ADHD in adults symptoms manifest in various ways, impacting daily life significantly. This exploration delves into the common signs and struggles faced by adults with ADHD, offering insights into understanding, diagnosis, and effective management strategies. From inattentive behaviors to hyperactive impulses, the article covers the spectrum of symptoms and their effects on different aspects of adult life, including work, relationships, and personal well-being.
The article will explore the core symptoms of ADHD, examining the nuances between inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive types. We’ll also compare symptoms in adults to those seen in children, highlighting potential overlaps and variations. Understanding the specific symptoms, along with their potential impact, is crucial for individuals, healthcare professionals, and loved ones seeking support and solutions.
Introduction to ADHD in Adults
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in adults is a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that interfere with daily functioning. These symptoms often manifest differently in adulthood than in childhood, making diagnosis sometimes challenging. It’s important to remember that ADHD is a spectrum disorder, meaning symptoms vary significantly from person to person.Common misconceptions about ADHD in adults often center around the idea that it’s solely a childhood condition.
Many adults struggle with undiagnosed ADHD, leading to significant difficulties in relationships, careers, and overall well-being. Understanding the nuances of ADHD in adults is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Prevalence of ADHD in Adults
ADHD is a prevalent condition in the adult population. Studies indicate a significant number of adults experience the symptoms. The exact prevalence rate is difficult to pinpoint due to variations in diagnostic criteria and methodologies across studies. However, research consistently shows that ADHD affects a substantial portion of the adult population, impacting their daily lives in various ways.
A common estimate places the prevalence of ADHD in adults at approximately 2.5% to 4%.
Symptoms of ADHD in Adults
Symptoms of ADHD in adults often differ from those seen in children. Adults may experience difficulties with focus and organization, leading to problems at work or in personal relationships. The symptoms can manifest as procrastination, difficulty completing tasks, and poor time management. Furthermore, they might struggle with managing multiple tasks simultaneously or find themselves easily distracted.
Adult ADHD symptoms can manifest in various ways, impacting daily life significantly. One often overlooked aspect is sleep. Finding the best sleep positions for health conditions like ADHD can greatly improve overall well-being. For instance, exploring the best and worst sleep positions for various health conditions can help you identify positions that might be more beneficial for managing ADHD symptoms best and worst sleep positions for health conditions.
Ultimately, understanding how sleep positions affect ADHD is key to a more restful and productive life.
Age Groups, Symptoms, and Prevalence Rates
| Age Group | Common Symptoms | Prevalence Rate (estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| 20s-30s | Difficulty focusing, procrastination, impulsivity, restlessness, disorganization, emotional dysregulation, and difficulties with time management. | 2.5% – 4% |
| 30s-40s | Symptoms often persist from childhood or emerge during adulthood. Difficulties with relationships, career, and financial management, leading to stress and anxiety. Problems with prioritizing tasks, remembering appointments, and managing household responsibilities. | 2.5% – 4% |
| 40s-50s | Symptoms may be masked by learned coping mechanisms. Individuals may experience significant challenges in maintaining careers and personal relationships. Difficulty with self-care, leading to health issues. | 2.5% – 4% |
| 50s and above | Symptoms may be misinterpreted as normal aging. Individuals might have difficulty adjusting to life changes, like retirement or loss of loved ones. Challenges in maintaining independence and social connections. | 2.5% – 4% |
Note: Prevalence rates are estimates based on various studies and may vary depending on the methodology used.
Common Symptoms

Understanding the diverse range of symptoms associated with ADHD in adults is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management. These symptoms can manifest differently from childhood ADHD, and often overlap with other conditions. Recognizing these patterns can help individuals and healthcare professionals navigate the complexities of ADHD in adulthood.
Inattentive ADHD Symptoms in Adults
Inattentive ADHD often presents with challenges in focusing and maintaining attention. Individuals may struggle with tasks requiring sustained mental effort, easily distracted by irrelevant stimuli, and forgetful. These symptoms can manifest in daily life, impacting work, relationships, and personal well-being. For example, someone with inattentive ADHD might have difficulty staying organized, completing projects, or remembering appointments.
- Difficulty paying attention to details or making careless mistakes in schoolwork, work, or other activities.
- Problems sustaining attention in tasks or activities, including conversations or lectures.
- Appearing to not listen when spoken to directly.
- Struggling to follow instructions or complete tasks, even simple ones.
- Difficulty organizing tasks and activities.
- Avoiding or disliking tasks requiring sustained mental effort.
- Losing things necessary for tasks or activities.
- Getting easily distracted by irrelevant stimuli.
- Forgetfulness in daily activities.
Hyperactive-Impulsive ADHD Symptoms in Adults
Hyperactive-impulsive ADHD in adults frequently involves restlessness, impulsivity, and difficulty controlling actions. These behaviors can range from fidgeting and interrupting conversations to making hasty decisions with potentially negative consequences. For example, someone with hyperactive-impulsive ADHD might find themselves constantly moving, talking excessively, or struggling to wait their turn.
- Fidgeting or squirming in their seat.
- Leaving their seat in situations where remaining seated is expected.
- Running or climbing excessively in situations inappropriate for doing so (in adults, this may manifest as extreme restlessness or an overwhelming need for activity).
- Difficulty engaging in leisure activities quietly.
- Talking excessively.
- Blurting out answers before questions have been completed.
- Difficulty waiting their turn.
- Interrupting or intruding on others.
- Feeling a sense of inner restlessness.
Overlap and Co-occurring Symptoms
It’s common for individuals with ADHD to experience a combination of inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive symptoms. The specific presentation can vary significantly from person to person, making diagnosis challenging. Additionally, ADHD frequently co-occurs with other conditions, such as anxiety, depression, and learning disabilities. These co-occurring conditions can complicate symptom presentation and require comprehensive assessment.
Comparison of Adult and Childhood ADHD Symptoms
Adult ADHD symptoms often differ from those seen in children. While some core symptoms may persist, others may manifest differently in adulthood. Children with ADHD may exhibit more disruptive behaviors, such as excessive running or interrupting. In contrast, adults may experience more subtle symptoms, like difficulty managing time or maintaining focus in work settings.
| Age Group | Symptom Presentation |
|---|---|
| Childhood | Disruptive behaviors, difficulty focusing in school, hyperactivity |
| Adolescence | Increased impulsivity, mood swings, difficulty with organization |
| Adulthood | Difficulty managing time, procrastination, relationship challenges, problems with focus in work or social settings |
Impact on Daily Life
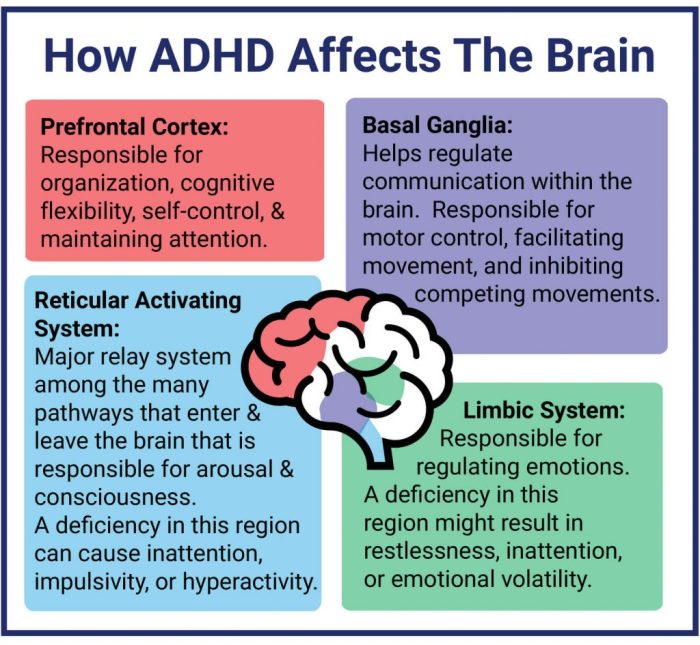
Adult ADHD often manifests in ways that significantly impact various facets of daily life. The symptoms, while often invisible, can create considerable challenges in navigating work, relationships, and personal finances. Understanding these impacts is crucial for both individuals living with ADHD and those who support them. Recognizing the challenges allows for targeted strategies and interventions to improve quality of life.The impact of ADHD symptoms extends far beyond simple forgetfulness or disorganization.
It touches upon fundamental aspects of functioning, often creating a sense of frustration, inadequacy, and isolation. The constant struggle with executive function deficits, impulsivity, and emotional dysregulation can profoundly affect relationships, career trajectory, and overall well-being.
Work Challenges
Difficulties with time management, task initiation, and organization are frequently cited challenges in the workplace. Individuals with ADHD may struggle to meet deadlines, prioritize tasks effectively, or maintain consistent productivity. This can lead to missed opportunities, decreased performance evaluations, and potential career stagnation. Many individuals with ADHD find success in roles that allow for flexibility and creativity, while structured, rigid environments can prove more challenging.
Relationship Impacts, Adhd in adults symptoms
ADHD can significantly impact interpersonal relationships. Impulsivity, emotional dysregulation, and difficulty with social cues can lead to misunderstandings, conflict, and strained connections. Sustaining healthy relationships requires conscious effort to manage symptoms and communicate effectively. Open communication, empathy, and understanding from partners, family members, and friends are crucial for building and maintaining strong bonds.
Financial Strain
The impact of ADHD extends to financial stability. Challenges with budgeting, impulse control, and organization can lead to financial difficulties. Missed payments, impulsive spending, and difficulty managing expenses can contribute to debt and financial instability. Strategies for managing finances, such as utilizing budgeting apps, establishing clear financial goals, and seeking professional financial advice, can significantly mitigate these risks.
Common Challenges
- Time Management: Difficulty prioritizing tasks, meeting deadlines, and staying on schedule is a common issue. This can lead to procrastination, missed appointments, and feelings of overwhelm.
- Organization: Maintaining organized spaces and systems can be incredibly challenging. This can affect productivity at work, efficiency at home, and overall well-being.
- Emotional Regulation: Managing emotional responses, including heightened sensitivity and rapid shifts in mood, can be difficult. This can strain relationships and impact daily functioning.
- Impulsivity: Acting without considering consequences can lead to mistakes in personal and professional life, impacting relationships and finances.
Impact Across Environments
| Environment | Common Challenges |
|---|---|
| Work | Difficulty meeting deadlines, prioritizing tasks, maintaining focus, organization of work materials, potential for impulsivity in decisions, and difficulty with structured routines. |
| Home | Difficulty with household chores, managing responsibilities, organization of personal spaces, potential for conflict stemming from impulsivity and emotional dysregulation, and maintaining a consistent schedule. |
| Social Settings | Difficulty with social cues, maintaining conversations, managing social anxiety, potential for impulsivity in social interactions, and maintaining appropriate social boundaries. |
Diagnosis and Assessment
Navigating the complexities of adult ADHD often starts with understanding the diagnostic process. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and management, empowering individuals to understand their challenges and develop strategies for success. It’s not a simple checklist; a thorough evaluation is essential to differentiate ADHD from other conditions that share similar symptoms.A key aspect of the diagnostic process involves identifying the specific criteria for ADHD, Artikeld in diagnostic manuals like the DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition).
These manuals provide standardized criteria for evaluating symptoms and their impact on daily functioning. Understanding these criteria is vital for both individuals seeking diagnosis and mental health professionals conducting evaluations.
Diagnostic Criteria for ADHD in Adults
The DSM-5 Artikels specific criteria for diagnosing ADHD in adults, focusing on persistent patterns of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity that began in childhood and continue into adulthood. These criteria encompass various symptom domains, including difficulty focusing, organizing tasks, and managing time effectively. Symptoms must significantly impact multiple areas of life, such as work, relationships, and personal well-being. Furthermore, the symptoms must have been present for a significant duration (typically six months or more) and cause clinically significant distress or impairment.
Role of Mental Health Professionals
Mental health professionals, such as psychiatrists, psychologists, and licensed therapists, play a crucial role in the diagnostic process. They possess the expertise to conduct comprehensive evaluations, considering a patient’s history, symptoms, and overall functioning. These professionals are trained to differentiate ADHD from other conditions with overlapping symptoms. They utilize various assessment tools to gather detailed information about the individual’s experiences and challenges.
Importance of Comprehensive Evaluations
A comprehensive evaluation is critical for an accurate diagnosis. It goes beyond simply identifying symptoms; it explores the individual’s full context. This includes considering co-occurring conditions, such as anxiety, depression, or learning disabilities. It also looks at the impact of ADHD on different life domains, such as work, relationships, and personal life. Without a thorough evaluation, the diagnosis may be incomplete, leading to ineffective treatment strategies.
For example, an individual experiencing anxiety alongside ADHD might benefit from a tailored treatment plan addressing both conditions.
Steps in a Typical ADHD Assessment Process
A structured assessment process is essential to ensure accuracy and reliability. The following steps Artikel a typical approach:
- Initial Consultation: This initial meeting involves gathering a detailed history of symptoms, their onset, duration, and impact on daily life. The professional will also assess the individual’s overall functioning and well-being.
- Symptom Assessment: The clinician utilizes validated questionnaires and scales to systematically assess the presence and severity of inattention and hyperactivity-impulsivity symptoms.
- Review of Past Medical and Psychiatric History: This involves a review of previous diagnoses, treatments, and any relevant medical information to identify potential co-occurring conditions.
- Interviews and Observations: This often involves structured interviews with the individual and, if possible, individuals familiar with their behavior (e.g., family members, partners). Observations during the session help provide additional insights.
- Additional Testing (if necessary): Depending on the case, additional assessments may be conducted, such as IQ testing, cognitive assessments, or other neuropsychological tests, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of cognitive strengths and weaknesses.
- Diagnosis and Treatment Planning: Following the evaluation, the clinician provides a diagnosis and develops a personalized treatment plan, considering the individual’s needs and preferences.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Initial Consultation | Gathering detailed history of symptoms and impact on daily life. |
| Symptom Assessment | Using validated questionnaires and scales to assess symptom presence and severity. |
| Past Medical/Psychiatric History Review | Reviewing previous diagnoses, treatments, and medical information. |
| Interviews and Observations | Structured interviews with individual and others familiar with their behavior. |
| Additional Testing | IQ, cognitive, or neuropsychological testing as needed. |
| Diagnosis and Treatment Planning | Developing a personalized treatment plan. |
Treatment Options: Adhd In Adults Symptoms
Navigating ADHD in adulthood can feel challenging, but effective treatments are available. A multi-faceted approach, often combining medication, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments, is frequently the most successful strategy for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Understanding the various options and their potential impact is crucial for making informed decisions.
Medication
Medication plays a significant role in managing ADHD symptoms in adults. Stimulant medications, such as methylphenidate (Ritalin, Concerta) and amphetamine-based medications (Adderall, Vyvanse), are commonly prescribed. These medications work by increasing the levels of neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and norepinephrine, in the brain, which can help improve focus, impulse control, and reduce hyperactivity. Non-stimulant medications, such as atomoxetine (Strattera), are also available and may be a suitable option for some individuals, particularly those who experience side effects with stimulants.
Therapy
Therapy is a crucial component of a comprehensive treatment plan. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a particularly effective approach for adults with ADHD. CBT helps individuals identify and modify unhelpful thought patterns and behaviors related to ADHD symptoms. Other therapeutic modalities, such as coaching and family therapy, can also be beneficial. Family therapy can provide support and understanding for family members affected by ADHD.
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes can significantly impact ADHD symptoms. These changes can include regular exercise, a balanced diet, sufficient sleep, and stress management techniques. Regular exercise, for instance, can help improve mood, reduce anxiety, and enhance focus. Prioritizing sleep is crucial as sleep deprivation can exacerbate ADHD symptoms. A well-balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can also support overall well-being and improve concentration.
Holistic Treatment Approach
A holistic treatment approach recognizes that ADHD is not simply a collection of symptoms but a complex condition impacting various aspects of an individual’s life. It emphasizes the interconnectedness of physical, mental, and emotional well-being. This approach emphasizes that addressing ADHD requires a multifaceted strategy that considers not just the symptoms but also the individual’s overall health, environment, and support system.
This includes the crucial element of self-advocacy.
Comparison of Treatment Options
| Treatment Option | Description | Potential Benefits | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medication (Stimulants) | Increase neurotransmitter levels in the brain. | Improved focus, impulse control, reduced hyperactivity. | Insomnia, appetite suppression, anxiety, headaches, stomach upset. |
| Medication (Non-Stimulants) | Affect neurotransmitter levels differently. | May be a good option for those who experience side effects with stimulants. | Fatigue, nausea, reduced appetite, liver problems. |
| Therapy (CBT) | Identify and modify unhelpful thoughts and behaviors. | Improved self-awareness, coping skills, and emotional regulation. | Requires commitment to therapy sessions, may not be immediately effective. |
| Lifestyle Changes | Regular exercise, balanced diet, sufficient sleep. | Improved physical health, reduced stress, improved mood. | Requires consistent effort and self-discipline. |
Strategies for Coping and Management
Living with ADHD in adulthood can be challenging, but with the right strategies, you can effectively manage your symptoms and lead a fulfilling life. Understanding your specific challenges and implementing tailored coping mechanisms is key to success. This section will explore practical techniques for improving time management, focus, and emotional regulation, empowering you to navigate daily life more effectively.Effective coping mechanisms for ADHD are not one-size-fits-all.
They require self-awareness and experimentation to find what works best for you. Consistent practice and a willingness to adapt are crucial for long-term success.
Time Management and Organization
Effective time management is often a significant hurdle for individuals with ADHD. The inability to prioritize tasks and the tendency to become easily sidetracked can lead to feelings of overwhelm and frustration. Developing strategies for organizing tasks and time is essential for managing daily life.
- Prioritization Techniques: Breaking down large tasks into smaller, more manageable steps. Utilizing methods like the Eisenhower Matrix (urgent/important) or the Pareto Principle (80/20 rule) to focus on high-impact activities. Example: Instead of tackling “clean the entire house” at once, break it down into “clean the bathroom,” “clean the kitchen,” etc. This creates smaller, less daunting goals.
- Scheduling and Planning: Utilizing digital or paper calendars and to-do lists. Setting realistic deadlines and allocating specific time blocks for tasks. Including buffer time for unexpected interruptions or delays. Example: Schedule 30 minutes for a specific task and include an additional 15 minutes to account for potential delays or distractions.
- Organization Systems: Implementing physical or digital organizational systems for storing materials and information. Using color-coding, labeling, or other visual cues to improve efficiency and reduce clutter. Example: Using different colored folders for different projects, or creating a designated space for important papers and documents.
Focus and Concentration
Maintaining focus and concentration is a significant challenge for individuals with ADHD. External and internal distractions can easily derail attention, leading to feelings of frustration and procrastination. Developing strategies for enhancing focus is essential for success in various aspects of life.
Adult ADHD symptoms can be tricky to spot, sometimes mimicking other issues. For instance, it’s important to consider how medications, especially over-the-counter ones, might affect older adults. Understanding the potential interactions and safety concerns of OTC drugs like pain relievers or cold remedies is crucial for everyone. Checking out the details on OTC drug safety in older adults can shed light on this.
Ultimately, recognizing ADHD symptoms in adults requires a careful assessment of various factors, including potential medication interactions.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practicing mindfulness exercises to increase self-awareness and improve attention span. Engaging in regular meditation to calm the mind and reduce distractions. Example: Dedicate 5-10 minutes each day to a mindfulness exercise, focusing on your breath and observing thoughts without judgment.
- Environmental Control: Creating a dedicated workspace free from distractions. Minimizing visual and auditory clutter. Using noise-canceling headphones or white noise machines to block out disruptive sounds. Example: Designate a quiet corner of your home as a workspace and minimize distractions, like closing unnecessary tabs on your computer.
- Focus Techniques: Employing techniques like the Pomodoro Technique (working in focused bursts with short breaks) or the Feynman Technique (breaking down complex information into simpler components). Example: Work in 25-minute intervals with 5-minute breaks. This structured approach can significantly improve focus and productivity.
Impulsivity and Emotional Regulation
Impulsivity and emotional dysregulation can significantly impact daily life for individuals with ADHD. Difficulty controlling reactions and managing emotions can lead to relationship conflicts and hinder personal growth. Developing strategies for managing these aspects is vital for overall well-being.
Adult ADHD symptoms can be tricky, often overlapping with other conditions. Figuring out the right approach to managing these symptoms, like many other health concerns, can be challenging. For example, when considering supplements during cancer treatment, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new regimen, such as should i take vitamins during cancer treatment.
Ultimately, a comprehensive approach, tailored to the individual, is key to effectively managing adult ADHD symptoms.
- Impulse Control Strategies: Identifying triggers for impulsive behaviors and developing strategies to manage them. Using coping mechanisms such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or mindfulness to regulate emotional responses. Example: If you tend to interrupt conversations, practice pausing and taking a deep breath before responding. This allows you to gather your thoughts and respond more thoughtfully.
- Emotional Regulation Techniques: Learning to identify and label emotions. Developing strategies for managing intense emotions through journaling, talking to a therapist, or seeking support from loved ones. Example: Keep a journal to track your emotional responses and identify patterns. Discuss feelings with a trusted friend or family member, or seek professional guidance.
- Positive Self-Talk: Replacing negative self-talk with positive affirmations. Focusing on personal strengths and accomplishments. Celebrating small victories to build self-esteem and motivation. Example: Instead of saying “I’m so stupid,” say “I’m going to learn from this mistake.” Focus on your successes and acknowledge your progress.
Supporting Resources and Information
Navigating ADHD as an adult can feel isolating. Knowing where to turn for support and reliable information is crucial for effective management and improved well-being. Understanding the available resources empowers individuals to take control of their condition and build a supportive network.Finding trustworthy information and support systems is vital for adults living with ADHD. This often involves accessing reliable sources, connecting with others facing similar challenges, and utilizing available tools.
The journey to managing ADHD effectively is greatly enhanced by leveraging these resources.
Reliable Sources of Information
Accurate information is paramount when dealing with ADHD. This includes understanding the condition’s nuances, available treatments, and coping strategies. Reputable sources offer evidence-based insights and can significantly aid in self-management. These resources are crucial in ensuring individuals receive the most effective support.
Support Networks for Adults with ADHD
Support networks play a critical role in navigating the challenges associated with ADHD. Connecting with others who understand the unique experiences and struggles can provide a sense of community and shared understanding. Sharing experiences and strategies with others in similar situations is invaluable. The feeling of not being alone is often a significant factor in managing the condition effectively.
Organizations and Resources Dedicated to Assisting Adults with ADHD
Numerous organizations and resources are dedicated to providing support and information for adults with ADHD. These entities often offer valuable guidance, educational materials, and avenues for connecting with others facing similar challenges. These resources are essential for navigating the complexities of living with ADHD.
Examples of Support Resources
| Category | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Support Groups | CHADD (Children and Adults with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder) | Provides local support groups, educational workshops, and advocacy efforts. |
| Websites | ADDitude Magazine | Offers articles, advice, and information for adults with ADHD. Provides a wealth of practical strategies. |
| Books | “Driven to Distraction” by Edward Hallowell and John Ratey | Provides a comprehensive overview of ADHD, including its impact on daily life and potential strategies for management. |
| Professional Organizations | The American Psychiatric Association (APA) | Provides reliable information about ADHD, its diagnosis, and treatment options. Offers a strong foundation of knowledge. |
Case Studies (Illustrative Examples)
Understanding ADHD in adults often involves exploring real-life scenarios. These case studies offer glimpses into the diverse challenges and triumphs experienced by individuals navigating daily life with ADHD. They highlight the impact of various interventions and strategies on different aspects of their lives.
Financial Management Challenges
Managing finances can be particularly tricky for adults with ADHD. Distractibility, impulsivity, and difficulty with organization often lead to missed payments, overspending, and accumulating debt. One individual, for example, struggled to stick to a budget. Their impulsive nature often led them to make large, unplanned purchases, while their tendency to lose track of bills and receipts made it difficult to monitor expenses accurately.
This resulted in a cycle of debt, and feelings of anxiety and frustration.
Positive Impact of Therapy
Therapy can be a powerful tool in helping adults with ADHD manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being. One individual, experiencing significant stress and anxiety related to their ADHD symptoms, found that cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) helped them develop coping mechanisms. They learned strategies to manage impulsivity, improve time management, and reduce procrastination. As a result, their relationships improved, and they felt more in control of their lives.
Medication Benefits for Focus
Medication can play a crucial role in enhancing focus and concentration for adults with ADHD. A case study of an individual struggling with consistent issues of focus in their job highlights the potential of medication. Prior to starting medication, this individual frequently experienced difficulty completing projects on time and experienced frustration from their inability to stay on task.
After starting a medication, they reported a significant improvement in their ability to concentrate and stay organized, leading to a more productive work environment and increased confidence.
Improved Organization Skills
Implementing specific strategies can significantly improve organization skills in adults with ADHD. One person, struggling to keep their home and workspace organized, found that using visual aids, like color-coded folders and a daily planner, proved highly effective. By breaking down tasks into smaller, manageable steps and utilizing visual cues, they gained a sense of accomplishment and order in their daily routines.
They found that their ability to track their progress and meet deadlines improved markedly.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, ADHD in adults symptoms are complex and diverse, impacting individuals in myriad ways. This comprehensive overview has highlighted the core symptoms, the challenges they pose, and the available resources for diagnosis and management. Ultimately, the key to navigating these challenges lies in recognizing the symptoms, seeking appropriate support, and implementing effective coping strategies. By fostering understanding and promoting open discussion, we can empower adults with ADHD to lead fulfilling and productive lives.




