Intramuscular injections progesterone oil offer a unique approach to hormone therapy, but understanding the intricacies is key. This exploration delves into the various aspects, from different formulations and administration routes to potential side effects and patient considerations. We’ll cover everything from the mechanisms of action to the crucial role of patient education and clinical monitoring.
Progesterone, a vital hormone, plays a crucial role in many bodily functions. Intramuscular injections of progesterone oil are a common method for administering this hormone, offering a sustained release. Different formulations exist, each with varying characteristics, influencing dosage regimens and potential side effects. Understanding these differences is essential for safe and effective treatment.
Intramuscular Progesterone Oil Injections
Intramuscular progesterone oil injections are a common method for administering progesterone, a crucial hormone for various physiological functions, particularly in reproductive health. These injections offer a sustained release of progesterone, providing a consistent hormone level over a period of time compared to other administration methods. Understanding the different formulations, routes, and dosage regimens is essential for safe and effective use.Intramuscular progesterone oil injections are frequently utilized in various medical scenarios.
For example, they are commonly employed in managing certain gynecological conditions, supporting fertility treatments, and in hormone replacement therapy. Proper administration and monitoring are crucial for optimal patient outcomes.
Progesterone Oil Formulations
Different progesterone oil formulations vary in their chemical composition and concentration. These differences affect the release rate and duration of action of the hormone. Some formulations use esters to modify the progesterone molecule, impacting its absorption and elimination rate in the body.
- Progesterone in oil: This formulation is a simple solution of progesterone in a suitable oil base. It typically offers a more gradual release of progesterone compared to other formulations.
- Progesterone esters: Progesterone esters, such as progesterone caproate, are frequently used. They are more potent, providing a longer duration of action than the base progesterone, but require careful monitoring of dosage.
Routes of Administration
The primary route of administration for intramuscular progesterone oil injections is the deep intramuscular route. This method ensures that the medication is injected into the muscle tissue, minimizing the risk of complications like pain or tissue damage at the injection site. The specific muscle chosen for injection (e.g., gluteus maximus, vastus lateralis) should be considered to avoid nerve or vascular damage.
Dosage Regimens
Dosage regimens for intramuscular progesterone oil injections are highly variable, depending on several factors. Factors influencing the dosage include the patient’s age, weight, medical history, the specific condition being treated, and the formulation of progesterone used.
- Initial dosage: The initial dosage is typically determined by a healthcare professional based on the individual patient’s needs and the severity of the condition being treated.
- Maintenance dosage: Maintenance dosage adjustments are made based on ongoing monitoring of the patient’s hormone levels and response to the treatment. Blood tests may be required to evaluate hormone levels and adjust the dosage accordingly.
- Factors influencing adjustments: Factors such as patient response, side effects, and changes in the underlying medical condition can necessitate dosage adjustments. Regular monitoring and communication between the patient and healthcare provider are vital.
Factors Influencing Dosage Adjustments
Several factors can influence the need for dosage adjustments in intramuscular progesterone oil injections. The patient’s response to the medication, any side effects experienced, and changes in the underlying medical condition are all key considerations. Healthcare professionals use these factors to make informed decisions regarding dosage modifications.
- Patient response: The patient’s response to the initial dosage is monitored closely. This includes tracking hormone levels, symptom improvement, and overall well-being.
- Side effects: Any side effects, such as pain, swelling, or tenderness at the injection site, are assessed and addressed appropriately. This may lead to dosage adjustments or changes in the injection site.
- Underlying conditions: Any changes in the underlying medical condition that may impact progesterone metabolism or require dosage adjustments should be promptly addressed by the healthcare provider.
Mechanisms of Action
Intramuscular progesterone oil injections exert their effects through a complex interplay of physiological mechanisms. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for appreciating the therapeutic potential and potential side effects of this hormone therapy. Progesterone, a crucial steroid hormone, plays a vital role in various bodily functions, impacting everything from menstrual cycles to pregnancy maintenance.Progesterone’s actions are not solely limited to a single target; rather, they are multifaceted and involve interactions with multiple hormone pathways and cellular processes.
The intramuscular route of administration ensures a sustained release of progesterone into the bloodstream, allowing for a prolonged effect compared to other administration methods. This sustained release is key to achieving the desired therapeutic outcomes.
Impact on Hormone Levels and Interactions
Progesterone influences a multitude of hormones within the body. Its primary action is to modulate the levels of other hormones, such as estrogen, luteinizing hormone (LH), and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). These hormonal interactions are critical for regulating various physiological processes, including reproduction and metabolism. For example, during pregnancy, progesterone plays a pivotal role in maintaining the pregnancy by suppressing the release of LH and FSH, preventing further ovulation and supporting the uterine lining.
This intricate interplay between hormones ensures a stable hormonal environment necessary for fetal development.
Effects on Target Tissues and Organs
Progesterone’s effects vary significantly depending on the target tissue or organ. In the reproductive system, progesterone is crucial for maintaining the uterine lining during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle and for supporting pregnancy. In the breast tissue, progesterone contributes to the development of the mammary glands, preparing them for lactation. Conversely, in the brain, progesterone affects mood regulation and sleep patterns, influencing cognitive function.
Influence on Cellular Processes and Functions, Intramuscular injections progesterone oil
Progesterone’s impact extends to the cellular level. It acts by binding to specific progesterone receptors (PRs) within target cells. This binding triggers a cascade of intracellular signaling events, leading to the modulation of gene expression. These cellular responses are crucial for regulating diverse physiological processes. For example, progesterone can induce the expression of proteins involved in cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis (programmed cell death).
This intricate regulation of cellular functions is essential for maintaining homeostasis and coordinating bodily responses.
Indications and Applications
Intramuscular progesterone oil injections offer a targeted delivery method for supplementing or managing progesterone levels in various medical conditions. Understanding the specific indications and applications is crucial for appropriate patient selection and treatment success. The benefits of this method, coupled with the potential for targeted action, make it a valuable tool in the arsenal of reproductive and hormonal therapies.This section details the diverse medical conditions where intramuscular progesterone oil injections are employed.
It will Artikel the clinical indications, expected outcomes, and highlight successful treatment examples. Careful consideration of these factors is essential for practitioners when determining the suitability of this treatment approach for individual patients.
Intramuscular injections of progesterone oil can be a crucial part of fertility treatments, but understanding how to deliver a baby how to deliver a baby is equally important. Ultimately, the success of these injections often depends on a healthy pregnancy, which is directly related to the overall process of childbirth. Proper medical guidance and support are key, and ongoing monitoring throughout the pregnancy is essential to ensure optimal outcomes for both the mother and the baby.
These injections are just one piece of the puzzle, but they are an important one.
Common Medical Conditions Treated
Intramuscular progesterone oil injections are commonly used in various medical conditions related to hormonal imbalances, particularly those affecting reproductive health. These injections are often employed to address specific symptoms and support the body’s natural processes.
- Infertility: Progesterone plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy uterine environment for embryo implantation. In cases of irregular or insufficient progesterone production, intramuscular injections can provide a supplemental dose, potentially improving the likelihood of conception.
- Amenorrhea: This condition, characterized by the absence of menstruation, can sometimes be linked to hormonal imbalances. Progesterone injections can be used to restore the cyclical hormonal pattern and induce menstruation. This can be especially helpful in women experiencing irregular cycles or those undergoing fertility treatments.
- Habitual Abortion: For women experiencing recurrent miscarriages, intramuscular progesterone oil injections can be used to maintain a supportive uterine environment during pregnancy. This helps to stabilize the hormonal balance and reduce the risk of further pregnancy loss.
- Premature Labor: In cases of threatened or preterm labor, progesterone injections can help to maintain pregnancy by supporting the uterine lining and stabilizing the hormonal environment.
- Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding: Progesterone supplementation can help regulate the uterine lining, potentially reducing the frequency and severity of heavy or irregular bleeding.
Clinical Indications
Specific clinical indications for intramuscular progesterone oil injections will depend on the underlying cause of the hormonal imbalance and the patient’s overall health status. A thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional is essential to determine the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment.
- Hormonal Imbalance Diagnosis: Before initiating treatment, a comprehensive hormonal evaluation is crucial to identify the specific hormonal deficiency or imbalance contributing to the presenting symptoms.
- Patient History Assessment: Detailed patient history, including medical history, reproductive history, and any current medications, helps determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
- Monitoring and Adjustment: Regular monitoring of hormone levels and clinical response is essential to adjust treatment regimens as needed to optimize effectiveness and minimize potential side effects.
Potential Benefits and Outcomes
Intramuscular progesterone oil injections offer several potential benefits and expected outcomes for patients, particularly in reproductive health management.
- Improved Pregnancy Rates: In cases of infertility or recurrent miscarriage, progesterone supplementation can improve the likelihood of successful pregnancy by maintaining a supportive uterine environment.
- Reduced Risk of Preterm Labor: Progesterone injections may help stabilize the hormonal environment, potentially reducing the risk of premature labor and improving pregnancy outcomes.
- Regulation of Menstrual Cycles: In cases of amenorrhea or irregular periods, progesterone injections can restore normal cyclical hormonal patterns and induce regular menstruation.
Successful Treatment Examples
Numerous case studies and clinical trials have documented successful treatment outcomes using intramuscular progesterone oil injections. These examples illustrate the potential for positive outcomes in carefully selected patients.
“A study published in the journal Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology demonstrated a significant increase in live birth rates among women with recurrent miscarriages who received progesterone supplementation.”
Preparation and Administration
Intramuscular progesterone oil injections offer a way to deliver progesterone directly into the muscle tissue, ensuring consistent hormone levels. Proper preparation and administration are crucial to achieving the desired therapeutic effect while minimizing potential risks. This section delves into the specifics of preparing and administering these injections, focusing on safety and efficacy.
Equipment and Materials
A sterile environment is paramount for intramuscular injections. The necessary equipment includes a sterile syringe, a vial of progesterone oil, a sterile alcohol swab, a needle with the appropriate gauge and length, and a sharps container. Ensure all materials are sterile and properly labeled. Using aseptic techniques is vital to prevent contamination. Additionally, a clean, well-lit workspace is essential.
Preparation Steps
To prepare the injection, first, gather all necessary materials. Clean the vial’s rubber stopper with an alcohol swab. Withdraw the correct dosage of progesterone oil using a sterile syringe. Verify the dosage against the prescribed amount and the vial label. Discard any unused portion of the injection.
Attach the needle to the syringe, ensuring a secure connection. The needle should be properly sized and appropriate for the injection site.
Administration Procedure
Proper site selection and technique are critical for safe injection. Choose a site that’s well-vascularized but avoids areas with nerves or blood vessels. The vastus lateralis muscle in the outer thigh is a common and safe site. Ensure the patient is comfortable and positioned appropriately. Clean the injection site with an alcohol swab and allow it to air dry completely.
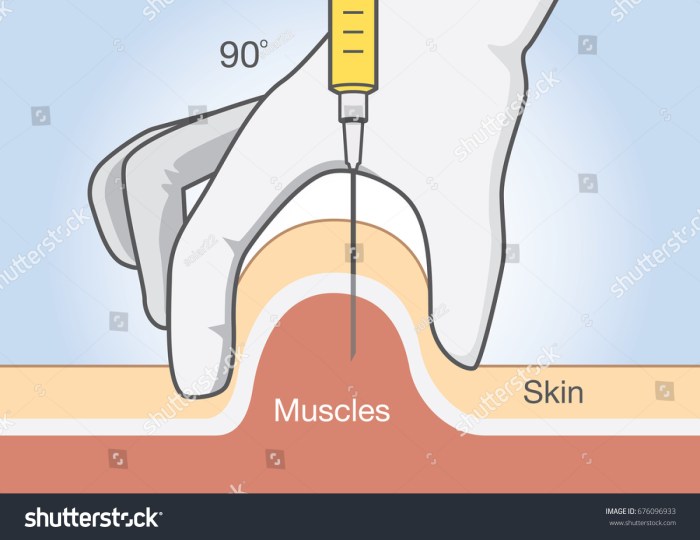
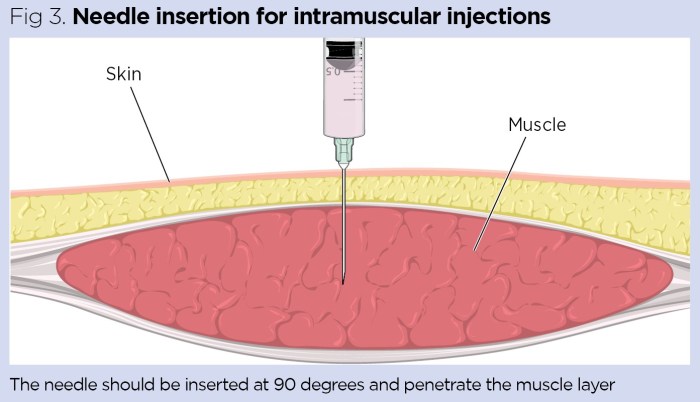
Hold the skin taut with one hand while inserting the needle with the other. The angle of insertion is crucial.
Injection Angle and Depth
The needle should be inserted at a 90-degree angle to the skin. The depth of insertion depends on the patient’s anatomy and the specific injection site. The needle should penetrate the muscle tissue, avoiding the subcutaneous fat layer. It’s important to monitor for any resistance or discomfort during the injection. Once the injection is complete, withdraw the needle and apply gentle pressure to the injection site with a sterile gauze pad.
Potential Complications and Prevention
| Potential Complications | Prevention Strategies |
|---|---|
| Hematoma (blood clot under the skin) | Using a small-gauge needle, injecting slowly, and applying pressure to the site after injection. |
| Pain or discomfort | Proper site selection, using the correct needle gauge and angle, and administering the injection slowly. |
| Infection | Strict adherence to aseptic technique, using sterile equipment, and ensuring the injection site is clean. |
| Local tissue reaction | Proper site selection, using a small-gauge needle, and injecting slowly. |
| Nerve damage | Careful site selection, avoiding areas near nerves, and injecting slowly. |
Potential Side Effects and Contraindications
Intramuscular progesterone oil injections, while beneficial for various conditions, come with potential side effects and contraindications that must be carefully considered. Understanding these aspects is crucial for ensuring patient safety and treatment efficacy. Proper monitoring and awareness of specific situations where the injection should be avoided or used with caution are essential for responsible medical practice.Careful attention to potential adverse reactions and contraindications is vital for successful treatment outcomes.
The decision to administer intramuscular progesterone oil injections should be made after a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history, current health status, and potential risks.
Intramuscular injections of progesterone oil are a common treatment option, but it’s important to consider the potential interplay with other health concerns. For instance, understanding the connection between hormonal imbalances and mental well-being is crucial. A deeper dive into potential mental health disorders, like those listed in this comprehensive resource on top mental health disorders a mental illness list , can help tailor treatment plans.
Ultimately, a holistic approach to health, including careful monitoring and consideration of the broader picture, is key when navigating treatments like intramuscular progesterone oil injections.
Potential Side Effects
Adverse reactions to intramuscular progesterone oil injections can vary in severity and presentation. Common side effects may include pain, swelling, and redness at the injection site. These local reactions typically resolve within a few days.Less common, but potentially more serious, side effects can include allergic reactions, such as hives, itching, or difficulty breathing. These reactions require immediate medical attention.
Intramuscular injections of progesterone oil are a common treatment for various hormonal imbalances. While the specifics of how this treatment affects the body are complex, it’s important to consider the broader impact on overall health. Interestingly, the way our bodies change over time, even something seemingly minor like how your nose grows with age, how your nose grows with age , can reveal a lot about our internal systems.
Ultimately, understanding these nuanced physiological changes is crucial for navigating treatments like intramuscular progesterone oil effectively.
Systemic effects, such as nausea, vomiting, or headache, may also occur. Furthermore, some patients may experience mood changes, breast tenderness, or changes in menstrual cycles.
Importance of Patient Monitoring
Close monitoring of patients during and after administration of intramuscular progesterone oil injections is paramount. Regular assessment of the injection site for signs of inflammation, infection, or allergic reactions is essential. Vital signs, such as temperature, blood pressure, and pulse, should be monitored. Any unusual symptoms, such as those mentioned above, should be promptly reported to the healthcare provider.
This proactive approach allows for early intervention and management of potential complications.
Situations Requiring Caution or Avoidance
Intramuscular progesterone oil injections should be used with extreme caution, or avoided altogether, in specific situations. Patients with known hypersensitivity to progesterone or any components of the injection formulation should not receive the treatment. Pre-existing liver or kidney disease may necessitate careful consideration, as progesterone metabolism can be affected in these cases. Patients with a history of blood clotting disorders or those on blood thinners should be closely monitored.
Furthermore, pregnant or breastfeeding women require careful evaluation and discussion of potential risks and benefits.
Contraindications
| Contraindication | Patient Population | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Known hypersensitivity to progesterone or components of the injection | All patients | Administration should be avoided to prevent severe allergic reactions. |
| Active deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism | Patients with a history of blood clotting disorders | Increased risk of thromboembolic events. Use with extreme caution, if at all, under close medical supervision. |
| Severe liver or kidney disease | Patients with impaired liver or kidney function | Potential for adverse drug reactions due to altered metabolism. Carefully evaluate the risks and benefits with the healthcare provider. |
| Pregnancy (unless specifically indicated by the healthcare provider) | Pregnant women | Potential effects on the developing fetus need careful consideration. Use only if benefits outweigh risks. |
| Breastfeeding (unless specifically indicated by the healthcare provider) | Breastfeeding mothers | Potential for transfer of progesterone to the infant. Use only if benefits outweigh risks. |
Patient Education and Counseling
Empowering patients with knowledge is crucial for successful intramuscular progesterone oil injection therapy. This section provides a comprehensive guide to help patients understand the treatment process, potential outcomes, and necessary precautions. Proper patient education minimizes anxiety and maximizes adherence to the prescribed regimen.
Injection Administration
Understanding the injection process is vital for patient comfort and safety. Patients should be instructed on the correct technique for administering the intramuscular injection, emphasizing sterile procedures. This includes proper hand hygiene, selecting the appropriate injection site (often the gluteal muscle), and the correct angle and depth of insertion. Visual aids, such as diagrams or videos, can greatly enhance comprehension.
Patients should be encouraged to practice the technique under supervision if needed.
Expected Outcomes
Patients should be informed about the expected outcomes of intramuscular progesterone oil injections. These injections aim to achieve specific hormonal balance, often leading to improved reproductive health outcomes, such as regularity in menstrual cycles or support for pregnancy maintenance. However, individual responses vary. It is important to emphasize that achieving desired outcomes may take time and that regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor progress.
A discussion about realistic expectations and potential delays in seeing results is important.
Potential Side Effects
Patients must be well-informed about potential side effects associated with intramuscular progesterone oil injections. Common side effects may include pain, swelling, or bruising at the injection site. More serious, though less frequent, side effects include allergic reactions, blood clots, or changes in mood. Patients should be instructed to report any unusual symptoms to their healthcare provider immediately.
Common Patient Questions
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| How long will it take to see results? | Results may vary depending on individual factors. Some patients may experience improvements within a few weeks, while others may take several months. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor progress. |
| Can I exercise after the injection? | Generally, light to moderate exercise is acceptable after the injection. However, strenuous activity or heavy lifting should be avoided for a short period to prevent discomfort or complications. Specific advice should be given by the healthcare provider. |
| Will this injection affect my daily activities? | Side effects, if any, are typically localized and temporary. Most patients can continue their normal daily activities, though some mild discomfort might be experienced at the injection site. |
| What should I do if I experience pain or swelling at the injection site? | Apply a cold compress to the injection site, and report any persistent or severe pain or swelling to the healthcare provider. Following the healthcare provider’s instructions is crucial. |
Resources for Further Exploration
- Patient brochures and pamphlets provided by the healthcare provider offer valuable information about the treatment and its potential side effects.
- Reliable online resources, such as reputable medical websites and patient support groups, can offer additional details and insights. However, it is important to verify the credibility of these sources before relying on them.
- Follow-up appointments with the healthcare provider provide an opportunity to discuss any questions or concerns in detail.
Interactions and Drug Compatibility
Progesterone oil injections, while generally safe, can interact with other medications, potentially altering their effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. Understanding these interactions is crucial for safe and effective patient care. Proper assessment of a patient’s complete medication list is essential before prescribing or administering progesterone injections.
Potential Drug Interactions
Interactions between progesterone oil and other medications can arise from several mechanisms, including competitive binding to receptors, altered metabolism, or changes in the pharmacokinetic profile of one or both drugs. This means that co-administration might lead to unexpected outcomes. For instance, certain medications may affect the way the body processes progesterone, potentially leading to higher or lower levels in the bloodstream.
Reviewing the Patient’s Medication List
A comprehensive review of the patient’s complete medication list is paramount before prescribing or administering progesterone oil injections. This includes prescription medications, over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, and vitamins. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of adverse interactions. A detailed medication history helps anticipate potential issues and adjust the treatment plan accordingly.
Table of Potential Interactions
The following table Artikels potential interactions between progesterone oil and other medications. This is not an exhaustive list, and individual patient responses may vary. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
| Medication Class | Potential Interaction | Impact on Progesterone | Impact on Other Medication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oral Contraceptives | Additive or antagonistic effects on hormone levels | May alter progesterone levels, leading to either enhanced or reduced effects | May alter the efficacy of the oral contraceptive |
| Anticonvulsants | Possible enzyme induction or inhibition | May affect the metabolism of progesterone | May affect the metabolism of the anticonvulsant |
| Steroid Hormones | Additive or antagonistic effects on hormone levels | Potentially alter the efficacy of progesterone therapy | May affect the efficacy of other steroid hormones |
| Antibiotics | Minor interaction, usually not clinically significant | Minimal effect on progesterone levels | Minimal effect on the antibiotic |
| Blood Thinners | Increased risk of bleeding | Potentially alter blood clotting factors | Potentially increase bleeding risk |
Importance of Patient Education
Patients should be informed about the potential interactions between progesterone oil and other medications they are currently taking. Open communication between the healthcare provider and the patient is crucial to ensure safe and effective treatment. Patients should be advised to promptly report any new or worsening symptoms, especially if they coincide with the start of progesterone injections. This proactive approach ensures prompt intervention if any adverse effects arise.
Clinical Monitoring and Evaluation
Intramuscular progesterone oil injections require careful monitoring to assess both the effectiveness of the treatment and the patient’s safety. Regular follow-up appointments and appropriate laboratory tests are crucial for ensuring the therapy is progressing as expected and identifying any potential adverse reactions. This section will detail the parameters to track, the relevant laboratory tests, and methods for evaluating treatment success or failure.
Parameters for Monitoring Effectiveness and Safety
Monitoring the effectiveness and safety of intramuscular progesterone oil injections involves tracking various parameters. These parameters provide insights into the treatment’s impact on the patient and allow for early detection of any complications. Key parameters include menstrual cycle regularity, symptom resolution, and vital signs. Also, monitoring for any adverse reactions like pain, swelling, or tenderness at the injection site is essential.
Laboratory Tests for Evaluation
Regular laboratory tests are important for assessing the treatment’s impact on the patient’s hormonal levels and overall health. These tests provide objective data to complement clinical observations. Examples of relevant laboratory tests include:
- Serum progesterone levels: This test measures the concentration of progesterone in the blood. Tracking these levels over time helps determine if the treatment is achieving the desired hormonal effect and can identify any potential imbalances. This test can be performed at various intervals throughout the treatment period. For example, levels can be checked at baseline, after a few weeks of treatment, and at intervals to maintain the effectiveness of the therapy.
- Complete blood count (CBC): A CBC measures different components of the blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. This test can help detect potential blood disorders or infections, which are important to identify early to manage properly.
- Liver function tests (LFTs): LFTs assess the health of the liver, an organ vital for many metabolic processes. Monitoring LFTs can be essential, as certain hormonal treatments can have an impact on liver function.
- Kidney function tests (KFTs): KFTs evaluate the health of the kidneys, ensuring proper elimination of waste products. In some cases, hormonal treatments might have a potential impact on kidney function. Regular monitoring is therefore essential.
Tracking and Documenting Changes in Patient Condition
Accurate documentation of patient responses to the treatment is critical for evaluating treatment efficacy and safety. Detailed records should include dates, times, and specific observations. This allows for a clear comparison of the patient’s condition before, during, and after the treatment. Detailed notes should include the patient’s subjective experience (e.g., pain, discomfort, or any changes in symptoms).
Furthermore, objective measurements, such as vital signs (blood pressure, pulse, temperature), should be recorded. These data, combined with the results of the laboratory tests, provide a comprehensive picture of the patient’s response to treatment.
Evaluating Treatment Success or Failure
Evaluating treatment success or failure depends on predefined criteria. These criteria should be specific to the patient’s condition and the goals of the treatment. Success might be measured by the resolution of symptoms, normalization of hormonal levels, or improvements in menstrual cycle regularity. Failure could be indicated by persistent symptoms, lack of response to treatment, or the development of adverse effects.
The patient’s reported symptoms, combined with objective laboratory test results, should provide a clear picture of treatment success or failure. It is important to compare the patient’s baseline condition with their current state after treatment. This comparison will aid in evaluating the overall impact of the therapy.
Safety Precautions and Considerations
Intramuscular progesterone oil injections, while often effective, require meticulous attention to safety protocols. Proper handling and administration are crucial to minimizing potential complications and ensuring patient well-being. This section highlights essential safety precautions to prevent infection, allergic reactions, and other adverse events.Safe injection practices encompass not only the procedure itself but also the careful disposal of used materials, and the recognition of potential risks.
Adherence to these precautions significantly reduces the risk of harm to patients.
Proper Disposal of Sharps
Safe disposal of used needles and syringes is paramount to prevent accidental needle stick injuries and potential transmission of infectious agents. Used sharps should never be recapped by hand. Instead, they should be placed in a puncture-resistant sharps container, immediately after use, and disposed of according to local regulations. These containers are specifically designed to prevent accidental exposure.
Infection Prevention
Maintaining strict aseptic technique during injection procedures is critical to prevent infections. This includes meticulous hand hygiene before and after the procedure, using sterile equipment, and ensuring the injection site is properly cleaned with an antiseptic solution before injection. Adhering to aseptic technique minimizes the risk of introducing pathogens into the patient’s body. All equipment should be sterile and inspected for any damage before use.
This includes the vial of progesterone oil.
Allergic Reaction Precautions
Allergic reactions to progesterone, though less common, can occur. Patients should be monitored closely for any signs of an allergic reaction, such as hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing, immediately following the injection. If a reaction occurs, the appropriate medical intervention should be initiated promptly. A pre-injection skin test, although not always necessary, can be performed to assess the patient’s sensitivity to the medication before administering the injection.
Sterile Technique in Injection Procedures
Maintaining sterile technique throughout the injection procedure is crucial to minimize the risk of infection. This includes ensuring the skin at the injection site is properly cleaned and disinfected with an antiseptic solution, using sterile gloves, and using aseptic technique for opening the medication vial and drawing up the injection. Proper handling of the injection equipment prevents contamination.
It is essential to avoid touching the needle or syringe to any surface that may be contaminated.
Best Practices for Patient Safety
A comprehensive approach to patient safety encompasses several key best practices:
- Thorough patient assessment before each injection, including a complete medical history and allergies, to identify potential contraindications or risks.
- Accurate documentation of the injection procedure, including date, time, medication details, dose, injection site, and any observed reactions.
- Proper patient education about the injection procedure, including potential side effects, importance of reporting any adverse reactions, and the need for follow-up appointments.
- Monitoring of the injection site for any signs of infection or complications, such as pain, redness, swelling, or tenderness, and notifying the healthcare provider if any of these symptoms arise.
- Following local guidelines and regulations for handling and disposing of medical waste.
Alternative Therapies and Treatment Approaches: Intramuscular Injections Progesterone Oil
Exploring alternative methods for administering progesterone and complementary therapies can provide a more holistic approach to managing hormone imbalances. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of various routes of administration is crucial for tailoring treatment to individual needs. This section delves into alternative progesterone delivery methods and explores complementary therapies, alongside successful patient case studies and relevant research findings.
Alternative Progesterone Delivery Methods
Different methods of administering progesterone offer varying advantages and disadvantages in terms of absorption, side effects, and convenience. Oral progesterone is often less effective than injectable forms due to significant first-pass metabolism. Topical applications, such as creams or gels, can offer localized effects, potentially minimizing systemic side effects. Vaginal progesterone is another option, especially for women experiencing vaginal dryness or other localized symptoms.
- Oral Progesterone: While oral progesterone is readily available, its first-pass metabolism through the liver significantly reduces its bioavailability. This often necessitates higher doses, increasing the risk of side effects. This method also has a variable absorption rate, leading to fluctuations in progesterone levels and potentially inconsistent therapeutic effects.
- Topical Progesterone: Topical applications, like creams or gels, allow for localized delivery, potentially minimizing systemic side effects. However, absorption can be unpredictable, and the treatment area may experience localized skin reactions. This method might be suitable for specific conditions, but comprehensive systemic hormonal regulation often requires other approaches.
- Vaginal Progesterone: This method is particularly relevant for vaginal dryness, atrophic vaginitis, and other localized symptoms. The absorption rate is typically higher than oral methods for the target tissue, but it may not address systemic hormone imbalances effectively.
Complementary Therapies
Several complementary therapies may complement intramuscular progesterone injections to enhance overall well-being and potentially mitigate side effects. Dietary changes, exercise, stress management techniques, and herbal remedies can play a supporting role in balancing hormone levels and improving overall health.
- Dietary Considerations: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, alongside adequate protein intake, can support overall hormonal health. Avoiding processed foods, refined sugars, and excessive caffeine can also contribute to a more stable hormonal environment.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and stress management techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can significantly impact hormone regulation. These lifestyle choices promote overall well-being and potentially reduce the strain on the endocrine system.
- Herbal Remedies: Some herbal remedies, like chasteberry, are believed to support hormonal balance. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating any herbal remedies, especially if combined with other medications. Their efficacy and safety need to be carefully considered.
Patient Case Studies
Real-world examples of successful patient outcomes often involve a combination of intramuscular progesterone injections and alternative therapies. For instance, a patient experiencing perimenopausal symptoms may benefit from a combination of progesterone injections, a tailored diet, and stress reduction techniques. The success of such interventions often depends on careful patient assessment, personalized treatment plans, and ongoing monitoring.
Research Findings
“Studies exploring the combined effects of alternative therapies and hormone replacement therapy, including progesterone injections, are limited but suggest potential synergistic effects in certain populations.”
Research findings are ongoing, and further investigation is required to establish definitive conclusions regarding the efficacy and safety of combined approaches. It is essential to critically evaluate the available evidence and consult with healthcare professionals to make informed decisions.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, intramuscular progesterone oil injections provide a targeted approach to hormone therapy, but careful consideration of various factors is crucial. This comprehensive guide covers the necessary aspects, including mechanisms of action, indications, preparation, potential side effects, and patient education. From understanding dosage adjustments to recognizing potential interactions, this exploration equips you with a solid foundation for navigating this treatment option.




