Gastric bypass surgery recovery is a multifaceted journey, demanding careful attention to both physical and emotional well-being. From the immediate post-operative period to long-term lifestyle adjustments, this guide provides a comprehensive overview of the process, highlighting key considerations for a successful recovery. Navigating the initial stages, nutritional needs, physical recovery, potential complications, and essential support systems is crucial for a positive outcome.
This guide delves into the intricate details of each stage, offering practical advice, sample meal plans, and valuable insights into managing potential challenges. It also emphasizes the significance of a robust support network and the importance of long-term lifestyle changes to maintain the benefits of the surgery.
Initial Stages of Recovery
The first week after gastric bypass surgery is a crucial period of adjustment and healing. Understanding the physical and emotional changes, along with the dietary and pain management strategies, is key to a smooth recovery. This period sets the stage for long-term success, and proactive preparation can significantly reduce stress and promote healing.
Immediate Post-Operative Period
The immediate post-operative period, often spanning the first 24-48 hours, focuses on monitoring vital signs, managing pain, and ensuring the surgical site heals properly. Patients are closely observed for any complications and receive necessary medications and support. This period often involves a gradual transition from intravenous fluids to oral intake, under careful supervision. Post-operative nausea and vomiting are common and can be managed with medication and dietary adjustments.
Common Physical Sensations
Many patients experience a range of physical sensations during the first week. These may include incisional pain, feelings of fullness or bloating, nausea, and fatigue. Some individuals might experience mild discomfort in the chest or upper abdomen. These sensations vary in intensity and duration, depending on the individual’s physiology and the specific procedure. It’s important to report any unusual or worsening symptoms to the medical team.
Emotional Responses
Emotional responses to surgery can be varied and complex. Feelings of anxiety, fear, or even depression are normal, particularly in the first few days. Patients might feel overwhelmed by the changes in their lifestyle and the restrictions they face. It’s crucial to acknowledge and address these emotions with support from loved ones and healthcare professionals. Maintaining a positive outlook, though challenging, can be crucial for a smoother recovery.
Dietary Restrictions and Guidelines
Dietary restrictions are critical for the first few weeks to allow the stomach pouch to heal and adjust to its new size. Initially, clear liquids are the primary focus, gradually progressing to pureed foods. Patients will need to consume small portions, and chewing is limited. The introduction of solid foods will occur slowly and carefully, with specific guidelines from the healthcare team to avoid complications.
Strict adherence to these guidelines is essential to minimize risks and maximize the healing process.
- Clear liquids (broth, water, clear juice) are typically the first foods allowed, to facilitate hydration and ease the transition from intravenous fluids. Small sips are essential.
- Pureed foods (smooth soups, pureed vegetables) are introduced as tolerated, to help with nutrient intake and to provide necessary sustenance, without putting stress on the delicate stomach pouch.
- Solid foods are gradually reintroduced, under the supervision of the healthcare team, with emphasis on soft and easily digestible foods.
Pain Management Strategies
Effective pain management is vital for a comfortable and efficient recovery. Healthcare professionals will provide a personalized pain management plan, which might include over-the-counter medications, prescription pain relievers, and potentially, interventional pain techniques. It’s essential to follow the prescribed dosage and schedule to manage pain effectively. Communication with the medical team is key for adjusting the plan as needed.
Support Systems
Family, friends, and support groups play a crucial role in navigating the early recovery period. Their emotional and practical support can ease the burden of the changes. Having a network of individuals who understand the process can provide encouragement, help with daily tasks, and offer a listening ear. Connecting with other patients who have undergone similar procedures can also be beneficial, sharing experiences and offering mutual support.
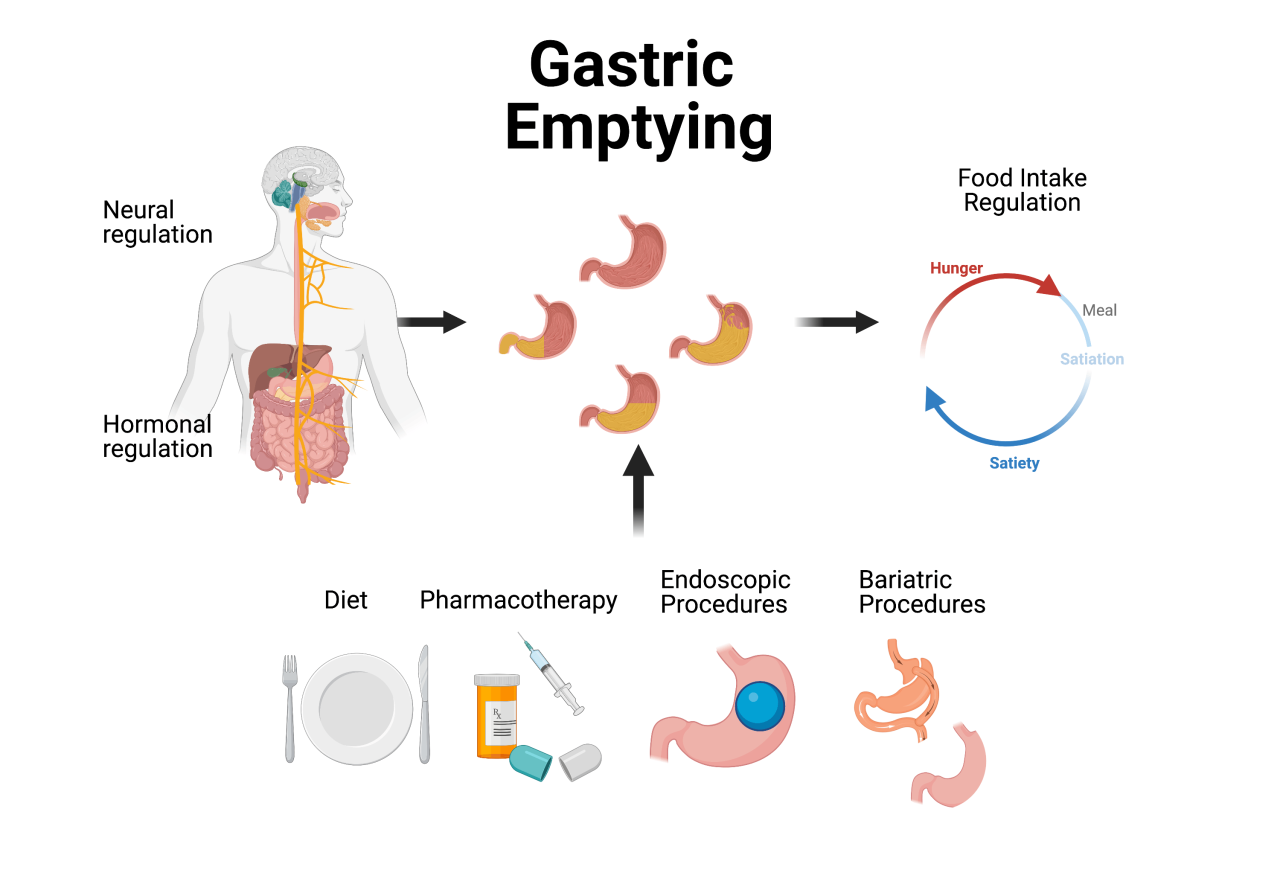
Nutritional Needs and Dietary Changes: Gastric Bypass Surgery Recovery
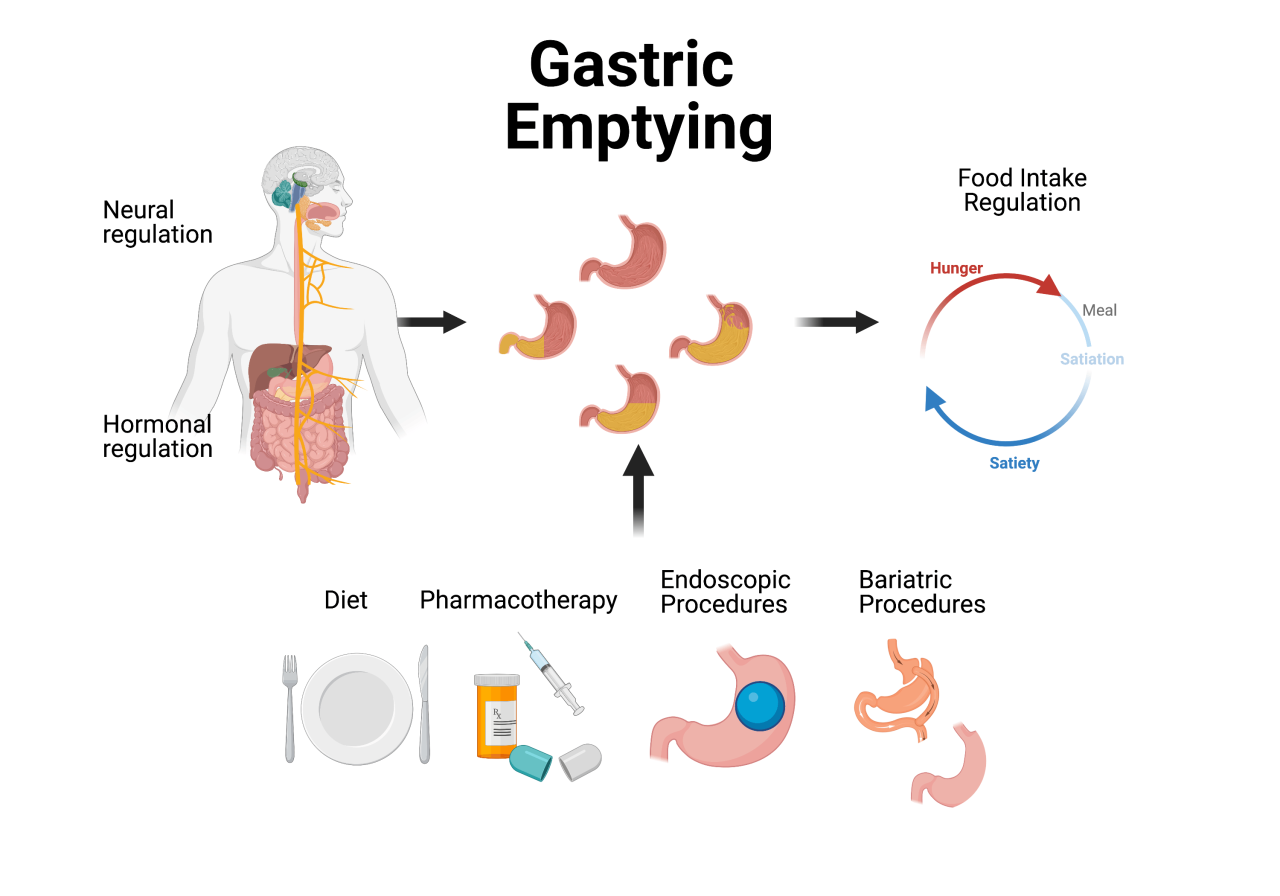
Gastric bypass surgery dramatically alters the digestive process, requiring significant dietary adjustments to ensure adequate nutrient intake and prevent complications. This new phase of recovery necessitates a meticulous approach to nutrition, focusing on small, frequent meals and specific food choices to optimize absorption and overall health. Long-term adherence to these dietary guidelines is crucial for long-term success and well-being.
Long-Term Dietary Changes
The transition to a new diet after gastric bypass is not a quick fix but a lifestyle adjustment. Small, frequent meals are essential. Consuming large portions or high-calorie foods can lead to complications like dumping syndrome, characterized by rapid emptying of the stomach contents into the small intestine. This can cause nausea, cramping, and diarrhea. Furthermore, a diet rich in fiber and whole foods is encouraged to ensure proper bowel movements and overall health.
Liquids and food should be consumed separately to prevent the dilution of stomach acid.
Recovering from gastric bypass surgery is a journey, and part of that journey involves paying close attention to your nutritional needs. While focusing on the vitamins and minerals essential for your body’s healing process, it’s also important to consider the nutritional needs of little ones. For instance, understanding how much vitamin C babies need is crucial for their development, and this knowledge can help you prioritize your own health and well-being as you navigate the recovery period.
how much vitamin c do babies need A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is key to a smooth recovery from gastric bypass surgery, and understanding these requirements is crucial for your overall well-being.
Sample Meal Plan (First Month Post-Surgery)
The initial period after surgery requires meticulous attention to portion sizes. This meal plan provides a framework for the first month, but individual needs may vary. Consult a registered dietitian or nutritionist for personalized guidance.
- Day 1-7: Liquid-only diet (clear broths, diluted juices, and protein shakes). Portion sizes are extremely small (1-2 ounces). Focus on hydration and nutrient intake. The goal is to allow the surgical site to heal and to gently introduce your body to the new digestive process.
- Day 8-14: Pureed foods (smoothies, pureed vegetables, and fruits). Portions are gradually increased to 1/4 cup to 1/2 cup, depending on your tolerance. This helps introduce soft, digestible foods. Observe your body’s response and adjust accordingly.
- Day 15-28: Soft, easily digestible foods (mashed potatoes, soft cooked vegetables, lean protein). Portion sizes are gradually increased to 1/2 cup to 1 cup, depending on tolerance. Avoid overly greasy, fried, or spicy foods. This phase focuses on introducing more solid foods, while still prioritizing easy digestion.
Importance of Vitamin and Mineral Supplementation
Vitamin and mineral deficiencies are a significant concern after gastric bypass. The reduced stomach capacity and altered absorption mechanisms can lead to deficiencies in essential nutrients. Supplementation is often necessary to maintain optimal health and prevent long-term complications. Regular blood tests are crucial to monitor nutrient levels and adjust supplementation accordingly. It is crucial to identify deficiencies early to prevent long-term health issues.
Potential Nutritional Complications
Nutrient deficiencies are a common complication. Malabsorption, where the body struggles to absorb essential nutrients, can lead to deficiencies in vitamins (like B12, D, and K) and minerals (like iron and calcium). These deficiencies can manifest as fatigue, anemia, bone loss, or other health problems. Regular monitoring by a healthcare professional is vital to address these issues proactively.
Recovering from gastric bypass surgery is a significant journey, filled with both physical and emotional adjustments. While focusing on nutrition is key, it’s interesting to consider how dietary choices might affect overall health and longevity, such as in the context of whether vegans live longer and age better. do vegans live longer and age better ? Ultimately, the key to a successful recovery after gastric bypass is consistent effort, a balanced approach to nutrition, and, importantly, a strong support system.
Nutritional Needs Comparison
| Nutrient | Pre-Surgery Needs | Post-Surgery Needs | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamins (e.g., B12, D, K) | Based on individual requirements | Often higher due to reduced absorption | Gastric bypass can significantly reduce vitamin absorption, necessitating higher intake through supplementation. |
| Minerals (e.g., iron, calcium) | Based on individual requirements | Potentially higher due to reduced absorption | Similar to vitamins, absorption of minerals can be affected by the surgery, thus requiring attention to intake through food and supplementation. |
| Calories | Based on individual needs and activity levels | Often lower due to reduced stomach capacity | The smaller stomach size limits the amount of food that can be consumed, so calorie intake needs to be carefully monitored and adjusted. |
Physical Recovery and Exercise
Post-gastric bypass surgery, physical recovery is a crucial aspect of overall well-being. Initial weeks and months require careful attention to limitations and gradual progression. Understanding the importance of proper exercise and physical therapy is vital for long-term success and a healthy lifestyle.Physical limitations are significant immediately following surgery. Discomfort, pain, and potential complications like wound healing issues, will influence your activity level.
A personalized approach, guided by your surgeon and physical therapist, is essential for safe and effective recovery.
Physical Limitations and Restrictions
The immediate post-operative period necessitates a focus on rest and healing. Movement should be limited to necessary activities. Activities that put stress on the incision site, abdominal muscles, or the newly formed digestive system must be avoided. This includes heavy lifting, strenuous exercise, and activities that could cause significant abdominal pressure. Specific restrictions will be Artikeld by your surgeon.
Appropriate Exercises and Physical Activity Levels
Gentle movement and controlled exercises are crucial for maintaining muscle strength and preventing complications like blood clots. Start with short periods of walking, followed by gradually increasing the duration and intensity as tolerated. Low-impact exercises like swimming, stationary cycling, or elliptical training are often recommended. Always consult your healthcare team before starting any exercise regimen.
Gradual Increase in Activity and Exercise Intensity
Progressing exercise should be gradual and monitored. Listen to your body, and avoid pushing yourself too hard, especially during the initial recovery phases. Increase the duration and intensity of exercises incrementally. Focus on building endurance and strength over time.
Importance of Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy plays a vital role in post-operative recovery. A physical therapist can provide tailored exercises and guidance on proper form, helping you regain strength and flexibility. This specialized approach ensures a safe and effective return to physical activity. It also addresses any potential physical limitations and concerns specific to your situation.
Exercise Recommendations for Varying Recovery Stages
| Recovery Stage | Exercise Type | Frequency | Duration | Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weeks 1-2 (Initial Recovery) | Light walking, gentle stretching, deep breathing exercises | 2-3 times daily | 5-10 minutes per session | Low |
| Weeks 3-4 (Building Strength) | Walking, stationary cycling, water aerobics, light weight training (with supervision) | 3-4 times daily | 15-20 minutes per session | Moderate |
| Weeks 5-8 (Improving Endurance) | Walking, swimming, cycling, light jogging, resistance training | 4-5 times daily | 20-30 minutes per session | Moderate to High (gradually increase) |
| Weeks 9-12 (Returning to Normal Activity) | Walking, jogging, swimming, cycling, strength training, light cardio | 4-5 times daily | 30-60 minutes per session | Moderate to High (gradually increase) |
Potential Complications and Risks
Gastric bypass surgery, while offering significant health benefits, carries potential risks and complications during the recovery period. Understanding these risks empowers patients to take proactive steps to minimize them and ensure a smoother healing process. Proper vigilance and adherence to post-operative instructions are crucial for a successful recovery.Post-surgical complications, though infrequent, can range from minor inconveniences to more serious conditions requiring medical intervention.
This section will delve into potential complications like infections, bleeding, blood clots, and other possible issues, outlining risk factors, preventative measures, and the importance of diligent follow-up care.
Infections
Infections are a common concern following any surgical procedure. Post-operative infections at the incision site or within the abdomen can occur. Factors increasing the risk of infection include weakened immune systems, poor hygiene, and the presence of pre-existing conditions. Maintaining meticulous hygiene, adhering to antibiotic prescriptions, and promptly reporting any signs of infection are essential.
Bleeding
Post-operative bleeding, although less common than infections, is a potential complication. Bleeding can range from minor seepage to significant blood loss. Factors such as blood-thinning medications, improper clotting mechanisms, and the surgical procedure itself can contribute to bleeding risks. Following the surgeon’s instructions regarding medications and activity levels can help reduce the likelihood of bleeding.
Recovering from gastric bypass surgery is a journey, not a sprint. One crucial aspect of the recovery process, alongside diet and exercise, is understanding what nutritional gaps might arise and how to address them. Finding the right supplements can be really helpful in supporting your body’s needs during this time. For example, researching what supplements help with weight loss can offer valuable insights into specific vitamins and minerals that might be lacking.
Ultimately, though, a balanced diet and regular check-ups with your doctor remain key to a successful gastric bypass recovery.
Blood Clots
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) are serious blood clot complications that can occur after surgery. DVT involves blood clots forming in the deep veins, often in the legs. PE happens when a blood clot travels to the lungs. Factors like immobility, obesity, and certain medical conditions increase the risk of blood clots. Early mobilization, use of compression stockings, and anticoagulant medications, if prescribed, can significantly reduce the likelihood of these complications.
Other Potential Complications
Other potential complications include leaks from the surgical site, internal adhesions, nutritional deficiencies, and dumping syndrome. Leaks can occur if the surgical anastomosis (connection) between the stomach and intestines is not properly healed, potentially leading to peritonitis. Internal adhesions, where tissues stick together, can affect digestion and mobility. Nutritional deficiencies can arise if the body doesn’t absorb necessary nutrients effectively.
Dumping syndrome, characterized by rapid emptying of food from the stomach, can cause unpleasant symptoms. Adherence to a prescribed diet, regular exercise, and meticulous follow-up care can mitigate the risk of these complications.
Importance of Follow-up Appointments
Regular follow-up appointments with the surgeon are vital for monitoring recovery and addressing any potential concerns. These appointments provide opportunities to discuss any emerging issues, assess the healing process, and receive necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. Surgeons use these appointments to identify and address problems early on, potentially preventing complications from escalating.
Recognizing Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing potential complications early is critical. Patients should be aware of the signs and symptoms of infection (fever, chills, redness, swelling, pus), bleeding (excessive drainage, persistent pain), blood clots (swelling, pain, redness in the legs, shortness of breath, chest pain), or other potential issues. Prompt reporting of any unusual symptoms to the surgeon is essential for timely intervention and appropriate management.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Long-Term Considerations
Gastric bypass surgery is a significant step toward a healthier lifestyle, but maintaining the benefits requires ongoing commitment. This transformative procedure doesn’t just change your body; it fundamentally alters your relationship with food and your overall well-being. This section focuses on the crucial role of long-term lifestyle adjustments to ensure the surgery’s positive impact endures.Successfully navigating the long-term aspects of gastric bypass is not about a quick fix but a conscious, ongoing dedication to healthy habits.
The goal is to integrate sustainable changes into your daily routine, fostering a lifestyle that promotes long-term weight management and overall health. This involves not only dietary adjustments but also a comprehensive approach to physical activity, emotional well-being, and mental health support.
Importance of Long-Term Lifestyle Changes
Gastric bypass surgery significantly reduces the size of the stomach, making it easier to feel full and reducing calorie intake. However, the procedure is not a magic bullet. To maintain the weight loss and prevent weight regain, adopting lasting lifestyle changes is essential. These changes affect not only physical health but also mental well-being, fostering a healthier relationship with food and body image.
Healthy Habits for Long-Term Success
Sustaining a healthy lifestyle post-surgery necessitates incorporating various healthy habits into your daily routine. These habits are not merely suggestions but crucial components of a long-term strategy for success.
- Balanced and Portion-Controlled Diet: Following a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains is paramount. Portion control is equally important, as even healthy foods can contribute to weight gain if consumed in excessive quantities. Monitoring portion sizes and paying attention to hunger and fullness cues are key components of this strategy.
- Regular Exercise Regimen: Physical activity is vital for maintaining a healthy weight and overall well-being. A consistent exercise routine, tailored to individual needs and preferences, can range from brisk walking to more intense activities like swimming or cycling. Finding activities you enjoy will help ensure long-term adherence.
- Mindful Eating Practices: Paying attention to hunger and fullness cues, eating slowly, and savoring each bite are crucial elements of mindful eating. This practice helps to avoid overeating and fosters a healthier relationship with food. Avoiding distractions while eating, such as TV or phones, can enhance mindful eating.
Mental Health Support
The emotional toll of undergoing surgery, particularly gastric bypass, can be substantial. Post-surgery, addressing emotional challenges and maintaining positive mental health is critical. Seeking support from a therapist or counselor, joining support groups, or connecting with others who have undergone similar procedures can be invaluable.
- Addressing Emotional Challenges: Emotional support is critical for successful long-term management of any major health procedure. This includes acknowledging and addressing potential feelings of anxiety, depression, or body image concerns. Addressing these challenges with professional guidance can pave the way for better mental well-being and long-term adherence to lifestyle changes.
- Maintaining Positive Self-Image: Developing a positive self-image is an ongoing process, especially after a significant life change. Focusing on personal accomplishments, setting realistic goals, and engaging in activities that boost self-esteem can contribute to maintaining a healthy self-image. Surrounding oneself with a supportive network can be instrumental in this process.
Strategies for Managing Emotional Challenges
Developing coping mechanisms for emotional challenges is an integral part of successful post-surgical recovery.
- Stress Management Techniques: Incorporating stress management techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, can be beneficial in managing stress and anxiety, both pre- and post-surgery. These techniques can effectively reduce the negative impact of stress on both physical and mental health.
- Seeking Professional Guidance: Seeking professional guidance from a therapist or counselor can be invaluable in navigating the emotional challenges associated with the surgery. A therapist can provide support and strategies for managing stress, anxiety, or depression. They can also help patients develop healthy coping mechanisms and address any emotional issues.
Lifestyle Changes Table
| Category | Specific Lifestyle Change | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Dietary Adjustments | Balanced diet with portion control | Focus on fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains; monitor portion sizes. |
| Dietary Adjustments | Mindful eating | Pay attention to hunger and fullness cues; eat slowly and savor each bite. |
| Exercise Routines | Regular physical activity | Establish a consistent exercise routine tailored to individual needs. |
| Emotional Support | Seek professional counseling | Address emotional challenges with the help of a therapist or counselor. |
| Emotional Support | Join support groups | Connect with others who have undergone similar procedures. |
Support Systems and Resources
Navigating the complexities of gastric bypass surgery recovery is often easier with a strong support system. Beyond medical professionals, a network of understanding individuals and resources can significantly impact a patient’s journey to long-term health and well-being. This section Artikels various support groups and resources available, emphasizing the importance of emotional and practical assistance during this transformative period.
Support Groups and Online Communities
Connecting with others who have undergone similar experiences can be invaluable. Sharing stories, advice, and coping mechanisms with peers facing similar challenges fosters a sense of camaraderie and shared understanding. This sense of community can significantly lessen feelings of isolation and provide encouragement during moments of difficulty.
- Numerous online forums and social media groups dedicated to gastric bypass surgery recovery exist. These platforms offer a space for patients to connect with others, ask questions, and share experiences. Examples include dedicated Facebook groups and online discussion boards. These virtual communities often provide a safe space to discuss dietary challenges, emotional adjustments, and practical tips.
- Online support groups provide an accessible and convenient way to connect with a community of individuals who understand the unique challenges of post-surgery life. These platforms allow patients to seek advice from those who have already navigated similar situations, offering a valuable resource for both practical and emotional support.
Family and Friends’ Role in Emotional Support
Family and friends play a crucial role in providing emotional support during recovery. Their understanding and encouragement can significantly contribute to a patient’s well-being. Active listening, patience, and practical assistance are essential elements in this support role.
- Family and friends can offer practical support, such as help with meal preparation, transportation, and household chores. This practical assistance is essential in enabling patients to focus on their recovery.
- Emotional support is equally crucial. Encouragement, understanding, and a willingness to listen to concerns can help patients feel supported and less isolated. Positive reinforcement and empathy from loved ones are invaluable during this challenging period.
Role of Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals, including dietitians and therapists, play a vital role in providing comprehensive support. Their expertise in nutrition, psychology, and emotional well-being can guide patients through the complexities of recovery.
- Dietitians specializing in bariatric surgery provide personalized guidance on the dietary changes required after the procedure. They help patients create sustainable eating habits, ensuring proper nutrient intake and minimizing potential nutritional deficiencies. They offer tailored meal plans and address specific dietary concerns related to the surgery.
- Therapists can help patients navigate the emotional adjustments associated with significant lifestyle changes. This can include addressing feelings of anxiety, depression, or body image concerns. They provide a safe space for patients to process their emotions and develop coping mechanisms.
Support Resource Table
| Resource | Contact Information | Website |
|---|---|---|
| National Institutes of Health (NIH) | (Various contact numbers and email addresses available on their website) | www.nih.gov |
| American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) | (Various contact numbers and email addresses available on their website) | www.asmbs.org |
| The Obesity Society | (Various contact numbers and email addresses available on their website) | www.obesity.org |
| Local Bariatric Support Groups | Search online for groups in your area | (Group-specific websites may vary) |
Specific Concerns and Considerations
Navigating the complexities of gastric bypass surgery recovery requires a proactive approach to potential challenges. This phase isn’t just about physical healing; it’s about understanding and managing the emotional, nutritional, and psychological aspects of this significant life change. Addressing potential complications early and effectively is key to a successful long-term outcome.
Weight Regain
Weight regain after gastric bypass surgery is a possibility, and understanding the factors contributing to it is crucial. Dietary indiscretions, inadequate physical activity, and emotional factors can all play a role. Maintaining a consistent, healthy lifestyle, including mindful eating habits and regular exercise, is vital for long-term weight management. Individuals should consult with their healthcare team for personalized guidance and support.
Examples of weight regain include a patient who initially lost a significant amount of weight but gradually regained it over time due to a combination of poor dietary choices and a lack of consistent exercise.
Dumping Syndrome, Gastric bypass surgery recovery
Dumping syndrome, a common post-surgical complication, arises from rapid emptying of the stomach contents into the small intestine. This can cause symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, cramping, and lightheadedness. The management of dumping syndrome often involves dietary modifications, such as avoiding sugary or high-fat foods, eating smaller, more frequent meals, and taking measures to prevent rapid emptying. Strategies to mitigate symptoms include consuming meals with more fiber to slow digestion, and avoiding highly concentrated sugars or large portions of highly caloric meals.
Patients should meticulously follow their prescribed dietary recommendations.
Other Potential Complications
Gastric bypass surgery, like any major surgical procedure, carries the risk of complications. These include nutritional deficiencies, bleeding, infections, and leaks at the surgical site. Early detection and appropriate medical intervention are crucial for managing these potential issues. This often requires diligent monitoring by healthcare professionals and adherence to prescribed medication regimens. Furthermore, patients need to promptly report any unusual symptoms or discomfort.
Pre-existing Medical Conditions
Patients with pre-existing medical conditions may face unique challenges during recovery. Cardiovascular conditions, diabetes, or other health issues can influence the recovery timeline and require careful management. For example, a patient with pre-existing diabetes might require more intensive monitoring of blood sugar levels after surgery, and a cardiovascular patient might need a more gradual approach to physical activity.
It is essential to discuss these conditions thoroughly with the surgical team to establish a personalized treatment plan.
Comparison of Different Types of Gastric Bypass Surgeries
Different types of gastric bypass surgeries, such as Roux-en-Y, sleeve gastrectomy, and others, have varying recovery profiles. The Roux-en-Y procedure often involves a longer recovery period, while the sleeve gastrectomy recovery period may be somewhat shorter. This variation in recovery time is often linked to the degree of stomach resection involved in each procedure. Patients should discuss the potential recovery differences with their surgeon to make an informed decision.
Causes and Management Strategies for Common Post-Surgical Complications
Post-surgical complications can stem from various factors, including improper wound healing, infection, or inadequate nutritional intake. Dietary deficiencies are a major concern that need to be addressed early. For example, vitamin B12 deficiencies may result from inadequate absorption due to the surgical alteration of the digestive tract. Managing these complications often involves a combination of medication, nutritional supplements, and close monitoring by healthcare professionals.
Appropriate nutritional guidance and a commitment to following the prescribed recovery plan is essential to minimize the likelihood of post-surgical complications.
Closure
Ultimately, a successful gastric bypass surgery recovery hinges on proactive planning, consistent effort, and a strong support system. This guide serves as a roadmap, equipping individuals with the knowledge and tools to navigate this significant life change. Remember, consistent communication with your healthcare team and active participation in your recovery journey are paramount to achieving lasting results. Your commitment and dedication will be key to your success.

















 The supplement often comes in capsule or powder form, and the label will typically list the amount of EGCG per serving. The specific chemical composition varies based on the extraction method and processing of the green tea leaves. Green tea extract’s effects on metabolism are not fully understood, and more research is needed.
The supplement often comes in capsule or powder form, and the label will typically list the amount of EGCG per serving. The specific chemical composition varies based on the extraction method and processing of the green tea leaves. Green tea extract’s effects on metabolism are not fully understood, and more research is needed. Caffeine’s impact on metabolism involves increasing heart rate and boosting energy levels. This can translate to a temporary increase in calories burned. However, relying solely on caffeine for weight loss is not recommended. The effects of caffeine on metabolism are often temporary and may vary between individuals.
Caffeine’s impact on metabolism involves increasing heart rate and boosting energy levels. This can translate to a temporary increase in calories burned. However, relying solely on caffeine for weight loss is not recommended. The effects of caffeine on metabolism are often temporary and may vary between individuals. Guarana’s chemical composition includes caffeine and other compounds, including tannins. The caffeine content contributes to the stimulant effects, which may increase energy expenditure and potentially boost metabolism. However, more research is needed to fully understand the complete metabolic effects of guarana beyond its caffeine content. Potential side effects are similar to those associated with caffeine.
Guarana’s chemical composition includes caffeine and other compounds, including tannins. The caffeine content contributes to the stimulant effects, which may increase energy expenditure and potentially boost metabolism. However, more research is needed to fully understand the complete metabolic effects of guarana beyond its caffeine content. Potential side effects are similar to those associated with caffeine.