Hyperthyroidism symptoms in females can manifest in various ways, impacting both physical and emotional well-being. This comprehensive guide explores the diverse range of symptoms, from common physical manifestations to subtle mental and emotional changes. Understanding the nuances of these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.
This exploration delves into the underlying causes, potential variations, and the interplay between hormones, symptoms, and overall health. We’ll examine common symptoms, potential overlaps with other conditions, and the importance of accurate diagnosis. Further, we’ll discuss management strategies, lifestyle considerations, and potential complications, offering a holistic perspective on navigating hyperthyroidism in women.
Introduction to Hyperthyroidism in Females
Hyperthyroidism is a condition characterized by an overactive thyroid gland, which produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones. This hormonal imbalance can disrupt various bodily functions, leading to a range of symptoms and potential health complications. Understanding the causes, hormonal mechanisms, and prevalence of hyperthyroidism in women is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.The underlying causes of hyperthyroidism in females are multifaceted and can include autoimmune disorders, certain medications, and rare tumors.
Autoimmune diseases like Graves’ disease are the most common cause, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, stimulating it to produce excessive hormones. Certain medications, including some used to treat other conditions, can also trigger hyperthyroidism. Less frequently, tumors of the thyroid gland, either benign or malignant, can cause overproduction of thyroid hormones.The crucial role of hormones in the development of hyperthyroidism is undeniable.
The thyroid gland, located in the neck, produces hormones like thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones regulate metabolism, impacting everything from heart rate and body temperature to energy levels and mood. An overproduction of these hormones disrupts the delicate balance of metabolic processes, resulting in a cascade of physiological changes. Elevated levels of thyroid hormones accelerate metabolic activity, leading to the characteristic symptoms of hyperthyroidism.Hyperthyroidism affects a significant portion of the female population.
While the exact prevalence varies based on geographic location and other factors, it’s estimated to affect a substantial number of women compared to men. The impact of hyperthyroidism can range from mild discomfort to severe health issues, impacting quality of life and requiring careful medical attention. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential to manage symptoms and prevent long-term complications.
Types of Hyperthyroidism and Their Characteristics
Different types of hyperthyroidism have varying underlying causes and specific impacts on females. Recognizing these distinctions is important for tailored treatment approaches.
| Type of Hyperthyroidism | Underlying Cause | Unique Characteristics | Impact on Females |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graves’ Disease | Autoimmune disorder | The body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, stimulating its overactivity. | Often associated with symptoms like anxiety, palpitations, and weight loss. Can also affect fertility and menstrual cycles. |
| Toxic Multinodular Goiter | Enlarged thyroid gland with multiple nodules | Multiple nodules within the thyroid gland become hyperactive, producing excess hormones. | May present with goiter (enlarged thyroid) and symptoms related to high hormone levels. |
| Solitary Toxic Adenoma | Single, hyperactive nodule in the thyroid | A single nodule in the thyroid gland becomes overactive, producing excess hormones. | Can cause goiter, and symptoms associated with high thyroid hormone levels. |
| Iodine-induced Hyperthyroidism | Excessive iodine intake | Large amounts of iodine can stimulate the thyroid gland to produce more hormones. | While less common, it can cause significant symptoms if iodine intake is excessive. |
Understanding these different types of hyperthyroidism allows healthcare professionals to tailor treatment strategies based on the specific cause, enabling more effective management of the condition in women.
Common Symptoms in Females
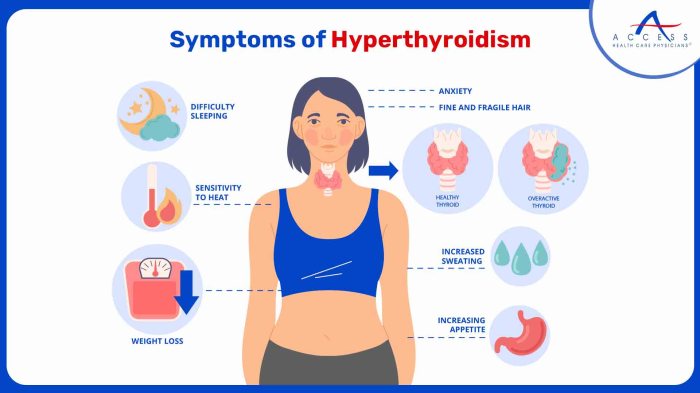
Hyperthyroidism, an overactive thyroid gland, manifests differently in various individuals, especially women. Understanding the common symptoms and potential variations is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. This often involves recognizing patterns and nuances in the symptoms to distinguish them from other health issues.The symptoms of hyperthyroidism in females can range from mild to severe, and their presentation can vary significantly between individuals.
Factors such as age, overall health, and the underlying cause of the hyperthyroidism can all influence the specific symptoms experienced. It’s important to remember that not everyone with hyperthyroidism will experience all of the symptoms, and the severity of the symptoms can differ widely.
Frequent Symptoms
A variety of symptoms can signal hyperthyroidism. The most frequent symptoms experienced by women often include nervousness, anxiety, and difficulty concentrating. These symptoms can be attributed to the increased metabolic rate associated with hyperthyroidism. Other frequent symptoms may include heat intolerance, increased perspiration, and palpitations or rapid heartbeat.
Feeling jittery and experiencing rapid heartbeats? These are common hyperthyroidism symptoms in females, often mimicking other health concerns. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment. While researching these issues, I stumbled upon a very helpful resource about RU486 the Abortion Pill A Comprehensive Guide, which I thought might be of interest to those exploring different healthcare options.
RU486 the Abortion Pill A Comprehensive Guide Ultimately, though, recognizing the diverse and sometimes overlapping symptoms of hyperthyroidism is key to seeking proper medical attention.
Variations in Symptoms
Individual experiences of hyperthyroidism can vary significantly. Some women may primarily experience psychological symptoms like anxiety and irritability, while others may primarily exhibit physical symptoms like weight loss or heat intolerance. The severity of the symptoms can also vary widely, with some women experiencing mild symptoms while others experience more pronounced symptoms.
Comparison with Other Thyroid Disorders
Hyperthyroidism’s symptoms can overlap with those of other thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism. While hypothyroidism is characterized by a slowed metabolism, hyperthyroidism exhibits the opposite. Distinguishing between the two requires careful medical evaluation and consideration of specific symptoms and their duration. Symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, and cold intolerance are often associated with hypothyroidism, contrasting with the heat intolerance, weight loss, and nervousness characteristic of hyperthyroidism.
Symptom Overlap with Other Conditions
It’s important to note that some symptoms of hyperthyroidism can overlap with symptoms of other conditions. For instance, anxiety and nervousness can be symptoms of various mental health issues. Similarly, palpitations and rapid heart rate can be indicative of various cardiac conditions. Careful medical evaluation is necessary to determine the underlying cause of the symptoms and to rule out other potential conditions.
Table of Common Symptoms
| Symptom | Severity (Mild/Moderate/Severe) | Frequency (Common/Occasional/Rare) |
|---|---|---|
| Anxiety/Nervousness | Moderate | Common |
| Heat Intolerance | Mild to Moderate | Common |
| Weight Loss | Moderate to Severe | Common |
| Increased Appetite | Mild to Moderate | Occasional |
| Rapid Heart Rate | Mild to Severe | Common |
| Tremors | Mild to Moderate | Common |
| Sleep Disturbances | Mild to Moderate | Common |
| Diarrhea | Mild to Moderate | Occasional |
| Fatigue | Mild to Moderate | Occasional |
Physical Symptoms: Hyperthyroidism Symptoms In Females
Hyperthyroidism, an overactive thyroid gland, can manifest in a wide array of physical symptoms that vary in severity and impact on daily life. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. Recognizing the physiological mechanisms behind these symptoms helps individuals and healthcare providers understand the underlying cause and develop appropriate treatment strategies.
Cardiovascular Symptoms
The overproduction of thyroid hormones significantly impacts the cardiovascular system. Increased heart rate and palpitations are common due to the thyroid hormones’ direct effect on the heart’s electrical activity. This heightened activity can lead to a rapid pulse, sometimes felt as a fluttering or pounding sensation in the chest. Individuals might experience shortness of breath or chest pain, particularly with exertion.
The increased heart rate can also elevate blood pressure. These symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe, life-threatening conditions if left untreated.
- Increased heart rate (tachycardia): Elevated thyroid hormone levels stimulate the heart to beat faster. This is a direct result of the hormones’ influence on the sinoatrial (SA) node, the heart’s natural pacemaker. Examples include a resting heart rate consistently above 100 beats per minute.
- Palpitations: A sensation of a rapid, fluttering, or pounding heart beat. This is often noticeable to the patient and can be distressing.
- Elevated blood pressure: The increased heart rate and the effect of thyroid hormones on blood vessels contribute to elevated blood pressure readings. This can increase the risk of cardiovascular complications if not managed.
- Shortness of breath: Increased metabolism and rapid heart rate can lead to an individual feeling short of breath, especially with physical activity.
- Chest pain: In some cases, individuals may experience chest pain, potentially mimicking angina (chest pain due to reduced blood flow to the heart). This warrants immediate medical attention.
Nervous System Symptoms
The nervous system is highly sensitive to thyroid hormone fluctuations. Hyperthyroidism can lead to nervousness, anxiety, and difficulty concentrating. These symptoms arise from the thyroid hormones’ influence on neurotransmitter systems in the brain, affecting mood and cognitive function.
- Anxiety and nervousness: The increased metabolism associated with hyperthyroidism can cause a heightened state of arousal and anxiety. Individuals may experience feelings of restlessness, worry, and irritability.
- Tremor: A fine tremor, often noticeable in the hands, is a common symptom. This arises from the increased activity in the nervous system. This tremor can be subtle or more pronounced, affecting daily activities like writing or holding objects.
- Difficulty concentrating: The hormonal imbalance can lead to problems with focus and concentration, affecting cognitive function.
- Insomnia: Hyperthyroidism can disrupt sleep patterns, causing difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. This contributes to fatigue and reduced energy levels.
Other Physical Symptoms
Other physical symptoms of hyperthyroidism encompass a broad range of effects on various bodily systems.
- Weight loss: Despite increased appetite, individuals with hyperthyroidism often experience unintentional weight loss due to the elevated metabolic rate. This is because the body burns calories at a faster pace.
- Heat intolerance: Individuals may experience excessive sweating and a feeling of warmth, even in cool environments. This is due to the increased metabolic rate that generates more heat.
- Diarrhea: The increased metabolism can lead to changes in bowel movements, including diarrhea. This is a result of accelerated digestive processes.
- Changes in menstrual cycles: In women, hyperthyroidism can lead to irregular or absent menstrual periods.
Symptom Manifestation Across Age Groups
The presentation of hyperthyroidism symptoms can vary significantly across different age groups. Younger women might experience more pronounced anxiety and nervousness, while older women may present with more cardiovascular issues.
Categorization of Physical Symptoms, Hyperthyroidism symptoms in females
| Body System | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular | Increased heart rate, palpitations, elevated blood pressure, shortness of breath, chest pain |
| Nervous System | Anxiety, nervousness, tremor, difficulty concentrating, insomnia |
| Gastrointestinal | Diarrhea |
| Endocrine | Weight loss, heat intolerance, changes in menstrual cycles |
Mental and Emotional Symptoms
Hyperthyroidism, while primarily affecting physical health, can significantly impact mental and emotional well-being. The hormonal imbalances associated with this condition can lead to a range of psychological symptoms, often making diagnosis challenging. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers to ensure comprehensive care.The fluctuating levels of thyroid hormones can disrupt the delicate balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, leading to mood swings, irritability, and difficulty concentrating.
This can manifest in a variety of ways, affecting daily life and interpersonal relationships.
Mood Swings and Emotional Instability
The rapid changes in thyroid hormone levels can contribute to dramatic mood swings. Individuals might experience periods of intense happiness followed by sudden bouts of sadness, anxiety, or irritability. This emotional rollercoaster can make it challenging to maintain stable relationships and navigate social situations. For example, a person might be overly enthusiastic one moment and withdrawn and tearful the next.
This unpredictability can be frustrating for both the individual and those around them.
Impact on Relationships and Social Interactions
These mood swings can significantly impact interpersonal relationships. Sudden shifts in mood can strain friendships and romantic partnerships, leading to misunderstandings and conflict. Social interactions might become difficult to manage, with individuals feeling overwhelmed or withdrawn due to the unpredictable emotional state. For example, a previously outgoing friend might become isolated due to their inability to consistently regulate their emotional responses.
Link Between Hyperthyroidism and Anxiety/Depression
The heightened physiological response in hyperthyroidism can also increase the risk of developing anxiety or depression. The constant feeling of restlessness, difficulty concentrating, and sleep disturbances associated with hyperthyroidism can exacerbate existing mental health conditions or contribute to the onset of new ones. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism highlighted a correlation between elevated thyroid hormone levels and increased rates of anxiety disorders.
Feeling jittery and experiencing unexplained weight loss? These could be signs of hyperthyroidism in women. Sometimes, these hormonal imbalances can manifest in unusual ways, like skin changes. For example, have you noticed any small, fleshy growths? If so, learning more about them is key, and What are Skin Tag Patches?
A Comprehensive Guide might offer some helpful insights. Understanding these skin changes can help you better manage potential hyperthyroidism symptoms and get the medical attention you need.
It’s important to note that these conditions often coexist and require careful assessment by healthcare professionals.
Potential Impact on Daily Life
| Mental/Emotional Symptom | Potential Impact on Daily Life |
|---|---|
| Mood swings | Difficulty maintaining relationships, decreased productivity at work or school, increased risk of conflicts with others. |
| Irritability | Increased frustration, heightened sensitivity to criticism, strained communication with family and friends. |
| Anxiety | Difficulty concentrating, racing thoughts, sleep disturbances, increased tension and worry, impacting daily tasks and responsibilities. |
| Depression | Loss of interest in activities, feelings of hopelessness, fatigue, withdrawal from social interactions, impacting work/school performance and overall well-being. |
| Difficulty concentrating | Problems with focus, impaired decision-making, difficulty completing tasks, impacting productivity and academic performance. |
Diagnostic Procedures
Unraveling the mystery of hyperthyroidism in women requires a meticulous approach to diagnosis. Accurate identification relies on a combination of clinical evaluation, patient history, and specific laboratory tests. These procedures are crucial for developing an appropriate treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs.
Common Diagnostic Tests
Several tests are commonly employed to diagnose hyperthyroidism in women. These tests evaluate thyroid function, identify potential underlying causes, and monitor treatment effectiveness. A comprehensive evaluation often involves a combination of these tests.
Thyroid Function Tests (TFTs)
Thyroid function tests (TFTs) are the cornerstone of hyperthyroidism diagnosis. These blood tests measure the levels of key hormones involved in thyroid regulation, including thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), free thyroxine (T4), and free triiodothyronine (T3). Elevated levels of T3 and T4, coupled with a suppressed TSH level, strongly suggest hyperthyroidism.
Radioactive Iodine Uptake Test (RAIU)
The radioactive iodine uptake (RAIU) test measures the thyroid gland’s ability to absorb iodine. This test is particularly helpful in distinguishing between different causes of hyperthyroidism. For instance, Graves’ disease typically shows a high uptake, while thyroid nodules may exhibit a varied uptake pattern. This test helps pinpoint the specific source of the hyperthyroid state.
Thyroid Scan
A thyroid scan, often performed alongside the RAIU test, provides a visual representation of the thyroid gland’s structure and function. It helps identify any nodules, goiters, or other abnormalities that may be contributing to the hyperthyroidism. The scan’s visualization capability is valuable in identifying the location and extent of any thyroid issues.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging provides a non-invasive way to visualize the thyroid gland and evaluate its size, shape, and any potential abnormalities. It is helpful in assessing the presence of nodules or other structural changes. The detailed anatomical information gleaned from ultrasound assists in further diagnostic steps.
Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy (FNAB)
In cases where a thyroid nodule is suspected, a fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) may be performed. This procedure involves extracting a small tissue sample from the nodule for microscopic examination. The biopsy helps determine if the nodule is benign or malignant. This is a crucial step for determining appropriate management strategies, particularly in cases of potential malignancy.
Table: Diagnostic Procedures for Hyperthyroidism
| Diagnostic Procedure | Associated Cost | Preparation Required |
|---|---|---|
| Thyroid Function Tests (TFTs) | Variable (depending on location and lab) | Fasting blood draw |
| Radioactive Iodine Uptake Test (RAIU) | Higher than TFTs | Fasting, possibly specific instructions from the ordering physician. |
| Thyroid Scan | Higher than TFTs | Fasting, possible need for contrast |
| Ultrasound | Moderate | No special preparation required. |
| Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy (FNAB) | Variable (depending on location and complexity) | NPO (nothing by mouth) and informed consent. |
Interpretation of Test Results
Interpreting test results requires careful consideration of the patient’s clinical presentation, medical history, and other relevant factors. A healthcare professional will correlate the test results with the symptoms and physical examination findings. The specific interpretation of each test is crucial in determining the cause and extent of the hyperthyroidism. For instance, a high T3 and T4, coupled with a low TSH, strongly points towards hyperthyroidism.
Variations in results may necessitate further testing and evaluation.
Management Strategies
Navigating hyperthyroidism requires a multifaceted approach tailored to each individual’s specific needs and health profile. Effective management focuses on controlling the excessive thyroid hormone production and mitigating its impact on the body. This often involves a combination of medication, lifestyle adjustments, and in some cases, surgery.Treatment options for hyperthyroidism are designed to reduce thyroid hormone levels to a normal range, thereby alleviating symptoms and preventing potential complications.
Feeling jittery and losing weight unexpectedly? Hyperthyroidism in women can manifest in some surprising ways, like rapid heart rate and anxiety. While managing these symptoms can be challenging, incorporating a healthy exercise routine, like swimming, could be a great way to support your overall well-being. Swimming for Weight Loss Your Aquatic Journey offers some fantastic tips on how to use this fantastic workout to shed pounds and improve your health.
Ultimately, understanding these symptoms and finding effective strategies to manage them is key to feeling your best, whether it’s through exercise or other methods.
The choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the severity of the condition, the patient’s overall health, and their preferences. Understanding the potential benefits and drawbacks of each approach is crucial for informed decision-making.
Treatment Options
Different treatment options for hyperthyroidism address the underlying cause and symptoms in various ways. Medication, radioactive iodine therapy, and surgery are common approaches. The selection of the most appropriate strategy is often determined by a consultation with an endocrinologist or other qualified healthcare professional.
- Anti-thyroid Medications: These drugs, such as methimazole and propylthiouracil, work by inhibiting the production of thyroid hormones. They are typically the first-line treatment for many patients, particularly those with mild to moderate hyperthyroidism. Anti-thyroid medications can be quite effective in controlling symptoms and restoring hormone balance. However, they often require long-term use and may have side effects, such as skin rashes, liver problems, or even a temporary decrease in white blood cell counts.
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy: This treatment involves ingesting a radioactive iodine solution. The iodine targets and destroys the thyroid cells, reducing the production of thyroid hormones. This is a highly effective method for permanently resolving hyperthyroidism in many cases. It often leads to a more rapid and sustained response compared to anti-thyroid drugs. Potential side effects include hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), which may necessitate lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy, and, in rare cases, thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid).
The cost is typically higher than anti-thyroid medications but may be considered for patients who prefer a potentially permanent solution or for those with severe side effects from anti-thyroid medication.
- Thyroid Surgery (Thyroidectomy): Surgical removal of all or part of the thyroid gland is a definitive treatment option for hyperthyroidism. It is generally considered for patients who are not suitable candidates for radioactive iodine therapy or who do not respond adequately to anti-thyroid medications. The surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia and is associated with potential risks, such as bleeding, damage to the parathyroid glands (which regulate calcium levels), and vocal cord problems.
Recovery time can vary, but most patients can return to normal activities within a few weeks. This is a more invasive procedure with potential risks, but it can be an effective option for those who have specific circumstances making other options less desirable.
Effectiveness and Side Effects
The effectiveness of each treatment varies, depending on the individual and the specific type of hyperthyroidism. Anti-thyroid medications are usually effective in controlling symptoms, but long-term use is often necessary. Radioactive iodine therapy is highly effective but can lead to permanent hypothyroidism. Surgical intervention is a definite treatment, but it carries the risk of complications.
Comparison of Treatment Approaches
The choice of treatment depends on a variety of factors. Anti-thyroid medications are often a first-line approach due to their relative safety and effectiveness. Radioactive iodine therapy is considered for those seeking a potentially permanent solution, while surgery is reserved for cases where other options are unsuitable or ineffective.
Importance of Long-Term Management
Long-term management is crucial for preventing complications and maintaining a good quality of life. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor thyroid hormone levels, adjust medication as needed, and address any potential side effects. Continuous monitoring ensures the best possible outcome and helps to manage any potential progression of the disease.
Cost Comparison of Treatments
| Treatment Option | Potential Side Effects | Approximate Costs |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-thyroid Medications | Skin rashes, liver problems, decreased white blood cell count | Moderate |
| Radioactive Iodine Therapy | Hypothyroidism, thyroiditis | High |
| Thyroid Surgery | Bleeding, parathyroid damage, vocal cord problems | High |
Note: Costs can vary significantly depending on individual circumstances and location. Insurance coverage also plays a role.
Lifestyle Considerations
Managing hyperthyroidism effectively often involves a multifaceted approach that goes beyond medication. Lifestyle changes can play a crucial role in mitigating symptoms and improving overall well-being. Adopting healthy habits can significantly impact the severity of symptoms and contribute to a more balanced and fulfilling life for individuals with hyperthyroidism.Lifestyle modifications can be highly effective in complementing medical treatments for hyperthyroidism.
By incorporating healthy dietary choices, regular exercise, and stress management techniques, individuals can experience a marked reduction in symptoms and enhance their overall health and quality of life. These lifestyle strategies work synergistically with medical interventions to achieve optimal results.
Dietary Recommendations
A balanced diet tailored to the needs of someone with hyperthyroidism is essential for managing symptoms. It is crucial to focus on nutrient-rich foods that can help regulate metabolism and control energy levels. Nutrient deficiencies are frequently exacerbated by hyperthyroidism, and a well-planned diet helps counter these deficiencies.
- Prioritize whole, unprocessed foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. These provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, supporting overall health and potentially reducing the impact of hyperthyroidism on the body.
- Limit refined carbohydrates, sugary drinks, and processed foods. These can lead to blood sugar fluctuations, exacerbating symptoms and contributing to weight gain, which can further complicate hyperthyroidism management.
- Increase intake of foods rich in iodine. While iodine is crucial for thyroid function, it’s important to note that individuals with hyperthyroidism should avoid excessive iodine intake. Consult a healthcare professional to determine appropriate iodine intake.
- Include foods rich in selenium, magnesium, and zinc. These minerals play vital roles in thyroid function and can help maintain metabolic balance.
Exercise Regimen
Regular physical activity is a cornerstone of managing hyperthyroidism. Exercise helps to regulate metabolism, reduce stress, and improve overall physical and mental well-being. A balanced exercise program tailored to individual needs and fitness levels can be beneficial.
- Incorporate a mix of cardiovascular exercise, such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity cardiovascular activity most days of the week. Cardiovascular exercise aids in weight management and can contribute to a healthier metabolic profile.
- Include strength training exercises to build muscle mass. Muscle mass helps regulate metabolism and can positively impact overall health, contributing to improved strength and stamina.
- Listen to your body and adjust exercise intensity based on your individual needs. It’s essential to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts to avoid overexertion. This ensures safety and optimal results.
Stress Management Techniques
Chronic stress can exacerbate hyperthyroidism symptoms. Implementing stress management techniques is vital for overall well-being and symptom control. These techniques can help regulate the body’s response to stress and support better management of hyperthyroidism.
- Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga. These techniques help calm the nervous system and reduce the physiological response to stress, potentially alleviating some of the symptoms associated with hyperthyroidism.
- Prioritize sufficient sleep. Adequate sleep is essential for overall health and can help regulate hormone levels, which are often affected by hyperthyroidism. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Engage in activities you enjoy, such as hobbies or spending time with loved ones. Engaging in activities you find enjoyable can help reduce stress and promote a sense of well-being, further contributing to symptom management.
Recommended Lifestyle Changes and Potential Benefits
| Lifestyle Change | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|
| Balanced Diet | Improved metabolism, regulated energy levels, reduced symptom severity |
| Regular Exercise | Weight management, reduced stress, improved physical and mental well-being |
| Stress Management Techniques | Reduced physiological response to stress, improved symptom control, overall well-being |
| Adequate Sleep | Regulated hormone levels, improved mood, reduced symptom severity |
Potential Complications
Hyperthyroidism, if left untreated, can lead to a cascade of serious health problems. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial to prevent these complications and maintain overall well-being. Understanding the potential consequences empowers individuals to advocate for their health and work with healthcare providers to manage this condition effectively.
Long-Term Complications
Untreated hyperthyroidism can have significant long-term effects on various bodily systems. The sustained elevated levels of thyroid hormones disrupt normal metabolic processes, potentially leading to organ damage and systemic issues. Prolonged exposure to high levels of thyroid hormones can result in permanent damage to organs.
Impact of Untreated Hyperthyroidism on Overall Health
Untreated hyperthyroidism can significantly impair overall health and quality of life. It can contribute to weakened bones, increased risk of heart problems, and difficulties with fertility and pregnancy. The persistent hormonal imbalance can also lead to mental health challenges, including anxiety and mood swings.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are vital in mitigating the risk of long-term complications. Early intervention allows healthcare professionals to effectively manage the hormonal imbalance, minimizing the potential for permanent damage to various organs. This proactive approach safeguards long-term health and well-being.
Preventative Measures to Mitigate Risk of Complications
Regular medical check-ups and adherence to prescribed treatment plans are crucial preventative measures. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, supports overall well-being and can help to reduce the risk of complications. Open communication with healthcare providers about any concerns or symptoms is also essential.
Potential Complications and Risk Factors
| Potential Complication | Associated Risk Factors |
|---|---|
| Thyroid Storm | Untreated or poorly controlled hyperthyroidism, infection, stress, surgery, or trauma. Patients with a history of thyroid storm are at increased risk for recurrence. |
| Osteoporosis | Prolonged elevated thyroid hormone levels, leading to bone loss and increased risk of fractures. Individuals with a family history of osteoporosis are also more susceptible. |
| Heart Problems (e.g., Atrial Fibrillation) | Sustained rapid heart rate and increased blood pressure from hyperthyroidism. Pre-existing heart conditions or a family history of cardiac issues can exacerbate the risk. |
| Eye Problems (e.g., Graves’ Ophthalmopathy) | Autoimmune component of hyperthyroidism can lead to inflammation and bulging of the eyes. Genetic predisposition can also play a role. |
| Fertility Issues | Irregular menstrual cycles and ovulation problems. These can affect both male and female fertility. |
| Mental Health Issues (e.g., Anxiety, Depression) | The hormonal imbalance associated with hyperthyroidism can affect mood regulation. Pre-existing mental health conditions may increase the risk. |
Last Point
In conclusion, hyperthyroidism symptoms in females can be multifaceted and vary greatly between individuals. Recognizing the diverse range of physical and mental symptoms is paramount for prompt diagnosis and effective management. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, highlighting the importance of early detection, appropriate treatment, and the crucial role of lifestyle adjustments. Ultimately, proactive steps toward understanding and managing these symptoms are key to promoting overall well-being.




