Drusen meaning and types sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a detailed exploration of these small, often overlooked structures in the eye. We’ll delve into the different types, their potential impact on vision, and the various associated conditions. Understanding drusen’s significance is crucial for anyone concerned about eye health.
This comprehensive guide provides a concise definition of drusen, explains their location and formation in the eye, and details their typical characteristics. We’ll explore the different types of drusen, discussing their unique features, underlying causes, and potential impact on vision. Furthermore, we’ll investigate the relationship between drusen and various eye diseases, highlighting the diagnostic methods and management strategies.
Introduction to Drusen
Drusen are tiny, yellowish deposits that commonly form in the macula, a crucial part of the retina responsible for central vision. They are a frequent finding during eye examinations, particularly in older individuals. These deposits, while often benign, can sometimes be associated with underlying conditions, warranting further investigation. Understanding drusen is vital for proper diagnosis and management.Drusen typically develop in the extracellular matrix of the retina, specifically within the Bruch’s membrane.
This membrane acts as a vital barrier between the retinal pigment epithelium and the choroid, the vascular layer beneath. Accumulation of these deposits can potentially disrupt the delicate balance of this structure, impacting retinal function over time. The exact mechanisms behind drusen formation are still being investigated, but genetic predisposition, age-related changes, and environmental factors are thought to play a role.
Drusen Characteristics
Drusen are microscopic, often appearing as yellowish-white or slightly gray spots in the retinal tissue. Their size varies, typically ranging from less than 100 microns to several hundred microns in diameter. Shape can range from round to oval, and their appearance may differ depending on the specific type. The appearance and distribution of drusen can be important clues for diagnosis and prognosis.
Common Symptoms Associated with Drusen, Drusen meaning and types
While many individuals with drusen experience no noticeable symptoms, some may experience mild vision changes, such as blurring or reduced sharpness. These changes are often subtle and may not be readily apparent without a comprehensive eye examination. It’s important to remember that drusen themselves do not directly cause pain. However, associated conditions might present with pain.
Classification of Drusen
Drusen are often categorized based on their appearance, location, and potential association with other eye conditions. This classification aids in assessing the potential implications of drusen.
Drusen, tiny yellowish spots on the retina, come in various types, each with slightly different characteristics. While understanding these types is important for diagnosis, sometimes similar skin issues, like scabs on the scalp, can mimic some retinal conditions. If you’re experiencing scalp issues, checking out resources like scabs on scalp causes diagnosis and treatment might help.
Regardless, proper diagnosis of drusen types relies on thorough eye exams and professional guidance.
| Drusen Type | Location | Characteristics | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Drusen | Bruch’s membrane | Small, homogenous, and often multiple; typically yellowish-white; relatively benign | Usually asymptomatic, or mild, subtle vision changes like blurring |
| Hard Drusen | Bruch’s membrane | Larger, more densely pigmented; can appear as raised or prominent; often associated with other retinal changes | Potentially associated with vision loss, but often no obvious symptoms initially |
| Soft Drusen | Bruch’s membrane | Smaller, more translucent; may appear diffuse or spread out; can be difficult to distinguish from simple drusen; often associated with age | Generally asymptomatic or mild vision changes |
| Geographic Drusen | Bruch’s membrane | Larger and often irregular in shape, frequently clustered together in a distinct area | May cause some degree of vision impairment depending on the extent of the drusen formation and its impact on the macula |
Types of Drusen
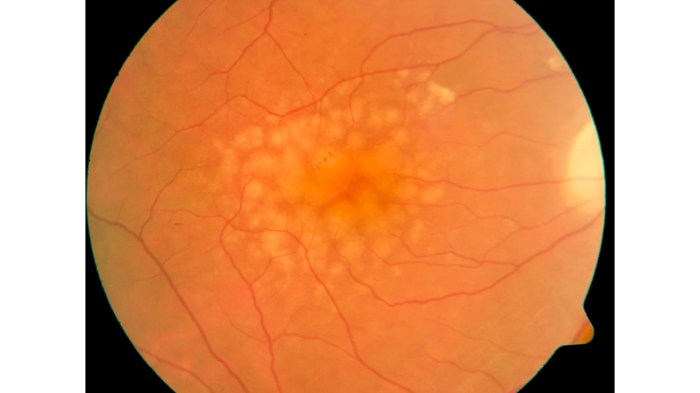
Drusen are microscopic deposits that can accumulate in the macula, a crucial part of the retina responsible for sharp central vision. Understanding the various types of drusen is essential for accurate diagnosis and management of macular diseases. Their diverse characteristics, from appearance to underlying causes, can influence the course of the disease and the best treatment strategies.
Classification of Drusen
Drusen are categorized based on their microscopic structure and appearance. This classification helps ophthalmologists differentiate between different types and assess the potential risk of macular degeneration. Precise identification allows for tailored treatment plans, aiming to mitigate the progression of vision loss.
Types, Descriptions, and Causes of Drusen
| Type | Description | Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Hard Drusen | Hard drusen are characterized by their dense, homogenous appearance. They appear as yellowish-white deposits under the retina. Microscopic examination reveals a tightly packed, compact structure composed primarily of extracellular material. | Hard drusen are generally considered to be a normal part of aging. Their formation is linked to the accumulation of extracellular debris and lipids in the Bruch’s membrane. Genetic predisposition and environmental factors may also play a role. |
| Soft Drusen | Soft drusen, in contrast, have a more diffuse and irregular appearance. Microscopically, they exhibit a less organized structure with a greater amount of extracellular material compared to hard drusen. They are usually smaller in size and less dense. | The exact causes of soft drusen formation are not fully understood, but they are also associated with the accumulation of extracellular debris in Bruch’s membrane. Certain genetic predispositions may influence the development of soft drusen. Environmental factors, such as oxidative stress and exposure to certain chemicals, could also play a role. |
| Large Drusen | Large drusen are defined by their larger size compared to both hard and soft drusen. They can sometimes be associated with increased risk of macular degeneration, though not always. The appearance varies depending on the composition and structure. | Large drusen often correlate with a combination of factors that accelerate the accumulation of extracellular material in Bruch’s membrane. These factors can include genetic predispositions, environmental stressors, and the natural aging process. The exact causal interplay is complex and under active investigation. |
Drusen and Associated Conditions
| Drusen Type | Appearance | Underlying Causes | Associated Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hard Drusen | Yellowish-white, dense, homogenous deposits | Accumulation of extracellular material, lipids, and potential genetic/environmental factors | Age-related macular degeneration (AMD), though not always a direct cause, but can be associated with AMD |
| Soft Drusen | Diffuse, irregular, smaller deposits | Accumulation of extracellular material, possible genetic and environmental factors | Increased risk of AMD, especially when in large clusters or accompanied by other retinal changes. |
| Large Drusen | Larger size compared to other types, appearance varies | Combination of factors that accelerate extracellular material accumulation in Bruch’s membrane, possibly including genetic predisposition, environmental stressors, and the aging process | Increased risk of AMD, but not always a definitive indicator. |
Drusen and Associated Conditions
Drusen, while often benign, can sometimes be associated with underlying eye conditions. Understanding this connection is crucial for early detection and appropriate management. The relationship between drusen and other eye diseases is complex, and the specific mechanisms involved are still under investigation. However, accumulating evidence suggests a potential role for drusen in the development or progression of certain conditions.Drusen are microscopic deposits that accumulate beneath the retina, the light-sensitive tissue lining the back of the eye.
While often asymptomatic, their presence can indicate a higher risk of developing age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and other ocular disorders. The nature of this association is still actively researched, and more information is needed to fully understand the mechanisms involved.
Potential Link to Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
Drusen are a significant risk factor for age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Studies have shown a strong correlation between the presence and characteristics of drusen and the development or progression of AMD. The accumulation of drusen can lead to the breakdown of the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp vision. This breakdown can cause vision loss and impairment.
In particular, large, hyper-reflective drusen are often associated with a greater risk of developing advanced AMD. Furthermore, the presence of drusen, especially in conjunction with other risk factors, can increase the likelihood of vision loss.
Drusen are tiny yellow deposits that can form in the macula, the central part of the retina. Different types exist, and while they’re often harmless, they can sometimes affect vision. Interestingly, recent studies on teen mental health during the pandemic, like the one found at pandemic teen mental health study , highlight the impact of stress on overall well-being.
This could potentially correlate with the prevalence of certain eye conditions, including drusen formation, though more research is needed to understand the precise connection. Understanding drusen and their various types is crucial for early detection and proper management.
Symptoms Associated with Drusen and Related Eye Conditions
Various symptoms can manifest when drusen are present in conjunction with specific eye diseases. Early detection is crucial, as these symptoms can often be subtle in the initial stages.
- Decreased visual acuity: A gradual decline in the ability to see fine details. This can be a common symptom of both drusen and AMD. In cases of advanced AMD, central vision can become significantly impaired.
- Blurred vision: A sense of haziness or indistinctness in vision. Blurred vision can be an early sign of progressive macular damage.
- Distortion of vision: Straight lines appearing wavy or crooked. This is a particular concern in cases of advanced AMD.
- Dark spots or blind spots in the center of vision: These are more pronounced signs of macular damage. They may appear gradually or suddenly, depending on the progression of the disease.
Diagnostic Methods for Drusen and Related Conditions
Several diagnostic methods are used to identify drusen and related eye conditions. These methods allow ophthalmologists to evaluate the retina and surrounding structures to determine the presence, size, and characteristics of drusen and assess any potential underlying conditions.
- Slit-lamp examination: This non-invasive procedure allows for a detailed view of the front structures of the eye, including the conjunctiva, cornea, and anterior chamber. Drusen are sometimes visible during this examination.
- Fundus photography: Images of the retina are taken, allowing for detailed visualization of drusen and their distribution. This technique can help in tracking changes over time.
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT): This advanced imaging technique provides detailed cross-sectional images of the retina and choroid. OCT can precisely measure the thickness of the retina and help identify drusen and associated macular changes.
- Fluorescein angiography: This procedure involves injecting a dye into the bloodstream and taking images of the retinal blood vessels. This technique can reveal the presence of choroidal neovascularization (CNV), a potential complication of AMD, which may be associated with certain types of drusen.
Comparison Table: Drusen vs. Similar Eye Conditions
| Feature | Drusen | Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) | Choroidal Neovascularization (CNV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | Often asymptomatic, may present with mild vision changes. | Gradual loss of central vision, distortion, dark spots, or blind spots. | Can occur with AMD, characterized by new blood vessel growth under the macula, potentially causing vision loss. |
| Cause | Accumulation of extracellular debris in the choroid. | Combination of genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and aging. | Often a complication of AMD. |
| Treatment | Generally no specific treatment, management of associated conditions. | Treatment focuses on slowing progression, includes supplements, and in advanced stages, potential laser therapy or injections. | Laser therapy or injections to stop or reduce abnormal blood vessel growth. |
Drusen and Visual Function

Drusen are yellowish deposits that can accumulate in the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp central vision. While often benign, their presence can sometimes affect visual function. Understanding the potential impact of drusen on vision is crucial for early detection and appropriate management.The relationship between drusen and visual function is complex and not always straightforward.
While some individuals with drusen experience no visual changes, others may notice subtle or significant impacts on their vision, including decreased visual acuity and changes in their visual field. Factors such as drusen size, location, and the presence of other ocular conditions play a crucial role in determining the extent of the visual impact.
Impact on Visual Acuity and Field
Drusen can potentially affect visual acuity, the sharpness of central vision, and the visual field, the entire area that can be seen when looking straight ahead. The impact is not always proportional to the size of the drusen. In some cases, even large drusen may not cause significant visual impairment, while smaller drusen in a critical location can have a notable effect.
This highlights the need for careful evaluation by an ophthalmologist.
Relationship Between Drusen Size and Visual Impact
The size of drusen is a key factor in assessing potential visual impact. Generally, larger drusen, especially those located in the macula, are more likely to cause a greater degree of visual disturbance. However, this is not a universal rule. Individual responses to drusen vary, and other factors, such as the presence of macular degeneration, can significantly influence the visual outcome.
For instance, a small drusen in a person with pre-existing age-related macular degeneration could have a disproportionately greater impact compared to a large drusen in someone with no other eye conditions.
Factors Influencing the Impact of Drusen on Vision
Several factors can influence the visual impact of drusen. These include the drusen’s location within the macula, the presence of other eye conditions (such as age-related macular degeneration), and the individual’s overall health. For example, a drusen cluster near the fovea (the central point of the macula) may have a more pronounced effect on central vision than a similar-sized drusen in a peripheral location.
The presence of other conditions, like macular degeneration, can increase the susceptibility to vision loss from drusen.
Comparison of Visual Effects of Different Drusen Types
Different drusen types may exhibit varying visual effects. For example, a high density of drusen or a specific type of drusen accumulation might be more likely to cause visual issues. Furthermore, the presence of drusen associated with other macular conditions can significantly affect vision.
Visual Impact of Drusen Types
| Drusen Type | Visual Impact | Associated Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Small, isolated drusen | Minimal or no visual impact | No noticeable symptoms |
| Large, confluent drusen (clusters of drusen) | Potential for reduced visual acuity and field | Blurred vision, reduced central vision, or peripheral vision loss |
| Drusen associated with other macular conditions (e.g., AMD) | Increased risk of significant visual loss | Progression of vision loss, potentially leading to legal blindness |
Drusen Management and Treatment: Drusen Meaning And Types
Drusen, while often benign, can sometimes be associated with underlying eye conditions or contribute to visual impairment. Effective management of drusen focuses on preventative measures, supportive care, and monitoring for potential complications. This approach often involves a multidisciplinary team and regular eye examinations.Drusen management primarily emphasizes proactive strategies to maintain good eye health and address any potential complications.
Regular check-ups, lifestyle adjustments, and prompt treatment of related eye diseases are crucial for preserving vision and overall well-being.
Drusen are those little yellowish deposits often found in the macula, affecting vision. They come in different types, each with varying implications for eye health. Understanding these types is crucial for proper diagnosis and management. Sometimes, similar issues can arise in the shoulder, like calcific tendonitis, which requires specific treatment approaches, such as those detailed in this resource on treatment options for calcific tendonitis of the shoulder.
Regardless, careful monitoring and appropriate care are key to managing drusen and maintaining good eye health.
Common Management Strategies
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and adequate hydration, plays a significant role in overall eye health and potentially in slowing the progression of drusen. Avoiding smoking and excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light can also be beneficial.
- Preventative Care: A healthy diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep are vital for overall health, including eye health. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids may help protect against oxidative stress, which could potentially contribute to drusen formation or progression. Avoiding smoking and limiting exposure to UV radiation are also important.
- Supportive Care: This involves managing any related eye conditions, such as glaucoma or macular degeneration. Treating conditions like dry eye syndrome and addressing any associated vision problems can help improve quality of life. Proper eyeglass or contact lens prescription adjustments may also be necessary.
Potential Treatments for Drusen-Related Eye Diseases
Treatment for drusen itself is not usually necessary, but associated conditions may require specific interventions. For instance, if drusen is associated with macular degeneration, treatments targeting the underlying disease process might be considered.
- Treatment for Macular Degeneration: If drusen is linked to age-related macular degeneration (AMD), treatment options may include anti-VEGF injections to reduce abnormal blood vessel growth, or other therapies as prescribed by the ophthalmologist.
- Treatment for Glaucoma: If glaucoma is present, the treatment will focus on reducing intraocular pressure to prevent further damage to the optic nerve. Medications, laser treatments, or surgery may be necessary.
Role of Regular Eye Examinations
Regular eye examinations are crucial for monitoring drusen and detecting any associated changes or complications early. Early detection allows for timely intervention and management, potentially slowing progression and preserving vision.Regular eye exams are vital for identifying any changes in the appearance or size of drusen, or for detecting the onset of associated eye conditions like glaucoma or macular degeneration.
This proactive approach allows for early intervention and potential prevention of further complications.
Types of Professionals Involved
A multidisciplinary approach involving several healthcare professionals is often employed in managing drusen and related conditions. Ophthalmologists are crucial in diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring.
- Ophthalmologists: Ophthalmologists are medical doctors specializing in eye care and are essential for diagnosing drusen and related conditions, such as macular degeneration or glaucoma. They perform examinations, interpret results, and manage associated treatments.
- Optometrists: Optometrists are healthcare professionals who examine the eyes, diagnose vision problems, and prescribe eyeglasses or contact lenses. They can play a supportive role in managing drusen and related visual concerns.
- Optometric Assistants: Optometric assistants provide support to optometrists and ophthalmologists during eye examinations and other procedures.
Diagnostic and Management Flowchart
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Initial eye examination by optometrist or ophthalmologist, including visual acuity and fundus examination. |
| 2 | If drusen detected, further evaluation by ophthalmologist to assess size, density, and location. |
| 3 | Assessment for associated conditions like glaucoma or macular degeneration. |
| 4 | Monitoring drusen progression through regular follow-up examinations. |
| 5 | Management of any associated conditions (e.g., glaucoma treatment, macular degeneration therapies). |
Drusen and Research
Drusen, those yellowish deposits in the macula, continue to fascinate and challenge researchers. Understanding their formation, progression, and potential link to age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is crucial for developing effective preventative and therapeutic strategies. Current research is exploring multiple avenues to unravel the mysteries surrounding these deposits.Recent studies have shed light on the complex interplay of genetic predispositions, environmental factors, and lifestyle choices that influence drusen development.
This understanding is essential for targeted interventions. New technologies and approaches are rapidly changing the landscape of drusen research.
Current Research Areas
Research into drusen focuses on several key areas. These include investigating the precise cellular and molecular mechanisms driving drusen formation, exploring the genetic factors that contribute to drusen accumulation, and identifying biomarkers that could predict drusen progression and associated conditions. Researchers are also examining the role of inflammation and oxidative stress in drusen development.
Potential of New Technologies
Advancements in imaging techniques, such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) and adaptive optics, are revolutionizing our ability to visualize and characterize drusen. These technologies allow for detailed analysis of drusen structure and composition, enabling researchers to identify subtle changes associated with disease progression. Furthermore, the application of artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze vast amounts of OCT data holds promise for developing automated diagnostic tools for drusen-related conditions.
Genetic sequencing and bioinformatics approaches are also providing valuable insights into the complex genetic underpinnings of drusen formation.
Knowledge Gaps
Despite significant progress, several knowledge gaps remain in our understanding of drusen. The precise mechanisms by which drusen form and grow are not fully elucidated. The relationship between drusen morphology and clinical outcomes, such as visual impairment, is still under investigation. Moreover, the long-term effects of different risk factors on drusen development and progression need further study.
Finally, a deeper understanding of the specific cellular and molecular components within drusen themselves is crucial.
New Treatments and Preventative Measures
Ongoing efforts to develop new treatments and preventative measures for drusen and related conditions are focused on several strategies. These include identifying and targeting key molecules involved in drusen formation, as well as exploring novel therapies to modulate inflammation and oxidative stress. Some researchers are investigating the potential of anti-angiogenic therapies to mitigate the progression of drusen-associated AMD.
Clinical trials are underway to evaluate the efficacy of various approaches in preventing or slowing drusen accumulation.
Key Research Questions
- What are the specific cellular and molecular pathways involved in drusen formation?
- How do genetic factors influence the risk and progression of drusen?
- Can specific biomarkers be identified to predict the development and progression of drusen-related conditions?
- What role do environmental factors, such as diet and lifestyle, play in drusen formation?
- Can novel therapies be developed to prevent or slow the progression of drusen accumulation?
- How can AI-driven analysis of imaging data be used to improve early diagnosis and monitoring of drusen?
Last Word
In conclusion, drusen, while seemingly minor, can have significant implications for eye health. This exploration of their meaning and types provides a deeper understanding of these structures and their potential connection to vision loss. Recognizing the potential impact of drusen and associated conditions underscores the importance of regular eye exams and appropriate management strategies. Further research continues to unveil more about these fascinating structures, ensuring that future generations will benefit from a more comprehensive understanding of their role in eye health.




