Gout tophi tophus what is it – Gout tophi tophus, what is it? This condition, characterized by painful deposits of uric acid crystals, can significantly impact daily life. Understanding the formation, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management. We’ll explore the underlying biology, diagnostic methods, and potential complications associated with gout tophi, providing a comprehensive overview of this often-misunderstood condition.
Gout tophi, also known as tophi, are small, hard deposits of uric acid crystals that form around joints. These deposits can lead to significant pain, inflammation, and potentially permanent joint damage. Understanding the factors that contribute to gout tophi formation, along with available treatment options, is key to preventing and managing this condition.
Gout Tophi: Understanding the Crystal Deposits
Gout tophi, or tophi, are a hallmark of gout, a painful and chronic condition. These are small to large, hard deposits of uric acid crystals that form in and around joints. Understanding their formation, characteristics, and potential complications is crucial for effective management of gout.
Definition and Overview of Gout Tophi
Gout tophi are masses of monosodium urate crystals, a byproduct of purine metabolism, that accumulate in tissues outside the blood vessels. These deposits, typically found around joints, can lead to significant joint damage and chronic pain if left untreated.
Biological Process of Tophi Formation
The buildup of uric acid, a waste product, in the bloodstream is the primary driver of gout tophi formation. When uric acid levels exceed the solubility limit of the body’s fluids, it precipitates out of solution, forming needle-shaped crystals. These crystals then attract inflammatory cells and proteins, leading to the formation of the characteristic tophi deposits.
Types of Gout Tophi
While not categorized into distinct types based on their composition, tophi vary in size and location depending on the severity and duration of gout. Larger tophi are more prone to becoming symptomatic and problematic.
Comparison with Similar Conditions
While tophi are specifically associated with gout, other conditions can present with similar symptoms or tissue deposits. For example, calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD) can cause similar deposits, but the underlying cause and crystal structure differ. A proper diagnosis requires a thorough medical evaluation, including a detailed medical history, physical examination, and potentially imaging studies.
Gout tophi, those painful deposits of uric acid crystals, can be a real pain. Understanding their formation is key, but sometimes it’s hard to connect that to other health issues. Interestingly, some research suggests a potential link between certain inflammatory conditions, like Crohn’s disease, and the development of gout. To delve deeper into potential causes and risk factors of Crohn’s disease, check out this helpful resource: crohns disease causes and risk factors.
Regardless of the specific cause, managing gout tophi effectively remains crucial for overall well-being.
Typical Locations of Gout Tophi Formation
Gout tophi commonly develop around joints, particularly those in the lower extremities, such as the big toe (first metatarsophalangeal joint), ankles, knees, and less frequently in the elbows and wrists. Their formation often reflects areas of chronic inflammation and high concentrations of urate crystals.
Gout tophi, or tophus, are those painful deposits of uric acid crystals that can form in and around joints. Understanding how these build up is key to managing the condition, and sometimes treatments can feel like a marathon. While exploring ways to alleviate the pain, I’ve also been curious about how effective allergy shots are in improving quality of life, and I found a great resource discussing do allergy shots really work.
Ultimately, learning about different treatment approaches, whether for allergies or gout, can lead to better self-management and a more comfortable existence.
Comparison Table: Gout Tophi vs. Other Conditions
| Condition | Description | Location | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gout Tophi | Deposits of monosodium urate crystals in tissues, often around joints. | Joints in the lower extremities (big toe, ankles, knees), occasionally elbows, wrists. | Pain, swelling, redness, tenderness, warmth around affected areas; tophi may be palpable as firm nodules. |
| Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease (CPPD) | Deposits of calcium pyrophosphate crystals in tissues, often around joints. | Similar locations to gout tophi, but can also occur in the shoulders, hips, and spine. | Pain, swelling, stiffness, and sometimes clicking or grinding sounds in the affected joints; deposits may be less clearly defined than gout tophi. |
| Pseudogout | A form of arthritis caused by CPPD crystal deposition. | Similar locations to gout tophi, but can also occur in the shoulders, hips, and spine. | Acute attacks of pain, swelling, and stiffness in affected joints. |
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Gout tophi, those painful deposits of uric acid crystals, don’t just appear overnight. They develop gradually, often starting with less noticeable symptoms. Understanding the progression and the various diagnostic methods is crucial for early intervention and effective management. Accurate diagnosis hinges on a combination of clinical evaluation, patient history, and potentially, specialized imaging.The symptoms of gout tophi, while initially subtle, can become increasingly severe if left untreated.
This progression underscores the importance of prompt medical attention and adherence to prescribed therapies. Early diagnosis allows for timely intervention to mitigate the long-term damage associated with these crystal deposits.
Common Symptoms of Gout Tophi
The initial symptoms often mimic other joint conditions, making early diagnosis challenging. Characteristic symptoms include persistent pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness around the affected joint. These symptoms frequently appear acutely, often triggered by a specific event like a high-purine meal. These symptoms can fluctuate in intensity. Sometimes, the affected area may feel warm to the touch.
Severity and Progression of Symptoms
The severity of symptoms can vary greatly from person to person and depend on the location and extent of the tophi formation. In the early stages, the pain might be intermittent, occurring only during periods of activity or after specific dietary choices. As the condition progresses, the pain becomes more constant, and the affected area may become significantly inflamed.
Large tophi can restrict joint movement and cause chronic pain, greatly impacting daily activities.
Methods for Diagnosing Gout Tophi
A thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history is crucial. This includes questions about dietary habits, family history of gout, and any recent illnesses or injuries. A physical examination, focusing on the affected joint, is performed to assess the presence of swelling, tenderness, and redness. The physician may also palpate the affected area for the characteristic hard, palpable nodules (tophi) that are indicative of gout.
Role of Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques play a vital role in confirming the diagnosis and assessing the extent of the damage. X-rays can reveal the presence of tophi, which appear as radiopaque deposits within the joint. Ultrasound is another valuable tool, providing a real-time view of the affected area and allowing visualization of the tophi and surrounding soft tissues. These techniques can also help distinguish gout tophi from other conditions that might mimic its symptoms.
Comparison of Diagnostic Tests
| Diagnostic Test | Description | Accuracy | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient History and Physical Examination | Gathering information about symptoms, lifestyle, and family history; physical assessment of affected area. | Moderate | Subjectivity in assessment, potential for misdiagnosis in early stages. |
| Serum Uric Acid Level | Blood test measuring uric acid levels. | High | Elevated levels don’t definitively diagnose gout; other conditions can cause elevated levels. |
| X-rays | Radiographic images of the affected joint. | High | May not reveal early-stage tophi; can’t show soft tissue detail. |
| Ultrasound | Imaging technique using sound waves to visualize soft tissues. | High | Limited ability to show bone structures; interpretation can be operator-dependent. |
Treatment and Management
Managing gout tophi requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both the acute attacks and the underlying condition. Effective treatment aims to reduce inflammation, dissolve existing crystals, prevent further crystal formation, and ultimately minimize the risk of future attacks and further tophi development. This involves a combination of medications, lifestyle modifications, and close monitoring by a healthcare professional.Successful gout tophi management involves a personalized strategy tailored to the individual’s specific needs and health status.
The goal is not just to alleviate symptoms but to prevent long-term complications and improve overall quality of life. Early intervention and consistent adherence to the treatment plan are crucial for positive outcomes.
Medication Options for Gout Tophi
Pharmaceutical interventions play a vital role in managing gout tophi. They are designed to reduce inflammation, inhibit uric acid production, or enhance uric acid excretion. These medications are often used in conjunction with lifestyle modifications to achieve optimal results.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): These medications, such as ibuprofen and naproxen, are frequently used to relieve pain and inflammation during acute gout attacks. They work by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which are key players in the inflammatory process. NSAIDs can be effective in reducing the size and number of tophi over time, but their effectiveness varies between individuals.
- Colchicine: This medication is another common choice for acute gout attacks. It inhibits the migration of white blood cells to the affected area, thus reducing inflammation and pain. Colchicine can also be effective in preventing future gout attacks in some cases, but it may cause gastrointestinal side effects, including nausea and vomiting.
- Corticosteroids: These powerful anti-inflammatory drugs, such as prednisone, can be prescribed for severe gout attacks or when other medications are not effective. Their rapid anti-inflammatory action can be very helpful, but long-term use is generally discouraged due to potential side effects.
- Uricosuric agents: These medications, such as probenecid and sulfinpyrazone, increase the excretion of uric acid by the kidneys. This helps lower the levels of uric acid in the blood, preventing the formation of new tophi and dissolving existing ones over time. Uricosuric agents are generally prescribed for long-term management of gout and require careful monitoring of kidney function.
- Xanthine oxidase inhibitors: These medications, such as allopurinol and febuxostat, reduce the production of uric acid by inhibiting the enzyme xanthine oxidase. This is a cornerstone treatment for long-term gout management, aiming to prevent future attacks and slow the growth of tophi. They are often prescribed in combination with lifestyle modifications.
Lifestyle Modifications for Gout Tophi Prevention
Lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of gout tophi recurrence. They act as supportive measures to the medication regimen, aiming to reduce the underlying causes of hyperuricemia.
- Dietary Adjustments: A diet low in purines, such as organ meats, red meat, and seafood, can help control uric acid levels. Limiting alcohol consumption, particularly beer, is also important, as alcohol can increase uric acid production. Increasing fluid intake to aid in uric acid excretion is also recommended.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can contribute to better overall health and lower uric acid levels. Weight loss, if applicable, can reduce the strain on the kidneys and improve their ability to filter uric acid.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps to improve overall health and can promote the excretion of uric acid. A balanced exercise routine, including cardio and strength training, is beneficial.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively affect overall health and contribute to inflammation. Incorporating stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can improve the management of gout.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Managing Gout Tophi
This Artikels a general approach; individual plans may vary based on the severity of the condition and other health factors.
- Consultation with a Rheumatologist: Seek professional guidance for accurate diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan.
- Medication Adherence: Follow the prescribed medication regimen diligently, ensuring proper dosage and timing.
- Dietary Modifications: Implement a purine-restricted diet and limit alcohol consumption.
- Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Regular Monitoring: Schedule regular check-ups to monitor uric acid levels, tophi size, and overall health.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Incorporate stress-reducing techniques and regular physical activity into your routine.
Examples of Successful Gout Tophi Management
Successful gout tophi management is often a long-term process, but consistent effort can lead to significant improvements. Examples include individuals who, through a combination of medication and lifestyle changes, experience a reduction in the size of tophi, a decrease in frequency of attacks, and an overall improvement in their quality of life. These positive outcomes are directly correlated with the patient’s adherence to the treatment plan.
Treatment Options and Potential Side Effects
| Treatment Option | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|
| NSAIDs | Gastrointestinal upset, kidney problems, heartburn, stomach ulcers |
| Colchicine | Gastrointestinal upset, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting |
| Corticosteroids | Increased risk of infections, osteoporosis, high blood pressure, diabetes, mood swings |
| Uricosuric agents | Kidney stones, nausea, vomiting, allergic reactions |
| Xanthine oxidase inhibitors | Gastrointestinal upset, skin rash, liver problems |
Complications and Prevention
Untreated gout tophi, or crystal deposits, can lead to significant complications, impacting joint function and overall health. Understanding these potential problems and preventative measures is crucial for managing gout effectively and improving quality of life. Early intervention, coupled with lifestyle modifications, can dramatically reduce the risk of developing severe complications.The long-term effects of untreated gout tophi are multifaceted and can range from localized pain and stiffness to systemic issues.
Ignoring the condition can lead to irreversible joint damage, making daily activities challenging and impacting mobility. Therefore, proactive steps to prevent tophi formation and address existing deposits are paramount.
Potential Complications of Gout Tophi
Gout tophi can cause a range of complications, including severe joint damage, chronic pain, and even kidney stones. The sharp, needle-like crystals within the tophi can erode cartilage and bone, leading to permanent deformities and reduced range of motion. Untreated tophi can also spread to other joints, creating a systemic inflammatory condition.
Long-Term Effects of Untreated Gout Tophi
The long-term effects of untreated gout tophi can be severe. Chronic inflammation can lead to joint destruction, making movement painful and restricted. In advanced cases, the affected joints may become severely deformed, impacting daily activities like walking, dressing, and eating. Furthermore, gout tophi can affect the kidneys, increasing the risk of kidney stones and even chronic kidney disease.
Gout tophi, those little crystals forming painful lumps, are a real pain. Understanding how long before bed you should stop eating can impact your overall health, which, in turn, can affect gout. Proper digestion is key for preventing inflammation, and following a consistent routine, like knowing how long before bed you should stop eating , can be crucial for managing these painful deposits.
Ultimately, managing gout tophi involves a holistic approach, and making the right choices about diet and lifestyle is key.
Strategies for Preventing Gout Tophi Development
Effective prevention strategies for gout tophi development focus on managing the underlying cause of hyperuricemia. This involves lifestyle modifications, medication adherence, and regular monitoring. Maintaining a healthy weight, consuming a balanced diet low in purines, and engaging in regular physical activity can significantly reduce the risk. Early diagnosis and intervention are essential in preventing tophi formation.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Intervention
Early diagnosis of gout and prompt intervention are critical in preventing tophi formation and minimizing potential complications. Early treatment with medication can help control uric acid levels, preventing further crystal deposition and halting the progression of joint damage. Early intervention often leads to better outcomes, reducing the risk of long-term complications.
Preventative Measures and Effectiveness, Gout tophi tophus what is it
Implementing a comprehensive approach to prevent gout tophi formation involves multiple strategies. A diet low in purines, which are substances that can increase uric acid levels, can significantly reduce the risk. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and adequate hydration are crucial for overall health and uric acid management.
Table: Risk Factors and Preventive Strategies
| Risk Factor | Preventive Strategy | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| High Purine Diet (e.g., red meat, seafood) | Consume a diet lower in purines, focusing on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. | High |
| Obesity | Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise. | Moderate to High |
| Dehydration | Drink plenty of water to help flush out excess uric acid. | Moderate |
| Lack of Exercise | Engage in regular physical activity. | Moderate to High |
| Family History of Gout | Monitor uric acid levels and seek medical advice if needed. | Moderate |
Visual Representation (Illustrative Content): Gout Tophi Tophus What Is It
Gout tophi, those painful deposits of uric acid crystals, aren’t just a clinical diagnosis; they’re visible structures with characteristic appearances. Understanding these visual representations, from macroscopic examination to microscopic analysis and imaging, is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management. This section delves into the visual characteristics of gout tophi, highlighting their different appearances across various modalities.Gout tophi are a key diagnostic feature of gout.
Their visual presentation, both macroscopically and microscopically, and on imaging studies, can assist in distinguishing gout from other conditions. The visual aspects of gout tophi provide essential information about the disease’s progression, severity, and treatment response.
Typical Appearance of a Gout Tophus
Gout tophi typically manifest as firm, hard nodules or lumps beneath the skin. These deposits can vary significantly in size, ranging from small, barely perceptible bumps to large, prominent masses. Their consistency is often described as gritty or stony. The color of the tophi is usually a chalky white or yellowish-white, but can sometimes appear slightly reddish or bluish depending on the surrounding tissue inflammation.
The overlying skin may be normal or slightly reddened and tender to the touch. Pain is often associated with the inflammation surrounding the tophi.
Gout Tophi on Imaging Scans
Imaging plays a vital role in diagnosing and monitoring gout tophi. X-rays are often the first imaging modality used. Early gout tophi may not be visible on X-rays, but as they progress, they show up as radiopaque (meaning they block X-rays) lesions, appearing as irregular, chalky white deposits, sometimes with surrounding bone erosion. Ultrasound imaging can reveal the characteristic hyperechoic (bright) appearance of the crystalline deposits within the soft tissues.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can show the extent of inflammation and soft tissue involvement surrounding the tophi, allowing for better assessment of the disease process.
Microscopic Structure of Gout Tophi
Microscopically, gout tophi are characterized by large accumulations of needle-shaped monosodium urate crystals. These crystals are arranged in clusters, forming the characteristic “needle-like” structures. The surrounding tissue may show signs of inflammation, including infiltration of inflammatory cells. The presence of these crystals, along with the characteristic tissue response, is crucial for a definitive diagnosis.
Table: Appearances of Gout Tophi Across Imaging Modalities
| Imaging Modality | Appearance |
|---|---|
| X-ray | Radiopaque, irregular, chalky white deposits, potentially with bone erosion. |
| Ultrasound | Hyperechoic (bright) lesions within the soft tissues, often with surrounding inflammation. |
| MRI | Soft tissue swelling and inflammation around the tophi, potentially highlighting the extent of the disease. |
Diagram: Progression of Gout Tophi Formation
A diagram depicting the progression of gout tophi formation would show the initial accumulation of monosodium urate crystals, progressing to the formation of small nodules, which then enlarge and coalesce to form larger, more visible tophi. The surrounding tissue would display increasing inflammation. The diagram would emphasize the gradual nature of tophi formation and the role of repeated episodes of hyperuricemia.
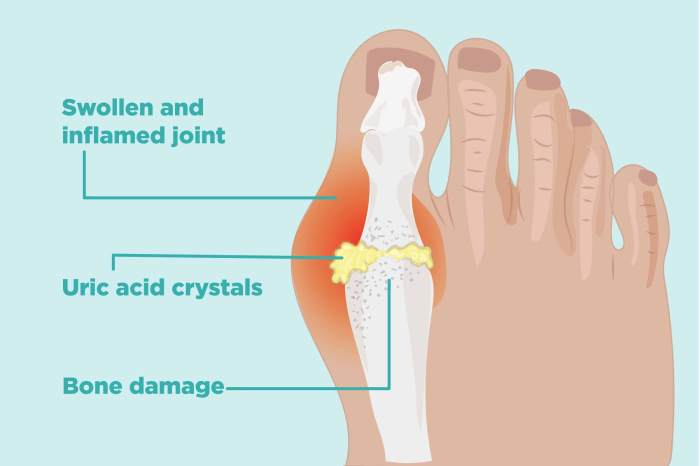
Illustration of a Joint Affected by Gout Tophi
Imagine a joint, specifically the big toe, swollen and red. A firm, chalky white nodule is prominent beneath the skin on the side of the joint. The skin over the nodule may be tender and warm to the touch. This visual representation depicts the characteristic appearance of a joint affected by gout tophi, emphasizing the visible deposit and surrounding inflammation.
The illustration would also show the potential for tophi to develop in other joints such as the ankles, knees, and wrists.
Closing Summary

In summary, gout tophi tophus is a complex condition demanding careful attention to its various aspects. Early diagnosis and proactive management are crucial for preventing long-term complications. By understanding the biological processes, symptoms, and available treatments, individuals can work with healthcare professionals to effectively manage gout tophi and improve their overall well-being.




