Hepatitis C symptoms in males can vary greatly, and understanding these nuances is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. This comprehensive exploration delves into the diverse range of symptoms, potential complications, and available treatment options, providing a holistic perspective for males affected by this condition.
This article examines the various ways Hepatitis C can manifest in men, from common symptoms like fatigue and abdominal pain to more severe complications. We’ll also discuss the importance of early diagnosis and the diverse treatment approaches available.
Introduction to Hepatitis C in Males
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver. It’s a significant global health concern, impacting millions worldwide. While it can affect people of all genders, understanding its transmission, prevalence, and potential impact on males is crucial for prevention and early intervention. This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health and seek necessary medical attention.Hepatitis C is primarily transmitted through contact with infected blood.
This can occur in various ways, making awareness of risk factors critical for prevention. Common routes of transmission relevant to males include sharing needles or other drug paraphernalia, exposure to infected blood during medical procedures (though this is less common now due to improved safety measures), and unprotected sexual contact, although this is less common than other routes.
Hey everyone, talking about hepatitis C symptoms in men can be tricky. Often, early signs are subtle, like fatigue or abdominal discomfort. However, understanding how high blood sugar levels affect the body, like in the case of high A1C, can be helpful in understanding the body’s response to other health concerns. For instance, learning more about what happens when a1c is too high here might shed light on some of the broader effects on the body.
Ultimately, recognizing those early symptoms in hepatitis C is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment.
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential for managing the infection and preventing potential long-term complications. The earlier Hepatitis C is detected and treated, the better the chances of a favorable outcome.
Common Routes of Hepatitis C Transmission in Males
Several factors contribute to the transmission of Hepatitis C in males. Understanding these routes is vital for implementing preventative measures. Sharing needles or other drug paraphernalia is a major contributor. Additionally, exposure to infected blood during medical procedures, while less common, is a risk factor. Unprotected sexual contact, although less prevalent compared to other transmission methods, can still contribute to transmission.
It’s essential to prioritize safe practices to minimize the risk of infection.
Learning about hepatitis C symptoms in men can be tough, especially when you consider the emotional rollercoaster. It’s important to acknowledge that dealing with a health condition like this can trigger a range of feelings, which often align with the four phases and tasks of grief. the four phases and tasks of grief can help us understand and process these emotions.
Ultimately, understanding these symptoms and how to navigate them is key to managing your health and well-being.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment of Hepatitis C are crucial for preventing severe liver damage and improving long-term health outcomes. Prompt intervention allows healthcare providers to initiate antiviral therapies, potentially halting the progression of the disease and reducing the risk of complications like cirrhosis or liver cancer. Individuals with Hepatitis C often experience few noticeable symptoms initially, making regular check-ups and screenings essential for early detection.
The availability of effective antiviral treatments has significantly improved outcomes for individuals with Hepatitis C.
Common Symptoms of Hepatitis C in Males
Many individuals with Hepatitis C experience few or no noticeable symptoms in the initial stages of infection. This makes regular check-ups and screenings critical for early detection and intervention. The symptoms can vary greatly in severity, frequency, and individual response.
| Symptoms | Severity | Frequency | Possible Complications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fatigue | Mild to moderate | Common | Reduced quality of life, potential for misdiagnosis |
| Abdominal pain | Mild to moderate | Variable | Potential indication of liver inflammation |
| Loss of appetite | Mild to moderate | Common | Potential for malnutrition, impacting overall health |
| Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes) | Variable | Less common initially | Sign of liver damage, requiring immediate medical attention |
| Nausea and vomiting | Mild to moderate | Variable | Can lead to dehydration, further impacting health |
| Joint pain | Mild to moderate | Variable | Potentially unrelated to liver condition, requiring further evaluation |
| Dark urine | Mild to moderate | Variable | Sign of liver dysfunction, warrants medical evaluation |
| Light-colored stools | Mild to moderate | Variable | Sign of liver dysfunction, warrants medical evaluation |
Common Symptoms in Males
Hepatitis C, while often asymptomatic in its early stages, can manifest with a range of symptoms in males. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and appropriate management. This section details the common symptoms, variations in presentation, and potential contributing factors. It also contrasts these symptoms with those of other liver diseases to highlight the unique characteristics of Hepatitis C.Hepatitis C’s symptoms can vary significantly between individuals.
Some men might experience no noticeable symptoms at all, while others may exhibit a constellation of signs and symptoms. These variations in symptom presentation are often attributed to factors such as the individual’s overall health, the severity of the infection, and the presence of other co-existing medical conditions. The absence of symptoms does not necessarily indicate the absence of the disease, and regular monitoring is crucial for early detection.
Prevalence of Symptoms, Hepatitis c symptoms in males
Many men with Hepatitis C experience nonspecific symptoms that can easily be mistaken for other conditions. These can include fatigue, malaise, loss of appetite, and general discomfort. It’s important to remember that these symptoms, while common, are not exclusive to Hepatitis C.
Symptom Variations Among Males
The severity and types of symptoms experienced by men with Hepatitis C can vary significantly. Some men may experience jaundice, characterized by a yellowish tinge to the skin and eyes, while others might not. This difference in symptom expression can be influenced by factors such as the viral load, the individual’s immune response, and the presence of other underlying health issues.
For instance, a man with a healthy immune system might experience milder symptoms compared to a man with compromised immunity. A higher viral load often correlates with a more pronounced symptom profile.
Possible Reasons for Symptom Variations
The varied presentation of symptoms in Hepatitis C can be attributed to several factors. Individual immune responses play a significant role; a robust immune system might effectively control the infection, leading to minimal symptoms. Conversely, a compromised immune system might allow the virus to replicate more aggressively, resulting in a more noticeable symptom profile. Additionally, the presence of co-existing health conditions can influence the severity and type of symptoms observed.
For example, a man with underlying liver disease might experience more pronounced symptoms compared to a man with a healthy liver.
Comparison with Other Liver Diseases
Symptoms of Hepatitis C can overlap with other liver diseases. For example, fatigue and loss of appetite are common to several conditions affecting the liver. Therefore, it is essential to consider the patient’s complete medical history and conduct thorough diagnostic tests to differentiate Hepatitis C from other potential causes. Distinguishing Hepatitis C from other liver diseases necessitates a comprehensive approach, incorporating clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and possibly imaging techniques.
Symptom Table
| Symptom | Description | Severity | Potential Impact on Daily Life |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fatigue | Persistent tiredness and lack of energy | Mild to severe, often fluctuating | Reduced productivity, difficulty concentrating, and social withdrawal. |
| Malaise | General feeling of discomfort and illness | Mild to moderate | Can interfere with daily activities and routine. |
| Loss of Appetite | Reduced desire to eat | Mild to moderate | Potential for weight loss and nutritional deficiencies. |
| Jaundice | Yellowing of the skin and eyes | Mild to severe | Can be noticeable and potentially cause anxiety. |
| Abdominal Pain | Discomfort in the upper abdomen | Mild to severe, often intermittent | Can affect eating habits and general well-being. |
Early Detection and Diagnosis
Catching Hepatitis C early is crucial for effective treatment and preventing long-term complications. Early detection significantly improves the chances of a full recovery and minimizes the risk of liver damage. Understanding the potential warning signs and the diagnostic process empowers individuals to take proactive steps towards their health.
While hepatitis C symptoms in men can sometimes be subtle, it’s crucial to be aware of potential indicators like fatigue and jaundice. Interestingly, research into alternative treatments for various conditions, like the potential benefits of medical marijuana in managing multiple sclerosis, medical marijuana and multiple sclerosis , is ongoing. Ultimately, proper diagnosis and treatment for hepatitis C symptoms in males require professional medical attention.
Potential Warning Signs
Early Hepatitis C often presents with subtle symptoms that may be mistaken for other conditions. Paying attention to these indicators can be the first step in seeking medical attention. A range of symptoms may or may not be present, and their severity can vary.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and lack of energy are common, often mistaken for other issues. This symptom can significantly impact daily life and productivity. In some cases, individuals might experience debilitating fatigue, making it hard to perform routine tasks.
- Abdominal pain: Discomfort or pain in the abdomen, sometimes described as a dull ache, can be a sign of liver inflammation. This symptom may be accompanied by other digestive issues.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes, often accompanied by dark urine and pale stools, is a visible sign of liver dysfunction. This symptom should prompt immediate medical evaluation.
- Loss of appetite: A reduced desire to eat can be a symptom of liver involvement. This can lead to nutritional deficiencies if not addressed.
- Nausea and vomiting: These digestive issues can be associated with liver inflammation. If accompanied by other symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider.
Diagnostic Procedures
Hepatitis C diagnosis involves a series of tests to confirm the presence and extent of the infection. These tests are vital for determining the appropriate course of treatment.
- Blood tests: Blood tests are essential for detecting the presence of Hepatitis C antibodies and the virus itself in the bloodstream. These tests can identify the specific strain of the virus, which is important for treatment planning. Specific tests like PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) are used to detect the virus’s genetic material, confirming active infection.
- Liver function tests (LFTs): LFTs measure the levels of various enzymes and proteins produced by the liver. Elevated levels often indicate liver inflammation or damage. These tests are crucial for assessing the severity of liver involvement.
- Liver biopsy: In some cases, a liver biopsy, a procedure involving a small tissue sample from the liver, might be necessary to assess the extent of liver damage. This is usually performed only if the other tests raise concerns about the severity of liver disease.
Importance of Regular Health Checkups
Regular health checkups are crucial for early detection of Hepatitis C, allowing for prompt intervention and better treatment outcomes. Annual checkups can help identify potential problems before they become severe. Early detection significantly reduces the risk of developing severe liver complications.
Diagnostic Tests Table
| Test | Description | Purpose | Expected Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatitis C Antibody Test | Detects the presence of antibodies against Hepatitis C in the blood. | Initial screening for Hepatitis C infection. | Positive result indicates past or present infection. |
| Hepatitis C RNA (PCR) Test | Identifies the Hepatitis C virus’s genetic material in the blood. | Confirms active infection and quantifies viral load. | Positive result confirms active infection; viral load indicates the level of viral activity. |
| Liver Function Tests (LFTs) | Measures the levels of enzymes and proteins produced by the liver. | Evaluates liver health and identifies potential damage. | Abnormal results (elevated levels) suggest liver inflammation or damage. |
| Liver Biopsy | A procedure to obtain a tissue sample from the liver for microscopic examination. | Provides a detailed assessment of liver tissue damage. | Results show the extent of fibrosis or cirrhosis, if present. |
Potential Complications in Males
Hepatitis C, if left untreated, can lead to a range of serious long-term health complications. These complications can significantly impact a man’s overall well-being and lifestyle, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis and prompt treatment. Understanding these potential issues is crucial for men who have been diagnosed with Hepatitis C, enabling them to proactively manage their health and seek appropriate medical care.Hepatitis C infection can progress silently for many years, often without noticeable symptoms.
This prolonged asymptomatic phase can mask the insidious development of complications. While the specific likelihood of developing complications varies based on factors like the individual’s immune response and the presence of other underlying health conditions, the potential consequences are substantial. Men, in particular, may face unique challenges related to these complications due to societal and cultural factors that can influence healthcare access and adherence to treatment regimens.
Long-Term Health Complications
Hepatitis C can lead to significant liver damage, including cirrhosis, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common type of liver cancer. These conditions can severely impair liver function, impacting various bodily processes and potentially necessitating life-altering interventions. For instance, cirrhosis can result in the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen, leading to discomfort and difficulty breathing.
Liver failure necessitates a liver transplant, a major surgical procedure with its own set of challenges and recovery periods.
Comparison with Other Demographics
While Hepatitis C can affect individuals of all genders and backgrounds, studies indicate that men may have a slightly increased risk of developing certain complications compared to women. Factors such as alcohol use, co-infection with other viral diseases, and differing access to healthcare can influence this disparity. However, it’s crucial to remember that individual experiences vary widely, and each person’s risk depends on numerous personal and medical factors.
The risk of complications also varies depending on the specific type of Hepatitis C infection. For example, genotype 1 is often associated with a higher risk of cirrhosis and liver cancer than other genotypes.
Impact on Lifestyle and Overall Well-being
The long-term complications of Hepatitis C can have a profound impact on a man’s quality of life. Chronic liver disease can lead to fatigue, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, and jaundice, impacting daily activities and social interactions. Treatment regimens can also be demanding, requiring adherence to strict medication schedules and potentially impacting work or personal responsibilities. In cases of liver failure, the need for frequent medical checkups and potential hospitalization can disrupt a man’s lifestyle significantly.
Moreover, the emotional toll of a chronic illness and the fear of future complications can lead to anxiety and depression. A man may face stigma and social isolation due to his condition.
Management Strategies
| Complication | Description | Risk Factors | Management Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cirrhosis | Permanent scarring of the liver | Chronic Hepatitis C infection, alcohol abuse, other liver diseases | Antiviral therapy, lifestyle modifications (alcohol cessation), monitoring for complications |
| Liver Failure | Complete loss of liver function | Advanced cirrhosis, complications from other liver diseases | Liver transplant, supportive care |
| Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) | Liver cancer | Chronic Hepatitis C infection, cirrhosis | Early detection through screening, antiviral therapy, surgical resection, or other treatments |
| Ascites | Accumulation of fluid in the abdomen | Cirrhosis | Diuretics, dietary restrictions, paracentesis |
Treatment Options for Males
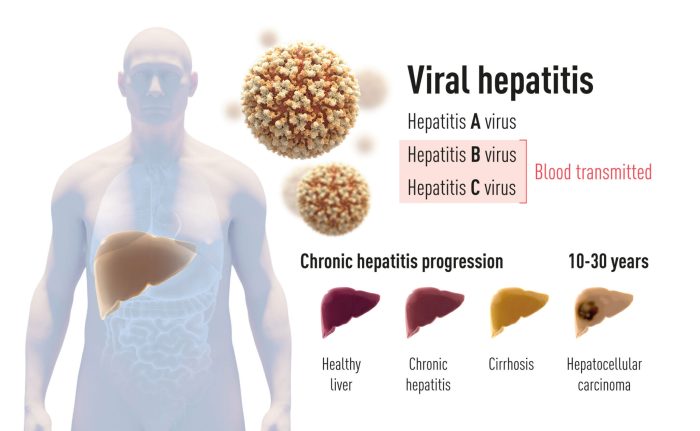
Hepatitis C, while often insidious, is treatable. Effective therapies are available, and early intervention significantly improves outcomes. Understanding the various treatment options and their associated factors is crucial for informed decisions regarding healthcare. Treatment success hinges on adherence to the prescribed regimen and proactive communication with healthcare providers.Treatment for hepatitis C in males focuses on eradicating the virus, preventing further liver damage, and improving overall health.
This often involves a combination of antiviral medications and lifestyle adjustments. Different treatment approaches vary in their effectiveness, side effects, and overall patient experience. The choice of treatment is typically individualized, considering factors such as the specific genotype of the virus, the patient’s overall health, and potential drug interactions.
Available Treatment Regimens
A range of antiviral medications, often in combination, forms the cornerstone of hepatitis C treatment. These drugs target different stages of the viral life cycle, inhibiting its replication and ultimately clearing the infection. The most common types include direct-acting antivirals (DAAs), which are highly effective and have significantly reduced side effects compared to older therapies.
Effectiveness of Different Approaches
The effectiveness of different treatment approaches varies based on several factors. Genotype plays a critical role, as some genotypes respond better to certain medications than others. Additionally, the stage of liver disease and the presence of other health conditions can impact treatment outcomes. Direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) have shown exceptional efficacy in achieving sustained virologic response (SVR), which means the virus is undetectable in the body.
The success rate of these therapies is often high, with some regimens achieving SVR in over 90% of patients.
Importance of Adherence
Adherence to the prescribed treatment plan is paramount for successful hepatitis C eradication. Missing doses or discontinuing treatment prematurely can significantly reduce the effectiveness of the regimen and potentially lead to the development of drug resistance. Regular communication with healthcare providers is essential to address any concerns or difficulties with the treatment plan. Patient education and support play a critical role in fostering adherence.
Comparison of Treatment Options
| Treatment | Description | Effectiveness | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir | A single-tablet combination of direct-acting antivirals | High, often achieving SVR rates above 95% across various genotypes. | Generally well-tolerated, but some patients may experience fatigue, headache, or mild gastrointestinal issues. |
| Glecaprevir/pibrentasvir | Another potent combination of direct-acting antivirals | High effectiveness, typically achieving SVR rates comparable to sofosbuvir/velpatasvir. | Potential for rash, elevated liver enzymes, and, in rare cases, more serious side effects. |
| Ledipasvir/sofosbuvir | A fixed-dose combination of direct-acting antivirals | High efficacy, particularly for genotypes 1 and 4. | Generally well-tolerated with mild side effects, but individual responses may vary. |
| Ribavirin | An older antiviral that is sometimes used in combination with other medications. | Effectiveness varies depending on the genotype and other factors. | Can cause significant side effects, including anemia, fatigue, and birth defects. Generally used less frequently due to the availability of more effective and better-tolerated DAAs. |
Lifestyle and Prevention: Hepatitis C Symptoms In Males
Protecting yourself from Hepatitis C involves a multifaceted approach that goes beyond just avoiding high-risk behaviors. A healthy lifestyle plays a crucial role in bolstering your immune system and overall well-being, making you less susceptible to infections. Understanding and practicing safe habits can significantly reduce the risk of contracting this virus.
Safe Practices and Avoiding High-Risk Behaviors
Safe practices are paramount in preventing Hepatitis C transmission. These practices encompass a wide range of behaviors, all aimed at reducing exposure to the virus. Avoiding risky behaviors, such as sharing needles or engaging in unprotected sexual activity with an infected partner, are crucial steps in personal safety. This approach, combined with proactive healthcare choices, significantly minimizes the chances of infection.
Significance of Preventive Measures
Preventive measures are essential in reducing the spread of Hepatitis C. Early detection and prompt treatment of infections are critical to limiting transmission. The importance of preventive measures lies in their ability to safeguard public health and reduce the burden of this chronic illness. Public awareness campaigns and education programs play a significant role in disseminating information about preventive measures and their efficacy.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Hepatitis C Risk
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce your risk of Hepatitis C infection. This involves focusing on a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep. These practices contribute to a strong immune system, making it less likely for the virus to take hold.
| Lifestyle Change | Description | Benefit | Implementation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Balanced Diet | A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides essential nutrients to support a healthy immune system. | Stronger immune response, reduced inflammation. | Plan meals around nutrient-rich foods. Include a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive saturated and unhealthy fats. |
| Regular Exercise | Physical activity strengthens the cardiovascular system and boosts the immune system, making the body more resilient to infections. | Improved cardiovascular health, enhanced immune function. | Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week. Include strength training exercises twice a week. |
| Stress Management | Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, making individuals more vulnerable to infections. | Reduced stress levels, improved immune response. | Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or spending time in nature. Seek professional help if stress becomes overwhelming. |
| Adequate Sleep | Sufficient sleep is crucial for the body’s natural repair and recovery processes, including immune function. | Improved immune function, better overall health. | Establish a regular sleep schedule. Create a relaxing bedtime routine. Ensure a dark, quiet, and comfortable sleep environment. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. |
Illustrative Case Studies (No Image Links)
Understanding Hepatitis C requires looking at how it affects different individuals. Real-world case studies highlight the variability in symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment responses. These examples demonstrate the importance of personalized healthcare approaches.Real-life experiences, while anonymized, can help illustrate the complexity of Hepatitis C and how various factors influence its course. Individual variations in symptoms and treatment outcomes emphasize the need for tailored medical care.
Case Study 1: Typical Presentation
This hypothetical case study Artikels a typical presentation of Hepatitis C in a male patient. John, a 45-year-old male, reported fatigue, mild jaundice, and abdominal discomfort. These symptoms were persistent for several months, and gradually worsened. He also noted occasional joint pain.John’s liver function tests revealed elevated liver enzymes, a key indicator of liver damage. Further blood tests confirmed the presence of Hepatitis C antibodies.
Molecular testing pinpointed the specific genotype of the virus, which influenced the subsequent treatment plan.Treatment for John involved a combination antiviral therapy, which was well-tolerated. Regular monitoring of liver function and viral load was crucial throughout the treatment period. The treatment successfully suppressed the virus, and John experienced a significant improvement in his symptoms over time. His recovery trajectory demonstrates the effectiveness of current antiviral therapies when implemented early.
Case Study 2: Atypical Presentation
This case study illustrates an atypical presentation of Hepatitis C. David, a 30-year-old male, experienced a gradual decline in energy and muscle weakness. While he initially attributed these symptoms to stress, they persisted and worsened over time. He also experienced unexplained weight loss and night sweats. Liver function tests revealed mild abnormalities.David’s symptoms were not directly related to the liver, which made the diagnosis more challenging.
While initial blood tests suggested possible viral infections, it wasn’t until more specialized tests were conducted that Hepatitis C was identified. The atypical symptom presentation and a delay in diagnosis impacted the timing of treatment initiation.David’s treatment response was initially slower compared to John’s. The specific genotype of the virus and other factors like concurrent conditions influenced the choice of treatment regimen.
This case highlights the importance of a thorough evaluation, including blood tests and possibly liver biopsies, to identify and diagnose Hepatitis C, even when symptoms are not typical.
Individual Variation in Response to Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C affects individuals differently. Factors such as the specific genotype of the virus, the patient’s overall health, and the presence of other conditions can significantly impact the disease progression and response to treatment. Individual variation underscores the need for personalized treatment strategies. No two patients experience the same trajectory of the disease, and treatment strategies must be adjusted accordingly.
Summary Table
| Case Study | Symptoms | Diagnosis | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| John (Typical) | Fatigue, mild jaundice, abdominal discomfort, joint pain | Elevated liver enzymes, Hepatitis C antibodies, specific genotype identified | Combination antiviral therapy, monitoring of liver function and viral load |
| David (Atypical) | Fatigue, muscle weakness, weight loss, night sweats | Specialized testing, blood tests, and possibly liver biopsies | Tailored antiviral regimen, considering the specific genotype of the virus and other factors |
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, understanding hepatitis C symptoms in males is vital for early intervention and improved health outcomes. The multifaceted nature of this condition necessitates a personalized approach to diagnosis, treatment, and lifestyle management. Remember, early detection and adherence to treatment plans are paramount for managing the condition effectively.
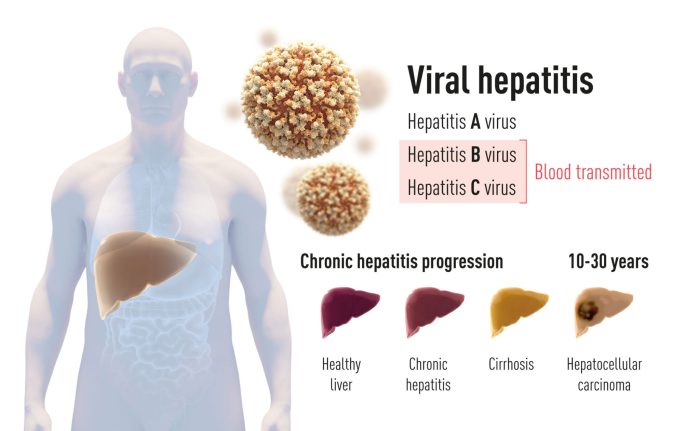

Leave a Reply