Osteoporosis fractures treatment and prevention is a crucial area of health concern, affecting millions worldwide. This guide delves into the complexities of this issue, from understanding the underlying causes of osteoporosis to exploring effective treatment and preventative strategies. We’ll examine various fracture types, risk factors, diagnostic methods, and a range of treatment approaches. This detailed exploration will equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate this critical health topic and make informed decisions for your well-being.
Understanding the intricate relationship between bone health and fractures is paramount. This comprehensive guide explores the multifaceted nature of osteoporosis, from its impact on bone density to the different types of fractures it can cause. We’ll also examine the critical role of lifestyle choices, nutrition, and medical interventions in both treating and preventing these fractures. The information provided aims to offer actionable insights to empower readers to take control of their bone health.
Introduction to Osteoporosis Fractures
Osteoporosis is a bone disease characterized by a decrease in bone mass and density, making bones fragile and more susceptible to fractures. This weakened bone structure significantly increases the risk of fractures, particularly in the hip, spine, and wrist. These fractures can have a profound impact on a person’s quality of life, leading to pain, disability, and reduced independence.The loss of bone density is a gradual process, often occurring silently over many years.
While the initial stages may not be noticeable, the increasing risk of fractures is a serious concern. Understanding the types of fractures associated with osteoporosis, their prevalence, and the impact on public health is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Preventing osteoporosis fractures often involves strengthening bones and improving balance. A key component of this is regular exercise, and choosing the right equipment can make a big difference. For example, consider the pros and cons of a walking pad versus a treadmill for your specific needs. This resource can help you decide what’s best for your fitness goals.
Ultimately, consistent physical activity, tailored to your individual needs, is crucial for maintaining bone health and reducing the risk of fractures.
Common Types of Osteoporosis Fractures
Osteoporosis significantly increases the risk of fractures in various areas of the body. Common types include fractures of the hip, spine, and wrist, each presenting unique characteristics and consequences. Understanding these specific fracture types allows for tailored treatment and preventative measures.
- Hip Fractures: These fractures, often occurring from a fall or minor trauma, are particularly serious due to the disruption in the individual’s ability to maintain balance and perform daily activities. They can lead to prolonged hospital stays and significant long-term functional limitations. A common example is a 70-year-old woman falling while walking and sustaining a hip fracture, requiring extensive rehabilitation.
- Vertebral Fractures: These fractures, often in the spine, frequently occur with minimal trauma or even spontaneously. The compression of the vertebrae can result in back pain, loss of height, and deformities in the spine. For instance, a sudden twisting motion can lead to a vertebral fracture, causing chronic back pain in a 65-year-old man.
- Wrist Fractures: These fractures, commonly the Colles’ fracture, are frequently seen in individuals who fall on an outstretched hand. The pain and disruption to daily tasks can be substantial. A 55-year-old woman falling and landing on her outstretched hand can lead to a wrist fracture, impacting her ability to perform tasks like writing or buttoning clothes.
Prevalence and Impact on Public Health
Osteoporosis fractures are a significant public health concern globally. The increasing aging population contributes to a higher prevalence of osteoporosis and the resulting fractures. The economic burden of these fractures, including healthcare costs and lost productivity, is substantial.
The World Health Organization estimates that millions of people suffer osteoporosis fractures annually. These fractures often lead to reduced mobility, pain, and a decrease in quality of life, significantly impacting the well-being of individuals and placing a burden on healthcare systems. Moreover, these fractures can lead to long-term disabilities, requiring extensive rehabilitation and support.
Fracture Characteristics
The following table summarizes the key characteristics of common osteoporosis fractures:
| Fracture Type | Common Causes | Symptoms | Treatment Approaches |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hip Fracture | Falls, minor trauma | Severe pain in the hip, inability to bear weight, shortening of the leg | Surgical repair (hip replacement), physiotherapy, pain management |
| Vertebral Fracture | Sudden twisting, bending, or minor trauma; osteoporosis | Back pain, loss of height, kyphosis (dowager’s hump) | Pain management, physical therapy, bracing, medication to improve bone density |
| Wrist Fracture | Fall on an outstretched hand | Pain, swelling, tenderness in the wrist, inability to move the wrist | Casting or splinting, physiotherapy, pain relief |
Risk Factors for Osteoporosis Fractures
Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened bones, significantly increases the risk of fractures. Understanding the factors contributing to this risk is crucial for prevention and effective treatment. This understanding empowers individuals to take proactive steps to maintain bone health and reduce their fracture risk.Numerous factors contribute to osteoporosis-related fractures, some controllable and others inherent to an individual’s circumstances.
Knowing these risk factors allows for personalized strategies to minimize fracture risk.
Modifiable Risk Factors, Osteoporosis fractures treatment and prevention
Modifiable risk factors are those that can be changed through lifestyle adjustments or medical interventions. Addressing these factors can significantly reduce the likelihood of osteoporosis-related fractures.
Taking care of your bones is crucial, especially when it comes to preventing osteoporosis fractures. A healthy diet and regular exercise are key, but did you know that incorporating some simple skincare routines can indirectly contribute to overall health? For example, using salt water for the face salt water for the face can promote a healthy glow, and this positive approach to skin care might just help you feel more confident and strong—which is important when building bone density and preventing fractures.
Ultimately, prioritizing bone health through diet and exercise remains the best approach for osteoporosis fractures treatment and prevention.
- Inadequate Calcium and Vitamin D Intake: Insufficient intake of these essential nutrients is a major contributor to weakened bones. Calcium is crucial for bone density, while vitamin D aids in calcium absorption. A balanced diet rich in calcium-rich foods like dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods, combined with adequate sun exposure or vitamin D supplements, can help maintain optimal bone health.
- Lack of Regular Weight-Bearing Exercise: Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, jogging, and dancing, stimulate bone formation and increase bone density. Regular physical activity is vital for maintaining strong bones and preventing fractures. Individuals should aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity weight-bearing exercise most days of the week.
- Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Smoking and excessive alcohol intake have been linked to decreased bone density. Nicotine and alcohol interfere with calcium absorption and bone metabolism, increasing the risk of fractures. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol consumption are essential steps towards improved bone health.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, such as corticosteroids, can have adverse effects on bone density, increasing the risk of fractures. Individuals taking these medications should discuss potential strategies to mitigate these risks with their healthcare providers.
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
Certain risk factors are inherent to an individual and cannot be altered. Understanding these factors is crucial for recognizing increased fracture risk and implementing preventative measures.
Treating and preventing osteoporosis fractures often involves lifestyle changes and medication. But did you know that adequate vitamin intake, like how much vitamin C do babies need, is also crucial for bone health in adults and children? Understanding the specific needs of infants, as detailed in this resource how much vitamin c do babies need , can be helpful for a holistic approach to overall bone health, especially when considering the role of vitamin C in collagen production, a key component in preventing fractures.
Ultimately, a comprehensive approach that incorporates proper nutrition is vital in preventing osteoporosis fractures.
- Age: Bone density naturally decreases with age, making older individuals more susceptible to fractures. This natural decline in bone mass is often accompanied by reduced physical activity and changes in lifestyle, compounding the risk. Age-related declines are a key factor in the increase in fracture incidence.
- Gender: Women are at a significantly higher risk of osteoporosis and fractures compared to men. This is primarily due to hormonal changes, particularly during menopause, which lead to a decrease in estrogen levels, a key hormone for bone health.
- Genetics: Family history of osteoporosis plays a role in an individual’s risk. Genetic predispositions can influence bone density and the rate of bone loss. Individuals with a family history of osteoporosis may need to be more vigilant about preventative measures.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as individuals of Asian and Caucasian descent, have a higher predisposition to osteoporosis. This is due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors, potentially influencing bone density and fracture risk.
Impact of Age, Gender, and Genetics on Fracture Risk
Age, gender, and genetics significantly influence fracture risk. Bone density naturally decreases with age, particularly after menopause in women. Genetic predispositions can impact bone density and susceptibility to osteoporosis, while the hormonal differences between men and women significantly impact fracture rates. These factors need to be considered when assessing an individual’s risk profile.
| Factor | Modifiable Risk Factor | Non-Modifiable Risk Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Age | Exercise, Diet | Chronological Age |
| Gender | Lifestyle choices | Biological Sex |
| Genetics | Dietary adjustments, Exercise regimen | Family history of osteoporosis |
| Ethnicity | Healthy lifestyle choices | Ethnic background |
Diagnosis and Assessment of Osteoporosis Fractures
Identifying osteoporosis and assessing fracture risk involves a multi-faceted approach. A crucial initial step is recognizing potential risk factors, such as age, family history, and lifestyle choices. Beyond these factors, precise diagnostic methods are essential for confirming a diagnosis and guiding treatment strategies. These methods help determine the extent of bone loss and predict future fracture risk.Osteoporosis diagnosis isn’t just about identifying the presence of the disease; it’s about understanding the individual’s fracture risk.
This allows for personalized interventions that target specific needs and potentially prevent future fractures. A comprehensive assessment, incorporating various diagnostic tools and patient history, helps healthcare professionals make informed decisions regarding treatment options and long-term management.
Diagnostic Methods for Osteoporosis
Various methods are used to diagnose osteoporosis and evaluate fracture risk. These methods aim to accurately measure bone density and assess the overall health of the skeletal system. Early detection is critical for implementing preventative measures and managing the disease effectively.
- Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA): This is the gold standard for bone density measurement. DXA scans measure bone mineral density (BMD) in specific areas, such as the hip and spine. The results are compared to a reference population, usually young adults, to determine the T-score. A T-score of -2.5 or lower indicates osteoporosis, while a T-score between -1 and -2.5 indicates osteopenia, a condition of low bone mass that precedes osteoporosis.
A Z-score compares bone density to age-matched peers.
- Quantitative Computed Tomography (QCT): QCT uses X-rays to measure bone density, primarily in the spine. It can provide detailed 3D images of the bone structure and can be useful in cases where DXA is less accurate. QCT is sometimes preferred over DXA in evaluating the spine, particularly in cases of vertebral fractures.
- Quantitative Ultrasound (QUS): QUS uses ultrasound waves to measure bone density, primarily in the heel. QUS is less expensive and more portable than DXA, making it suitable for screening in certain populations. However, QUS may not be as accurate as DXA in all cases.
Role of Bone Density Testing in Fracture Risk Assessment
Bone density testing, particularly DXA, plays a crucial role in assessing fracture risk. It directly measures the amount of mineral in a given area of bone, providing a quantitative measure of bone health. This allows for a more objective assessment of the individual’s risk compared to relying solely on patient history. The T-score, as mentioned earlier, is a key output of DXA scans.
- Fracture Risk Calculators: These tools use data from the DXA scan, patient history, and other factors (like age, sex, and previous fractures) to estimate the probability of a future fracture. These tools help clinicians tailor preventive strategies to the individual patient’s needs.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Evaluating Patients
A comprehensive approach is needed to evaluate patients suspected of having osteoporosis-related fractures. This approach combines clinical assessment, diagnostic testing, and risk stratification.
- Patient History: Gather detailed information about the patient’s medical history, including any previous fractures, medications, lifestyle factors (diet, exercise, smoking), and family history of osteoporosis.
- Physical Examination: Conduct a thorough physical examination to assess overall health, identify any contributing factors, and evaluate posture and muscle strength. Inspect for any visible signs of bone loss, such as spinal deformities (kyphosis).
- Diagnostic Testing: Perform relevant diagnostic tests, including DXA scans, QCT, or QUS, as appropriate, to assess bone density and evaluate fracture risk.
- Fracture Risk Assessment: Utilize fracture risk calculators to estimate the probability of future fractures, incorporating data from the diagnostic tests and patient history.
- Treatment Planning: Develop a personalized treatment plan based on the assessment findings, which may include lifestyle modifications, medications, and other interventions to manage and prevent future fractures.
Diagnostic Tools and Applications
| Diagnostic Tool | Application in Fracture Evaluation |
|---|---|
| Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA) | Measures bone mineral density (BMD) at specific skeletal sites (e.g., hip, spine). Provides T-score and Z-score for comparison with reference populations, assessing osteoporosis or osteopenia. |
| Quantitative Computed Tomography (QCT) | Measures bone density, especially in the spine. Can provide detailed 3D images, useful for evaluating vertebral fractures. |
| Quantitative Ultrasound (QUS) | Measures bone density, primarily in the heel. A less expensive and portable screening method, useful in certain populations. |
Treatment Approaches for Osteoporosis Fractures
Treating osteoporosis fractures requires a multifaceted approach encompassing pharmacological interventions, lifestyle modifications, and rehabilitation strategies. The goal is not just to heal the immediate fracture but to prevent future occurrences and improve overall bone health. This involves addressing the underlying causes of osteoporosis and supporting the body’s natural healing processes.
Pharmacological Treatments for Osteoporosis
Pharmacological treatments aim to increase bone density and reduce the risk of future fractures. These treatments often target the mechanisms by which bone is broken down and rebuilt. Understanding the mechanisms of action and potential side effects is crucial for informed decision-making.
- Bisphosphonates, such as alendronate and risedronate, inhibit bone resorption, leading to a net increase in bone mass. They are generally well-tolerated, but can cause gastrointestinal side effects like heartburn or esophageal irritation. Taking these medications with a full glass of water and remaining upright for at least 30 minutes afterward is crucial for minimizing these risks.
- Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs), like raloxifene, mimic the effects of estrogen on bone, slowing bone loss and reducing the risk of fractures. Potential side effects include hot flashes and blood clots. It’s essential to discuss these risks with a healthcare provider.
- Denosumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets a protein involved in bone resorption. This leads to a significant increase in bone density. Possible side effects include infections, low blood calcium levels, and, rarely, osteonecrosis of the jaw. Monitoring for these side effects is critical.
- Teriparatide (a parathyroid hormone analog) stimulates bone formation. It’s often used for individuals with severe osteoporosis. Side effects include nausea, dizziness, and leg cramps. Continuous monitoring of calcium levels and kidney function is important.
Non-Pharmacological Strategies for Fracture Prevention and Treatment
Lifestyle modifications and targeted exercise programs play a vital role in preventing future fractures and promoting bone health. These approaches work synergistically with pharmacological treatments to maximize results.
- A balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is essential for bone health. Dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified foods are excellent sources. Vitamin D supplementation may be necessary, especially for individuals with limited sun exposure. A balanced diet ensures adequate intake of essential nutrients crucial for bone health.
- Regular weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, jogging, and dancing, stimulate bone formation and improve muscle strength, reducing the risk of falls. Resistance training strengthens bones and muscles, improving balance and coordination, preventing falls and subsequent fractures.
- Smoking cessation and limiting alcohol intake are critical lifestyle changes for improving bone health. Smoking inhibits bone formation and increases bone loss, while excessive alcohol consumption interferes with calcium absorption and bone metabolism. Quitting smoking and reducing alcohol intake significantly contributes to overall well-being and bone health.
Role of Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation
Physiotherapy and rehabilitation play a critical role in fracture recovery and prevention. They focus on restoring function, improving mobility, and preventing future falls.
- Physiotherapists develop personalized exercise programs to regain strength, flexibility, and balance. This is particularly important for individuals who have suffered fractures to prevent future injuries.
- Rehabilitation strategies also focus on fall prevention education and techniques. Learning strategies to prevent falls is a crucial component of recovery, preventing future fractures and injuries.
- Pain management techniques and assistive devices, if necessary, are integral parts of the rehabilitation process. This personalized approach considers individual needs and goals for effective recovery.
Comparison of Treatment Options for Various Fracture Types
| Fracture Type | Pharmacological Options | Non-Pharmacological Options | Physiotherapy/Rehab |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hip Fracture | Bisphosphonates, Denosumab, Teriparatide | Balanced diet, weight-bearing exercise, fall prevention strategies | Specific exercises for hip mobility, balance training, and gait rehabilitation |
| Vertebral Compression Fracture | Bisphosphonates, Denosumab, Teriparatide, SERMs | Posture improvement exercises, core strengthening, fall prevention strategies | Postural correction exercises, spinal stabilization, pain management |
| Wrist Fracture | Bisphosphonates, Denosumab | Weight-bearing exercise, fall prevention strategies, adequate calcium intake | Wrist strengthening exercises, range of motion exercises, and pain management |
Prevention Strategies for Osteoporosis Fractures: Osteoporosis Fractures Treatment And Prevention
Preventing osteoporosis fractures hinges on proactive lifestyle choices and interventions. Early intervention is crucial, as the development of osteoporosis often occurs silently, leading to increased risk of fragility fractures. Taking preventive steps can significantly reduce this risk, improving overall bone health and quality of life.
Crucial Role of Calcium and Vitamin D
Calcium and vitamin D are fundamental to bone health. Calcium is a major component of bone tissue, while vitamin D facilitates calcium absorption in the gut. Insufficient intake of these essential nutrients can lead to reduced bone density, increasing the susceptibility to fractures. A balanced diet rich in calcium-rich foods, such as dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods, is vital.
Adequate sun exposure or vitamin D supplements can also ensure sufficient levels.
Importance of Weight-Bearing Exercises
Weight-bearing exercises are crucial for stimulating bone growth and maintaining bone density. These exercises force the bones to work against gravity, prompting the body to strengthen them. Examples include walking, jogging, dancing, and stair climbing. Regular participation in these activities can significantly improve bone health and reduce fracture risk. In addition to weight-bearing exercises, resistance training strengthens muscles that support bones, contributing to overall skeletal health.
Other Lifestyle Factors for Fracture Prevention
Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption are also vital. Excess weight can put added stress on bones, while smoking and excessive alcohol intake can interfere with calcium absorption and bone remodeling processes. Regular monitoring of medication use, including those that may affect bone health, is also essential.
Actionable Steps to Prevent Osteoporosis Fractures
- Consume a balanced diet: Focus on calcium-rich foods like dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods. Ensure adequate vitamin D intake through sunlight exposure or supplements, as needed. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
- Engage in regular weight-bearing exercises: Incorporate activities like walking, jogging, dancing, and stair climbing into your routine. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Maintaining a healthy body weight can help reduce stress on bones and minimize fracture risk. Consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized guidance.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption: Smoking and excessive alcohol intake can negatively impact bone health and increase the risk of fractures. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption are important steps to take.
- Discuss medication use with a doctor: Some medications can affect bone density. Review medications with a healthcare professional to identify potential risks and discuss strategies to mitigate them.
- Consider bone density testing: If you are at increased risk for osteoporosis, discuss bone density testing with your doctor. Early detection can allow for prompt intervention and preventative measures.
Case Studies and Examples of Osteoporosis Fractures
Understanding real-world cases of osteoporosis fractures helps illustrate the challenges and successful interventions in managing this condition. These case studies highlight the importance of early diagnosis, proactive treatment, and patient adherence to a personalized care plan to prevent further complications and improve quality of life.
Case Study 1: Atypical Femoral Fracture in an Elderly Patient
This case involves a 78-year-old female patient who presented with a spontaneous fracture of the femoral shaft. Her medical history revealed a diagnosis of osteoporosis, a long-term use of glucocorticoids, and a history of falls. The atypical nature of the fracture suggested a potential underlying cause beyond simple osteoporosis, such as medication-related bone loss or an unusual stress fracture.
Further investigation, including bone density scans and a detailed review of medications, revealed the correlation between the glucocorticoid use and the reduced bone mineral density. Treatment involved surgical stabilization of the fracture, coupled with a comprehensive management plan to reduce the risk of future fractures, including medication adjustments, fall prevention strategies, and ongoing monitoring of bone health. A key takeaway from this case is the importance of recognizing atypical fractures as potential indicators of underlying conditions and the necessity of a multidisciplinary approach to treatment.
Case Study 2: Vertebral Compression Fracture in a Postmenopausal Woman
A 65-year-old postmenopausal woman experienced a sudden onset of back pain following a minor fall. Physical examination revealed a compression fracture of a thoracic vertebra. Initial diagnosis involved a bone density scan, which confirmed osteoporosis. Treatment involved pain management strategies, such as medication and physical therapy. A tailored exercise program focusing on core strengthening and posture correction was implemented.
In addition, a regimen of bisphosphonates, a medication for osteoporosis, was prescribed to enhance bone density and reduce the risk of future fractures. The patient showed significant improvement in pain and functionality within several months of treatment, highlighting the efficacy of early intervention in vertebral fractures. The case demonstrates that treatment for vertebral compression fractures should involve a multi-faceted approach targeting pain relief, strengthening, and bone health improvement.
Case Study 3: Distal Radius Fracture in a Young Adult with Secondary Osteoporosis
A 30-year-old male patient presented with a distal radius fracture following a fall. While the fracture was initially considered a typical trauma-related injury, further investigation revealed a diagnosis of secondary osteoporosis, linked to a long-term history of hyperthyroidism. Treatment involved a surgical procedure to stabilize the fracture, followed by a comprehensive plan to address the underlying hyperthyroidism and promote bone health.
This case emphasizes the need to investigate secondary causes of osteoporosis, especially in younger patients with unexpected fractures. It highlights the importance of a collaborative approach between endocrinologists and orthopedic surgeons to manage both the fracture and the underlying medical condition. Further management strategies included thyroid medication to stabilize thyroid levels, and regular monitoring to track the progression of bone health.
Illustrative Information about Osteoporosis Fractures
Understanding osteoporosis fractures requires a deep dive into the intricate workings of bone tissue and the factors that influence its health. This section will provide a detailed look at bone structure, remodeling, hormonal influences, and the crucial role of bone mineral density (BMD) in fracture prevention.
Bone Tissue Structure and Function
Bone tissue, far from being inert, is a dynamic and complex living tissue. It’s composed of a framework of collagen fibers, a protein that provides flexibility, interwoven with calcium phosphate crystals, which contribute to its strength and hardness. This unique combination gives bone its remarkable ability to withstand stress while maintaining a degree of flexibility. Bone tissue constantly undergoes a process of remodeling, a crucial aspect of maintaining its health and preventing fractures.
The delicate balance between bone formation and resorption is essential for optimal bone strength. Disruptions in this balance, as seen in osteoporosis, can lead to significant structural weakening.
Bone Remodeling
Bone remodeling is a continuous process of bone resorption (breakdown) and bone formation (building). Osteoclasts, specialized cells, are responsible for bone resorption, while osteoblasts, another type of cell, are responsible for bone formation. These cells work in a coordinated fashion, maintaining a healthy equilibrium. This process is essential for bone repair and adaptation to stress. Think of it as a constant cycle of renovation within your skeleton.

Impact of Osteoporosis on Bone Density
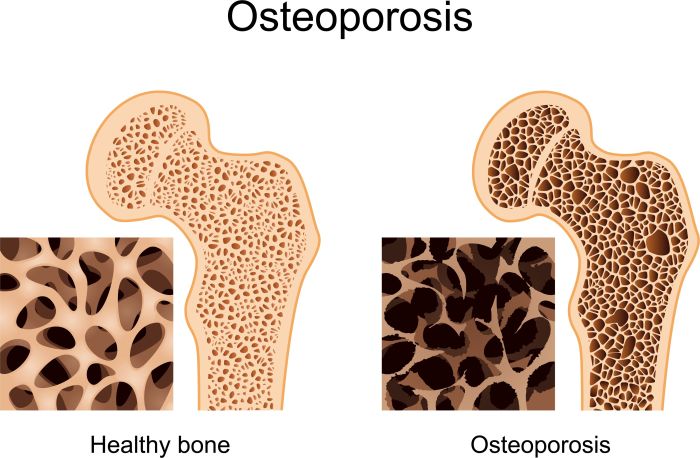
Osteoporosis weakens bones by reducing bone density, making them more porous and susceptible to fractures. This reduction in bone density is primarily due to an imbalance in the bone remodeling process, with resorption exceeding formation. This imbalance leads to decreased bone mass, and consequently, diminished strength and resilience. The image below depicts the difference in bone density between healthy bone and bone affected by osteoporosis.
The healthy bone will appear denser, while the osteoporosis-affected bone will show a significant decrease in density and increased porosity. 
Hormonal Factors in Bone Health
Hormonal factors play a crucial role in bone health. Estrogen, for example, is vital in maintaining bone density. Decreased estrogen levels, as seen during menopause, can significantly increase the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Other hormones, like parathyroid hormone (PTH), also influence calcium metabolism and bone turnover, contributing to the complex interplay of hormonal factors in bone health.
Imbalances in these hormonal systems can lead to significant skeletal vulnerabilities.
Bone Mineral Density (BMD)
Bone mineral density (BMD) is a measure of the amount of mineral content in a given area of bone. It’s a crucial indicator of bone strength and fracture risk. BMD is typically measured using a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scan. This non-invasive procedure uses low-dose X-rays to assess bone density, primarily in the hip and spine. The results are often expressed as a T-score, which compares an individual’s BMD to the average BMD of a healthy young adult of the same sex.
A T-score below -2.5 indicates osteoporosis, while a T-score between -1.0 and -2.5 indicates osteopenia, a condition that increases the risk of osteoporosis.
Example: A T-score of -2.5 in the femoral neck (part of the hip) would suggest osteoporosis in that area.
End of Discussion
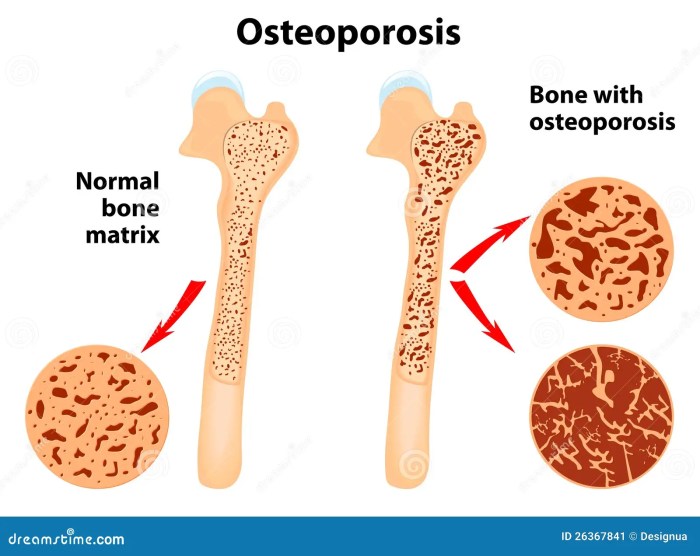
In conclusion, osteoporosis fractures treatment and prevention requires a multifaceted approach that considers various factors, from lifestyle choices to medical interventions. This guide has highlighted the importance of early diagnosis, proactive risk management, and personalized treatment plans. By understanding the underlying mechanisms, risk factors, and available treatment options, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of osteoporosis fractures and maintain optimal bone health throughout their lives.
Remember, proactive steps today can lead to a healthier, more active tomorrow.




