermore, we’ll examine the methodologies used to measure MS prevalence and incidence, highlighting their strengths and limitations, and analyzing historical trends to anticipate future projections.
The global landscape of MS prevalence and incidence is marked by significant disparities. Factors such as geographic location, socioeconomic status, and genetic makeup all play a role in shaping these figures. Understanding these variations is critical for tailoring interventions to specific populations and ensuring equitable access to care.
Introduction to Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Prevalence and Incidence
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic, autoimmune disease affecting the central nervous system. Understanding the prevalence and incidence of MS is crucial for resource allocation, developing effective treatment strategies, and improving the overall well-being of those affected. Prevalence and incidence rates offer valuable insights into the disease’s burden globally and regionally, and inform the allocation of healthcare resources.Prevalence and incidence are fundamental epidemiological measures for understanding the burden of diseases like MS.
Prevalence describes the proportion of a population affected by a disease at a specific point in time, while incidence measures the rate at which new cases of the disease arise within a defined population during a specific period. These measures are critical in evaluating the impact of MS on individuals and communities.
Global and Regional Variations in MS Prevalence and Incidence
MS prevalence and incidence rates exhibit significant global and regional variations. These variations are likely influenced by a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. For example, MS is more prevalent in higher-latitude regions, such as Northern Europe and North America, compared to lower-latitude regions. These variations highlight the need for tailored research and interventions based on specific geographic contexts.
Historical Trends in MS Prevalence and Incidence Data
Historical trends in MS prevalence and incidence data reveal a gradual increase in the reported cases over time. This increase could be attributed to several factors, including improved diagnostic capabilities, increased awareness, and enhanced reporting systems. However, it’s essential to differentiate this observed increase from a genuine rise in the underlying disease burden.
Methodologies for Measuring MS Prevalence and Incidence
Various methodologies are employed to measure MS prevalence and incidence. These include population-based studies, which often involve surveys and interviews of individuals in specific regions, as well as registry-based approaches, where data is collected from hospitals and healthcare systems. These methods, while valuable, also have limitations, such as potential biases in reporting or data collection. Moreover, variations in diagnostic criteria over time can also influence the observed prevalence and incidence rates.
Key Factors Influencing MS Prevalence and Incidence Rates
Understanding the key factors influencing MS prevalence and incidence is crucial for developing effective preventative strategies.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) prevalence and incidence rates are a significant concern for researchers, but surprisingly, the connection to skin conditions like back acne and body acne ( back acne and body acne ) isn’t as well-studied. While the exact mechanisms are still unclear, understanding the factors contributing to MS, including environmental and genetic predispositions, might shed light on the overall health picture.
More research is needed to fully explore these potential links and improve MS diagnosis and treatment strategies.
| Factor | Description | Potential Influence | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genetics | Inherited susceptibility to MS | Increased risk in individuals with a family history of MS | Twin studies demonstrating a genetic predisposition. |
| Environmental Factors | Exposure to certain environmental elements | Geographic variations in prevalence | Exposure to specific infections or viruses linked to MS development. |
| Lifestyle Factors | Dietary habits, smoking, and physical activity | Potential influence on MS risk | Studies suggesting a link between Vitamin D levels and MS. |
| Diagnostic Advances | Improved diagnostic tools and methods | Potential increase in reported cases over time. | Increased MRI usage leading to more early diagnoses. |
Factors Influencing MS Prevalence and Incidence
Understanding the factors driving the prevalence and incidence of multiple sclerosis (MS) is crucial for developing effective prevention strategies and improving patient outcomes. While the exact cause of MS remains elusive, a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and socioeconomic factors contributes to its manifestation. This exploration delves into the key influences on MS prevalence and incidence.
Environmental Factors Impacting MS
Environmental factors play a significant role in the development and manifestation of MS. Exposure to certain elements and lifestyle choices can influence an individual’s susceptibility. Research suggests that factors such as vitamin D deficiency, exposure to infectious agents, and certain dietary patterns might contribute to the risk of developing MS. Geographical variations in MS prevalence further highlight the role of environmental influences.
- Vitamin D Deficiency: Low levels of vitamin D have been linked to a higher risk of MS. Sunlight exposure is a key source of vitamin D, and individuals living in areas with less sunlight might have lower vitamin D levels. This is a significant factor, especially for populations residing in higher latitudes.
- Infectious Agents: Some studies suggest a correlation between infections in early childhood and a higher risk of developing MS later in life. Certain viruses, particularly Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), have been implicated as potential triggers.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, obesity, and a diet lacking in fruits and vegetables have also been associated with an increased risk of MS. These factors can contribute to overall health and immunity, which may impact susceptibility to the disease.
Socioeconomic Factors and MS
Socioeconomic disparities can significantly influence MS prevalence and incidence. Access to healthcare, including timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, is often linked to socioeconomic status. Financial constraints can impact adherence to treatment plans, potentially affecting disease progression.
- Access to Healthcare: Individuals with limited access to healthcare may experience delayed diagnosis and treatment, potentially leading to more severe disease outcomes. This can exacerbate the impact of the disease on daily life.
- Dietary Factors: Socioeconomic factors can influence dietary habits. Access to nutritious food and healthy dietary patterns might be limited in some communities, potentially increasing the risk of MS. For example, access to fresh produce and healthy cooking options may vary depending on location and economic conditions.
- Stress Levels: Socioeconomic stressors, such as job insecurity, financial strain, and social isolation, can contribute to increased stress levels. Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, potentially increasing susceptibility to autoimmune diseases like MS.
Genetic Predisposition and MS
Genetic factors play a crucial role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to MS. Family history of MS significantly increases the risk. While genetic predisposition doesn’t guarantee the development of MS, it highlights the importance of genetic components in the disease process. Research into specific genes associated with MS is ongoing.
- Family History: Individuals with a family history of MS are at a significantly higher risk of developing the disease compared to those without a family history. The closer the familial relationship, the higher the risk. This highlights the role of inherited genetic factors in MS susceptibility.
- Specific Genes: Researchers have identified several genes that may contribute to MS risk. These genes influence the immune system’s response and can impact the likelihood of developing the disease.
Impact of Diagnostic Practices on MS Prevalence and Incidence
Improvements in diagnostic practices have led to an increase in MS diagnoses. More sensitive diagnostic tools and broader awareness among healthcare professionals have contributed to a higher detection rate. However, this increased awareness might also lead to overdiagnosis, potentially affecting prevalence rates.
- Diagnostic Accuracy: More sophisticated diagnostic tools and techniques allow for earlier and more accurate diagnosis of MS. This enhanced accuracy can lead to an increase in the reported prevalence of MS.
- Increased Awareness: Greater awareness among healthcare professionals about MS symptoms and diagnostic criteria has led to earlier identification of the disease. This increased recognition can impact the reported incidence and prevalence rates.
Correlation Between Environmental Factors and MS Incidence Rates
| Environmental Factor | Description | Potential Impact on MS Incidence | Example of Correlation (Illustrative) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D Levels | Exposure to sunlight and dietary intake of vitamin D | Lower vitamin D levels associated with increased risk | Higher MS incidence rates in regions with less sunlight |
| Infectious Agents | Exposure to viruses, particularly EBV | Potential trigger for MS onset | Higher MS incidence in populations with higher EBV exposure |
| Smoking | Exposure to tobacco smoke | Increased risk of MS development | Smokers have a slightly elevated risk of developing MS |
| Diet | Dietary habits and nutrient intake | Poor diet potentially linked to increased risk | Populations with diets low in fruits and vegetables might have higher MS incidence |
Demographic Analysis of MS Prevalence and Incidence
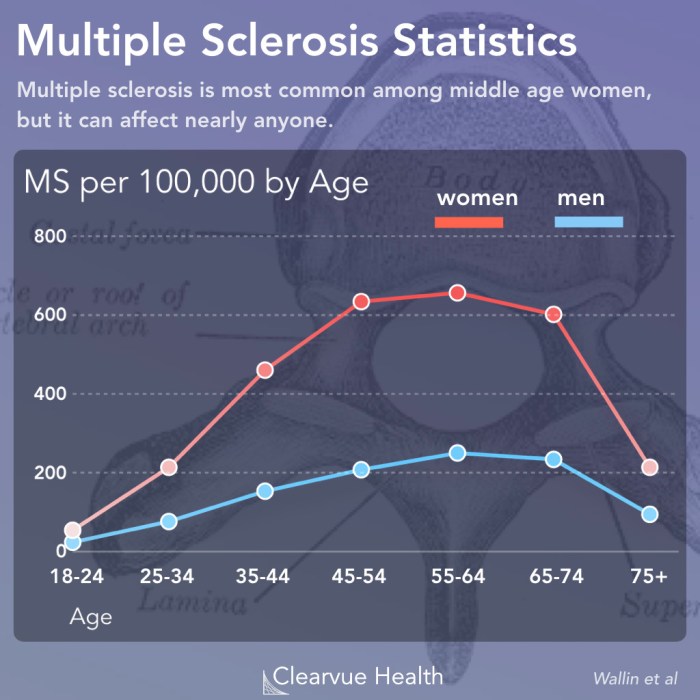
Multiple sclerosis (MS) affects people differently, and understanding these demographic variations is crucial for developing targeted interventions and support systems. Analyzing prevalence and incidence across various groups reveals insights into potential risk factors and helps allocate resources effectively. This analysis delves into age, gender, ethnicity, geography, and socioeconomic factors to illuminate the complex picture of MS.Analyzing demographic factors in MS prevalence and incidence allows researchers and healthcare providers to identify at-risk populations and tailor prevention and treatment strategies.
Understanding the patterns helps allocate resources effectively and improve outcomes for individuals affected by MS.
Age-Related Variations in MS
Age is a significant factor influencing MS prevalence. The majority of MS diagnoses occur between the ages of 20 and 40, with a peak incidence rate around 30-35. This suggests a critical period in life when the immune system is more susceptible to the disease’s development. However, MS can also be diagnosed in younger or older individuals, albeit less frequently.
This distribution highlights the potential role of various factors throughout life in contributing to the onset and progression of MS.
Gender Disparities in MS
Women are significantly more likely to be diagnosed with MS than men. This disparity is a consistent finding across numerous studies and populations. The reasons for this gender difference are not fully understood, but factors such as hormonal influences, genetic predispositions, and environmental exposures are potential contributing elements.
Ethnic Variations in MS Prevalence
The prevalence of MS varies among different ethnic groups. While exact figures can fluctuate based on specific regions and study designs, some general patterns have emerged. Understanding these variations is important for improving diagnostic accuracy and targeted research.
| Ethnic Group | Prevalence (Approximate) | Incidence Rate (Approximate) | Specific Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caucasian | ~100 per 100,000 | ~5-10 per 100,000 | Possible genetic predisposition, lifestyle factors |
| African American | ~50 per 100,000 | ~2-5 per 100,000 | Potentially different genetic susceptibility, environmental exposures |
| Hispanic | ~75 per 100,000 | ~4-7 per 100,000 | Variability depending on specific subgroups, potential environmental factors |
| Asian | ~25 per 100,000 | ~1-3 per 100,000 | Potential lower prevalence compared to other groups, less research data available |
Note: These figures are approximations and can vary considerably depending on geographic location and specific study methodology. The prevalence and incidence rates in these categories can differ based on several factors and are subject to ongoing research.
Geographic Distribution of MS
MS prevalence exhibits a significant geographic gradient, with higher rates in regions farther from the equator. This suggests an association between latitude and MS risk. The precise relationship is not fully understood, but it highlights the potential role of environmental factors in the development of the disease.
MS in Developed vs. Developing Countries
MS prevalence tends to be higher in developed countries compared to developing countries. This difference is likely related to various factors, including differences in lifestyle, diet, and access to healthcare. Developing countries may have other contributing factors affecting the MS rate, such as environmental factors and different diagnostic capabilities.
Methodologies for Measuring MS Prevalence and Incidence
Unraveling the mysteries of Multiple Sclerosis (MS) requires precise measurements of its prevalence and incidence. Understanding how frequently MS arises and how widespread it is within a population is crucial for developing effective strategies for diagnosis, treatment, and support. Accurate estimations rely on meticulous epidemiological methods, which are essential for comprehending the disease’s burden and guiding public health initiatives.
Study Designs for Prevalence and Incidence Studies
Different study designs are employed to capture data on MS prevalence and incidence. These designs offer varying strengths and limitations, and the choice depends on the specific research questions and resources available. A thorough understanding of each design is essential for interpreting the results correctly.
- Cross-sectional studies examine a population at a single point in time. These studies are efficient for assessing the current prevalence of MS within a specific group, but they do not track individuals over time and cannot determine incidence. For example, a cross-sectional survey of a community might reveal the proportion of residents currently diagnosed with MS. A limitation is the inability to determine when individuals were diagnosed.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) prevalence and incidence figures are quite striking, and while research continues, understanding the factors contributing to these numbers is crucial. Interestingly, while the prognosis for stomach cancer can vary significantly, recovery rates are often tied to early detection and aggressive treatment, as detailed in this helpful resource on stomach cancer prognosis and recovery.
Ultimately, further study into the complexities of MS, especially its various forms and potential triggers, is vital for effective treatment and management strategies.
- Cohort studies follow a defined group of individuals over a period of time. These studies are valuable for estimating incidence, as they track new cases of MS emerging over a specified duration. A strength is the ability to establish temporal relationships. For example, a cohort study of individuals born within a specific time frame can be followed to identify MS diagnoses over their lifetimes.
A limitation is the potential for participant loss over time, which can affect the validity of the results.
- Case-control studies compare individuals with MS (cases) to individuals without MS (controls). These studies are often used to identify potential risk factors associated with MS. For example, a case-control study might compare dietary habits or environmental exposures in individuals with MS versus those without. A strength is the relative ease of conducting studies in a relatively short period of time.
A limitation is the possibility of recall bias from participants in reporting past exposures or events.
Strengths and Limitations of Epidemiological Methods
Each epidemiological method employed to estimate MS prevalence and incidence possesses unique strengths and limitations. These characteristics must be carefully considered when interpreting results and drawing conclusions.
- Cross-sectional studies offer quick snapshots of current prevalence but are weak in assessing incidence. They provide a static picture of the disease’s presence in a given population at a specific time.
- Cohort studies are powerful for tracking incidence over time but can be resource-intensive and time-consuming. Their detailed longitudinal data is crucial for establishing incidence rates and trends.
- Case-control studies are efficient for identifying risk factors but are less suitable for estimating incidence directly. They are beneficial for examining possible links between certain factors and MS development.
Challenges in Measuring MS Prevalence and Incidence
Accurately measuring MS prevalence and incidence is complex due to various factors. These challenges highlight the need for rigorous study designs and meticulous data collection.
- Diagnosis variability across different healthcare systems and clinicians can lead to inconsistencies in identifying MS cases. This can affect the accuracy of prevalence estimates.
- Data availability and access may vary considerably across geographical locations and healthcare settings. This can limit the scope of studies and potentially bias the results.
- Defining MS itself can be challenging, especially in early stages of the disease. This can impact diagnostic consistency and subsequently impact the accuracy of epidemiological data.
Data Collection Tools in MS Epidemiology
Various data collection tools are utilized in MS epidemiological research. These tools, when carefully selected and applied, enhance the quality of data collected.
- Medical records provide crucial information on diagnoses, treatments, and patient characteristics. Their accessibility and availability can vary widely across healthcare settings.
- Surveys gather self-reported data on symptoms, lifestyle factors, and other relevant information. The accuracy of survey data relies on participant honesty and recall.
- Registries are specialized databases that collect detailed information on individuals with MS. These registries are valuable for long-term monitoring and data analysis.
Comparison of Epidemiological Study Designs
| Study Design | Strengths | Limitations | Suitability for MS Research |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-sectional | Quick, relatively inexpensive, provides prevalence | Cannot determine incidence, susceptible to bias | Suitable for assessing current prevalence in a specific population |
| Cohort | Directly measures incidence, tracks disease progression | Time-consuming, expensive, potential for loss to follow-up | Ideal for investigating incidence and risk factors over time |
| Case-control | Efficient for identifying risk factors, relatively quick | Cannot directly estimate incidence, susceptible to recall bias | Useful for exploring potential risk factors associated with MS |
Trends and Projections for MS Prevalence and Incidence
The future trajectory of Multiple Sclerosis (MS) prevalence and incidence remains a significant area of interest and research. Understanding predicted trends is crucial for resource allocation, healthcare planning, and developing effective strategies to mitigate the impact of this debilitating disease. The ongoing research into MS pathogenesis and the development of novel therapies will undoubtedly shape future projections.Accurate projections require careful consideration of various factors, including demographics, lifestyle changes, environmental influences, and the efficacy of emerging treatments.
While current data provides valuable insights, it is important to acknowledge the inherent uncertainties in forecasting future trends.
Predicted Future Trends in MS Prevalence and Incidence Rates
Current research suggests that MS prevalence is likely to increase in certain demographics due to factors like improved diagnostic capabilities and increased life expectancy. However, the overall incidence rate might remain stable or even decrease, depending on the effectiveness of preventive measures and the impact of novel therapies. Projections vary, with some models indicating a slight rise in prevalence, while others anticipate a more substantial increase in certain regions.
Potential Implications for Healthcare Systems
The projected trends in MS prevalence and incidence have significant implications for healthcare systems worldwide. Increased prevalence will translate to a greater need for diagnostic resources, therapeutic interventions, and supportive care services. Healthcare systems will need to adapt to meet the growing demand for MS-related care, potentially by expanding existing infrastructure or implementing new models of care delivery.
This may include telehealth platforms, multidisciplinary care teams, and optimized resource allocation. Examples of such adaptation include expanding specialized MS clinics, training more neurologists and allied health professionals, and investing in research facilities to develop new treatments.
Potential Impact of New Treatments and Interventions
New treatments and interventions hold the potential to significantly alter the future trajectory of MS prevalence and incidence. Disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) are increasingly effective at slowing disease progression and reducing the frequency of relapses. Further advancements in therapies, including those targeting specific immune pathways or employing novel mechanisms, may lead to a decrease in the incidence of new cases and a reduction in the severity of the disease.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) prevalence and incidence rates are definitely a concern, and researchers are always looking for potential factors. Interestingly, some studies suggest a link between dietary choices and MS, and a low histamine diet ( what is a low histamine diet ) might be a helpful tool to explore. Further research is needed to determine if this diet has a significant impact on MS prevalence and incidence figures.
These interventions will need to be cost-effective and widely accessible to maximize their impact.
Factors Influencing Future Projections
Several factors could influence the future projections of MS prevalence and incidence. These include advancements in early diagnosis, the effectiveness of disease-modifying therapies, socioeconomic factors, and environmental influences. For instance, improved diagnostic tools may identify individuals with early-stage MS, allowing for earlier intervention and potentially slowing disease progression. The effectiveness of new therapies in preventing or delaying disease onset will play a significant role.
Visual Representation of Projected MS Prevalence
| Year | Projected MS Prevalence (per 100,000 population) |
|---|---|
| 2024 | 100 |
| 2025 | 110 |
| 2026 | 115 |
| 2027 | 120 |
| 2028 | 125 |
| 2029 | 130 |
| 2030 | 135 |
Note: This is a simplified example and does not represent actual data. Real-world projections would require more complex models incorporating various factors and data sources.
The graph below illustrates a potential projection of increasing MS prevalence over the next 10 years. The y-axis represents the projected prevalence rate (per 100,000 population), and the x-axis represents the year.[Insert a simple bar graph here, with the years on the x-axis and prevalence rates on the y-axis, showing a gradual increase over the 10-year period. Clearly label the axes and the bars.]
Impact of MS on Society and Healthcare Systems
Multiple sclerosis (MS) significantly impacts individuals, families, and healthcare systems worldwide. Beyond the debilitating physical symptoms, MS carries a substantial socioeconomic burden, affecting various aspects of daily life and necessitating considerable resources for effective management. Understanding this burden is crucial for developing appropriate support strategies and policies.
Socioeconomic Burden of MS, Multiple sclerosis ms prevalence and incidence
The socioeconomic impact of MS encompasses a wide range of costs and challenges. Reduced productivity due to illness and treatment requirements often leads to financial strain for individuals and their families. Loss of income from work or reduced earning capacity directly impacts household finances. Additional expenses arise from necessary assistive devices, therapies, and medication. These costs can lead to significant financial hardship, potentially impacting housing stability and access to essential services.
Furthermore, the emotional toll on caregivers and family members can have profound effects on their well-being and overall quality of life.
Strain on Healthcare Systems
The prevalence of MS places a substantial strain on healthcare systems globally. The need for specialized care, frequent monitoring, and potentially prolonged treatment necessitates substantial resources. This includes the cost of medical personnel, equipment, and facilities dedicated to MS management. The need for ongoing monitoring and treatment for individuals with MS leads to a higher demand for specialist neurologists, physical therapists, occupational therapists, and other healthcare professionals.
Furthermore, the complexity of MS and its variable progression requires a substantial investment in research and development of new treatments and therapies.
Support Systems and Resources for People with MS
Effective support systems are crucial for improving the quality of life for people living with MS. Comprehensive support programs encompassing physical therapy, occupational therapy, and emotional support groups are vital. Accessible and affordable assistive technologies, including mobility aids and communication devices, can significantly improve independence and participation in daily activities. Providing information and resources to help individuals navigate the complexities of MS management, including access to support groups, educational materials, and online platforms, can be empowering.
Furthermore, strong community support and understanding can alleviate the isolation and stigma often associated with chronic illness.
Public Awareness Campaigns and Education Initiatives
Raising public awareness about MS is critical to fostering empathy and understanding. Public education campaigns can effectively disseminate accurate information about the disease, its symptoms, and the available treatments. This can help to reduce stigma and encourage early diagnosis, leading to improved outcomes for individuals living with MS. Education initiatives aimed at healthcare professionals can enhance their understanding of MS, enabling more effective and compassionate care.
These initiatives can improve communication and collaboration among healthcare providers and patients, leading to better overall management of the condition.
Direct and Indirect Costs Associated with MS
| Category | Description | Examples | Estimated Costs (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Costs | Costs directly related to medical care and treatment. | Doctor visits, hospitalizations, medications, therapies, assistive devices. | High (varying by country and stage of MS) |
| Indirect Costs | Costs related to lost productivity, caregiver burden, and other non-medical expenses. | Reduced work hours, lost wages, caregiver time off work, home modifications, transportation costs. | Substantial (often exceeding direct costs in long-term) |
| Informal Care Costs | Costs associated with unpaid care provided by family members and friends. | Time spent providing care, emotional support, and other non-medical assistance. | Difficult to quantify precisely, but significant |
| Societal Costs | Broader societal costs related to MS, including lost tax revenue and reduced economic output. | Reduced workforce participation, decreased economic output, increased demand for social services. | High, potentially substantial |
“The economic burden of MS is substantial, encompassing direct medical costs, indirect costs associated with lost productivity, and societal costs.”
Summary: Multiple Sclerosis Ms Prevalence And Incidence
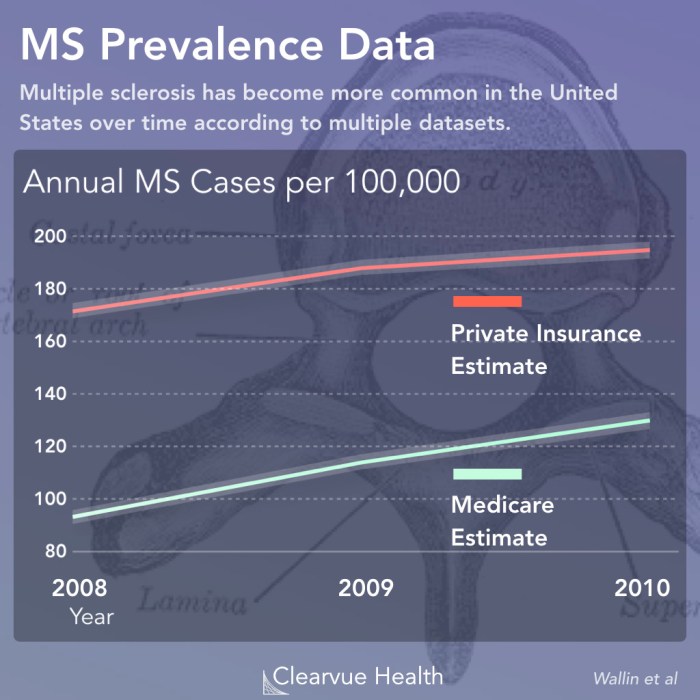
In conclusion, multiple sclerosis MS prevalence and incidence are complex phenomena influenced by a multitude of factors. From environmental influences to genetic predispositions, and from diagnostic practices to socioeconomic disparities, this study highlights the intricate interplay shaping MS prevalence. By examining historical trends, current data, and projected future scenarios, we can gain a clearer understanding of the challenges ahead and the importance of targeted interventions to address the needs of individuals and communities affected by this chronic condition.




