Daith piercing for migraine relief has sparked much interest, offering a potential alternative therapy for those seeking relief from these debilitating headaches. This exploration delves into the intriguing connection between a tiny ear piercing and a significant health concern. We’ll examine the science, the potential benefits, the risks, and ultimately, the importance of informed decisions when considering this unconventional approach.
Daith piercings are a relatively common form of body modification, involving a small puncture in the daith cartilage of the ear. The daith area is anatomically unique, and the procedure itself is relatively straightforward, though it requires proper aftercare. Migraines, on the other hand, are a complex neurological disorder with a range of potential triggers and symptoms. Understanding both the piercing and the migraine is crucial to navigating the potential connection.
Introduction to Daith Piercings
A daith piercing is a popular body modification that involves piercing the daith cartilage, a specific area within the ear. This delicate cartilage, located near the outer edge of the ear, is known for its unique anatomical structure and the potential for specific physiological responses. The piercing itself typically involves a small, stud-like piece of jewelry, which, when properly cared for, heals well.The daith area is situated within the intricate network of the ear’s cartilage, and its positioning and anatomical relationship to other structures in the ear contribute to the unique aspects of this piercing.
Understanding the ear’s anatomy and the daith cartilage’s location is crucial for a successful healing process. The daith cartilage is thinner than other ear cartilages, which requires particular care and attention to aftercare instructions.
Daith Piercing Procedure
The procedure for a daith piercing is generally straightforward. A skilled piercer will use a sterile needle to create a small puncture in the daith cartilage. Local anesthetic is often used to minimize discomfort during the procedure. The piercer will then insert the chosen jewelry, ensuring proper placement and alignment. Post-piercing care is crucial for successful healing and minimizing complications.
Daith Piercing Aftercare
Proper aftercare is essential for a daith piercing to heal without complications. This involves meticulous cleaning of the piercing site, using saline solutions or recommended aftercare products, as instructed by the piercer. It’s vital to avoid picking or touching the piercing site, and to maintain good hygiene practices to prevent infection. A piercer’s specific aftercare instructions should be followed closely.
Types of Daith Piercings
Different daith piercings can be categorized by the number of piercings and the type of jewelry used.
| Type | Jewelry Types | Healing Time (approx.) | Potential Complications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Daith | Small studs, hoops (generally small in size) | 6-8 weeks | Infection, rejection, jewelry migration |
| Double Daith | Small studs, or a single barbell with two ends | 6-8 weeks | Infection, rejection, jewelry migration, uneven healing |
| Multiple Daith | Variety of jewelry options, including bars, hoops, or combinations | Variable, depends on the number of piercings | Infection, rejection, jewelry migration, uneven healing, potential for cartilage damage if not properly spaced |
Note: Healing times and potential complications may vary depending on individual factors such as skin type, aftercare adherence, and piercer skill.
Migraine Overview
Migraines are debilitating neurological disorders that affect millions worldwide. They are characterized by severe, throbbing head pain, often accompanied by other symptoms that can significantly impact daily life. Understanding the causes, types, and impact of migraines is crucial for effective management and treatment.Migraines are complex and not fully understood, but research suggests a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors plays a role in their development.
The exact mechanisms triggering migraine attacks remain a subject of ongoing investigation, but current understanding points towards disruptions in the brain’s neural pathways and vascular system.
Biological Causes of Migraines
The precise biological mechanisms behind migraines are still under investigation. However, research suggests a complex interplay of factors, including genetics, environmental triggers, and hormonal fluctuations. Neurochemical imbalances, such as changes in serotonin levels, and alterations in the brain’s blood flow regulation are suspected to be key components in the development of a migraine attack. Furthermore, the activation of trigeminal nerve pathways, which transmit pain signals to the brain, seems to be a crucial aspect in migraine initiation and progression.
Symptoms and Diagnostic Criteria for Migraines
Migraines are typically characterized by severe, throbbing head pain, often unilateral (on one side of the head). The pain is often described as pulsating and can be aggravated by routine physical activity. Common accompanying symptoms include nausea, vomiting, and extreme sensitivity to light and sound (photophobia and phonophobia). Diagnostic criteria for migraines are Artikeld by the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD-3).
These criteria consider the duration, frequency, and associated symptoms of the headaches to differentiate migraines from other types of headaches. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management.
Classification of Migraine Types
Migraines are classified into different types based on their frequency and characteristics. Episodic migraines are characterized by attacks that occur less than 15 days per month. In contrast, chronic migraines occur on 15 or more days per month. Furthermore, some migraines are classified by their accompanying symptoms, such as aura migraines, which are preceded by sensory disturbances (visual, sensory, or language).
Other subtypes include hemiplegic migraine (with neurological symptoms) and basilar migraine (affecting brainstem functions).
Impact on Daily Life and Quality of Life
Migraines can significantly impact daily life and quality of life. The intensity of the pain and accompanying symptoms can limit an individual’s ability to work, attend school, or participate in social activities. The unpredictability of migraine attacks can lead to anxiety and stress, further compounding the negative impact on overall well-being. Chronic migraine sufferers often experience significant impairment in their ability to perform routine tasks and maintain social connections.
Migraine Triggers
Understanding migraine triggers is crucial for prevention and management. Different triggers affect individuals differently, highlighting the personalized nature of migraines. A variety of factors can initiate or exacerbate migraine attacks.
| Category | Trigger Example | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lifestyle Factors | Lack of sleep | Insufficient sleep duration or poor sleep quality. | Increases susceptibility to migraine attacks. |
| Lifestyle Factors | Skipping meals | Irregular eating patterns or prolonged periods without food. | Can lead to low blood sugar levels, triggering a migraine. |
| Environmental Elements | Changes in weather | Sudden shifts in temperature, barometric pressure, or humidity. | Can trigger migraines in susceptible individuals. |
| Environmental Elements | Strong smells | Exposure to perfumes, smoke, or other potent odors. | Irritates the nervous system and can induce migraines. |
| Emotional Stressors | Stressful events | Major life changes, work-related pressure, or personal conflicts. | Can increase the likelihood and intensity of migraine attacks. |
| Emotional Stressors | Anxiety | Increased levels of anxiety and emotional distress. | Can act as a trigger, influencing the body’s response to pain signals. |
Daith Piercing and Migraine
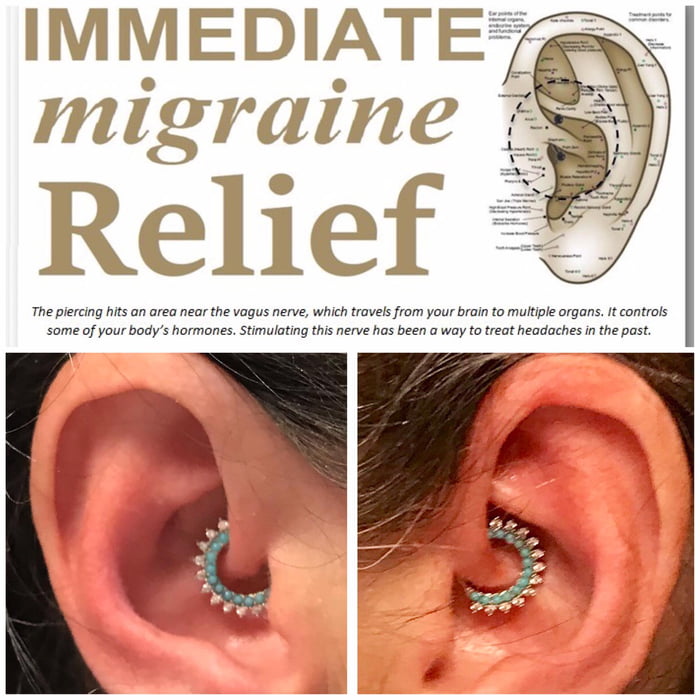
The allure of alternative remedies for migraines is undeniable. Many people seek holistic approaches, and among these, the daith piercing has gained some traction as a potential migraine relief strategy. While anecdotal evidence suggests a link, rigorous scientific investigation is crucial to understanding the potential correlation and the underlying mechanisms.The potential correlation between daith piercings and migraine relief is a topic that sparks considerable interest.
Many individuals claim that getting a daith piercing can reduce or even eliminate their migraine frequency and intensity. However, it’s important to approach these claims with a critical eye, recognizing that personal experiences don’t always translate into scientifically validated results.
Potential Mechanisms of Action
Several theories attempt to explain the possible migraine-reducing effects of a daith piercing. One popular theory suggests that the piercing stimulates specific nerves in the ear, which may influence pain pathways in the brain. Another theory proposes that the piercing creates a sensory input that can potentially distract or redirect the brain’s focus from migraine triggers. Furthermore, some believe that the localized inflammation or the body’s response to the piercing might have an impact on migraine triggers, though this lacks scientific backing.
I’ve been reading a lot about daith piercings for migraine relief lately, and it’s fascinating how some people find relief. It’s a pretty common holistic approach, but it’s important to remember that individual results vary. Finding ways to manage migraine symptoms holistically can be really helpful, and that might include paying attention to the foods that make you feel full.
Foods that make you feel full are crucial for overall well-being and can play a role in reducing cravings and potentially stabilizing blood sugar, both of which might indirectly impact migraine frequency. Ultimately, if you’re considering a daith piercing for migraine, it’s best to talk to your doctor or a qualified professional to see if it’s the right choice for you.
Anecdotal Evidence and Theories
Numerous individuals report experiencing reduced migraine frequency or severity after receiving a daith piercing. These accounts, while compelling, aren’t scientific evidence. These anecdotal experiences are often based on personal observations and are not controlled or verified in a scientific setting. The subjective nature of migraine pain makes it challenging to definitively quantify the effects of a daith piercing.
Physiological Reasons for Lack of Scientific Support
The lack of strong scientific support for a causal link between daith piercings and migraine relief can be attributed to several physiological factors. The complex nature of migraine, involving multiple factors like genetics, environmental stimuli, and hormonal fluctuations, makes it difficult to isolate the effects of a daith piercing. Furthermore, there’s a lack of controlled clinical trials that rigorously evaluate the impact of daith piercings on migraine frequency and intensity.
It’s crucial to recognize that the human body is a complex system, and the interaction of various factors makes it challenging to isolate the effect of a daith piercing.
Studies Investigating the Correlation
While there’s a significant gap in rigorous scientific studies, a few investigations have explored the potential connection between daith piercings and migraines. However, these studies often suffer from methodological limitations, making it difficult to draw definitive conclusions. A systematic review of the existing research is necessary to understand the strengths and weaknesses of each study.
| Study | Methodology | Findings | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example Study 1 | Case series of patients with migraine reporting experiences with daith piercings. | Some participants reported decreased migraine frequency. | Lack of control group, small sample size, subjective reporting. |
| Example Study 2 | Observational study comparing migraine frequency in individuals with and without daith piercings. | No statistically significant difference in migraine frequency was observed. | Confounding factors, limited data collection. |
| Example Study 3 | Review of existing literature. | Limited evidence of a direct correlation between daith piercings and migraine relief. | Heterogeneity of studies, methodological flaws in many studies. |
Alternative Therapies for Migraine Relief
Beyond conventional treatments, a range of alternative therapies are explored for migraine relief. These methods often target underlying causes and address symptoms holistically, appealing to those seeking complementary approaches to manage their migraines. While not a replacement for medical advice, these therapies can potentially complement existing treatment plans.Alternative therapies for migraines vary significantly in their mechanisms of action, and the evidence supporting their effectiveness is often less robust than that for conventional medications.
It’s crucial to consult with healthcare professionals before incorporating any new therapy into a migraine management plan, especially those with pre-existing health conditions or on medication. The potential benefits and drawbacks of each approach need careful consideration.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine practice, involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. Advocates suggest that acupuncture stimulates the flow of energy (Qi) and balances the body’s natural healing mechanisms. Clinical trials have yielded mixed results regarding its effectiveness for migraine prevention and treatment. Some studies show a reduction in migraine frequency and intensity, while others find no significant difference compared to placebo.
The safety profile of acupuncture is generally considered good, although potential side effects such as bruising, bleeding, and infection at the insertion site are possible. Individual tolerance varies.
Biofeedback
Biofeedback techniques train individuals to become aware of and control physiological responses, such as heart rate, muscle tension, and blood pressure. By monitoring these responses through instruments, patients learn to modify their body’s reactions to stressors, potentially mitigating migraine triggers. Evidence suggests that biofeedback can help manage migraine symptoms, though the long-term effectiveness for prevention isn’t definitively established.
The safety of biofeedback is generally considered high, with potential side effects limited to discomfort or anxiety during the learning process. Regular practice and patient engagement are essential for success.
Dietary Changes
Dietary modifications can play a crucial role in managing migraines. Identifying and eliminating trigger foods, such as certain types of cheeses, processed foods, or chocolate, can reduce migraine frequency. The impact of dietary changes can vary greatly from individual to individual. Careful dietary planning and tracking can help pinpoint problematic foods and contribute to better migraine management.
The safety of dietary changes is generally high, but specific dietary restrictions may require careful planning to avoid nutrient deficiencies. Consulting a registered dietitian or nutritionist can be helpful in developing a tailored dietary plan.
Massage Therapy
Massage therapy involves manipulating soft tissues of the body to relieve muscle tension, reduce stress, and promote relaxation. Massage therapy is frequently cited as a complementary therapy for migraine relief. Studies suggest that massage therapy can reduce migraine frequency and intensity in some individuals. The safety of massage therapy is generally considered high, but potential side effects, such as bruising or soreness, are possible.
Ever considered a daith piercing for migraine relief? It’s a fascinating alternative treatment, but as with any health decision, it’s essential to understand the potential risks and benefits. Thinking about other health considerations, it’s important to be aware of the safety of the flu shot for individuals with diabetes, and the factors to consider when making decisions on your health.
This resource, diabetes and the flu shot is it safe , offers valuable insight into the subject. Ultimately, a thorough discussion with a healthcare professional is crucial for determining the best course of action for any health concern, including daith piercings for migraine management.
The type of massage, the therapist’s experience, and the individual’s sensitivity should be carefully considered.
Lifestyle Modifications for Migraine Management
Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, managing stress effectively, and practicing regular exercise are crucial lifestyle modifications for migraine management. Consistent sleep patterns can stabilize the body’s natural rhythms, which can influence migraine triggers. Effective stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help reduce the impact of stress on migraine frequency. Regular exercise, along with a balanced diet, contributes to overall well-being and may help regulate hormonal fluctuations, potentially influencing migraine patterns.
These lifestyle adjustments should be tailored to individual needs and preferences, incorporating strategies that promote both physical and mental well-being.
Comparison of Alternative Therapies
| Therapy | Effectiveness | Safety | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acupuncture | Mixed results; some studies show effectiveness, others don’t. | Generally considered safe, but potential for bruising, bleeding, or infection. | Bruising, bleeding, infection at insertion site. |
| Biofeedback | May help manage symptoms, but long-term prevention is unclear. | Generally safe; discomfort or anxiety during training possible. | Discomfort, anxiety during training. |
| Dietary Changes | Varied; identifying and eliminating triggers can reduce frequency. | Generally safe, but potential for nutrient deficiencies if not planned carefully. | Potential nutrient deficiencies if not planned properly. |
| Massage Therapy | May reduce frequency and intensity in some individuals. | Generally safe, but potential for bruising or soreness. | Bruising, soreness. |
Importance of Professional Advice
While the idea of a daith piercing offering migraine relief is intriguing, it’s crucial to approach this alternative therapy with caution and a strong foundation of professional guidance. Many factors influence the effectiveness and safety of any procedure, especially when considering its impact on a pre-existing condition like migraines.Seeking medical advice before considering any procedure, including a daith piercing, is paramount.
A comprehensive evaluation by a medical professional can determine if a daith piercing is suitable for an individual and if it aligns with their overall health status. This evaluation is vital to minimize potential risks and complications.
Assessing Suitability for Daith Piercings
A medical doctor can assess a patient’s overall health, including their medical history, any current medications, and their general well-being. This assessment is critical in determining if a daith piercing is a suitable option, considering potential interactions with existing health conditions. Furthermore, the doctor can evaluate the patient’s ability to manage the potential pain and healing process associated with the procedure.
This evaluation also includes assessing the patient’s mental state, as stress and anxiety can influence migraine triggers.
Potential Risks and Complications
Daith piercings, like any piercing, carry potential risks, including infection, scarring, and allergic reactions. These risks are amplified when considering the potential interaction with a pre-existing condition like migraines. Migraines themselves can be associated with various complications, including severe pain, nausea, and potential neurological issues. The combination of these factors necessitates careful consideration and a thorough understanding of the potential risks.
Informed Consent and Limitations of Alternative Therapies, Daith piercing for migraine
Informed consent is critical when considering alternative therapies. Patients must understand the potential benefits, risks, and limitations of a daith piercing for migraine relief. A medical professional can provide detailed information, ensuring patients make an informed decision. It’s essential to acknowledge that alternative therapies, while sometimes helpful, may not be a complete solution for all conditions. Their effectiveness varies greatly between individuals, and they should not be considered a replacement for conventional medical treatments.
Ever wondered about daith piercings and their potential to help with migraines? While the science isn’t entirely conclusive, some people swear by it. It’s interesting to consider how different approaches to wellness can impact us, and the way we fuel our bodies plays a role too. For example, choosing the right way to mix your protein powder, whether with milk or water, can make a big difference.
Check out this article on protein powder with milk or water for tips on optimizing your protein intake. Ultimately, the best approach to managing migraines might be a combination of lifestyle choices and potential alternative therapies like daith piercings.
Understanding the limitations of alternative therapies is essential for realistic expectations and responsible decision-making.
Medical Professional Advice Summary
“While some individuals report experiencing a reduction in migraine frequency or intensity after a daith piercing, it’s crucial to emphasize that this is not a guaranteed or universally effective treatment. A daith piercing should not be considered a substitute for conventional medical care for migraines. Patients should always consult with their medical doctor to determine the suitability of a daith piercing based on their individual health history and current condition. A comprehensive evaluation, including a thorough discussion of potential risks and complications, is vital for informed consent.”
Patient Experiences (Anecdotal)
While scientific studies on the relationship between daith piercings and migraine relief are still emerging, anecdotal evidence from patients provides valuable insights into potential benefits and experiences. It’s crucial to understand that these accounts are not conclusive proof, but rather a glimpse into the diverse perspectives of individuals who have sought this alternative therapy. This section explores some of these experiences and highlights the limitations of relying solely on such evidence.
Varied Experiences with Daith Piercings and Migraines
Many individuals report a reduction in migraine frequency or intensity after getting a daith piercing. However, the experience is highly variable, influenced by factors such as the individual’s pre-existing migraine patterns, the piercing’s placement, and the patient’s overall health and lifestyle. Some patients find significant relief, while others report little to no impact. This highlights the complexity of migraine treatment and the importance of individualized approaches.
Limitations of Anecdotal Evidence
Anecdotal accounts, while offering valuable insights, lack the rigorous methodology of controlled scientific studies. They are subjective reports, influenced by individual biases and expectations. Correlation does not equal causation; a reported reduction in migraines after a daith piercing may be due to various factors unrelated to the piercing itself, such as lifestyle changes or other concurrent treatments. Therefore, while these experiences are worth considering, they shouldn’t be the sole basis for making decisions about migraine treatment.
Table of Patient Experiences
The following table summarizes some anecdotal experiences, categorized by the type of experience, piercing details, and perceived impact on migraines. Remember, these are individual accounts and do not represent a definitive study.
| Type of Experience | Details of the Piercing | Perceived Impact on Migraines | Important Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Significant Reduction in Frequency | Daith piercing placed in a standard location, performed by a certified piercer. Patient reported consistent migraine history for several years prior to the piercing. | Patient reported a 75% reduction in migraine frequency following the piercing. | The patient had no other significant changes in lifestyle, medication, or treatment prior to or following the piercing. |
| Partial Reduction in Intensity | Daith piercing placed slightly off-center, performed by a certified piercer. Patient had experienced episodic migraines for several months before the piercing. | Patient reported a 30% decrease in migraine intensity after the piercing. | Patient also started a new stress-reduction technique concurrently with the piercing. |
| No Perceived Impact | Daith piercing placed in a standard location, performed by a certified piercer. Patient had experienced chronic migraines for over a decade prior to the piercing. | Patient reported no significant change in migraine frequency or intensity after the piercing. | The patient experienced migraines following a major life change and an increase in stress levels before and after the piercing. |
| Increased Migraine Frequency | Daith piercing placed in an unusual location, performed by a non-certified piercer. Patient reported infrequent migraines before the piercing. | Patient reported a 25% increase in migraine frequency after the piercing. | Patient reported an infection at the piercing site. |
Future Research Directions
Exploring the potential link between daith piercings and migraine relief requires a rigorous and well-designed approach. While anecdotal evidence and preliminary observations suggest a possible correlation, more robust scientific investigation is needed to determine if a causal relationship exists. This section Artikels potential avenues for future research, focusing on methodological approaches and the types of data necessary to support any conclusions.
Potential Research Methodologies
To explore the potential link between daith piercings and migraine relief, future research should employ rigorous methodologies to minimize bias and increase the reliability of findings. This includes well-defined inclusion and exclusion criteria for participants, ensuring a representative sample. Furthermore, control groups are essential to isolate the effect of the piercing itself. Blinding participants and researchers to the treatment group (piercing vs.
no piercing) is crucial to eliminate bias in assessment and reporting.
Data Collection Strategies
A comprehensive data collection strategy is essential to support any claims regarding the effectiveness of daith piercings in migraine relief. This includes baseline data on migraine frequency, intensity, and duration. Post-piercing data collection should be meticulously documented, measuring the changes in migraine characteristics over a specified period. This data should also include subjective reports from participants, using validated questionnaires to assess pain levels and quality of life.
Objective measures such as electroencephalography (EEG) or other neuroimaging techniques could potentially offer further insight into the neural mechanisms involved.
Potential Future Studies
| Study Design | Intervention | Control Group | Data Collection |
|---|---|---|---|
| Randomized Controlled Trial (RCT) | Participants with chronic migraine are randomly assigned to either receive a daith piercing or a sham piercing (placebo). | Participants assigned to the sham piercing group will undergo a procedure mimicking the daith piercing, but without the actual piercing. | Measure migraine frequency, intensity, and duration pre- and post-intervention. Use validated questionnaires for pain assessment and quality of life. Collect data on adverse events and any changes in the use of migraine medications. |
| Cohort Study | Track a group of individuals with chronic migraines who have undergone daith piercings over a defined period. | A control group with chronic migraines who have not undergone daith piercings. | Collect data on migraine characteristics, piercing-related issues, and the impact of the piercing on pain intensity and frequency. Follow up visits and data collection over a prolonged time frame will be crucial. |
| Case-Control Study | Compare migraine characteristics between a group of individuals with chronic migraines who have received daith piercings and a group of individuals with chronic migraines who have not. | Participants in the control group will be matched with those in the study group based on factors such as age, sex, migraine type, and medication usage. | Assess migraine frequency, severity, and response to treatment. Gather detailed medical history, including medication use and prior treatments. |
| Longitudinal Observational Study | Follow a group of migraine sufferers over an extended period to observe the long-term effects of daith piercings on migraine frequency and severity. | A control group with chronic migraines who have not undergone daith piercings. | Regular assessments of migraine characteristics, piercing-related complications, and changes in pain management. This design allows for the investigation of potential long-term effects. |
Ending Remarks: Daith Piercing For Migraine
While anecdotal evidence suggests a potential link between daith piercings and migraine relief, it’s crucial to emphasize that scientific research is still needed to definitively confirm this connection. This exploration highlights the importance of seeking professional medical advice before considering any alternative therapies, especially those involving body modification. A thorough understanding of the potential risks and benefits, coupled with a personalized approach, is key to making well-informed decisions about managing migraines.




