The thyroid peroxidase antibody test is a crucial diagnostic tool for identifying autoimmune thyroid conditions. Understanding this test involves exploring its purpose, procedure, potential factors influencing results, and the significance of interpreting those results. This guide delves into the various aspects of the test, from its fundamental role in medical diagnostics to the practical implications for diagnosis and treatment.
This test helps doctors determine if your immune system is attacking the thyroid gland, a small but vital gland responsible for producing hormones that regulate metabolism and other essential functions in your body. It’s a valuable tool for understanding potential thyroid problems, enabling proactive management and personalized treatment strategies.
Introduction to Thyroid Peroxidase Antibody Test
The thyroid peroxidase antibody test, often abbreviated as TPO antibody test, is a blood test used to detect the presence of antibodies targeting thyroid peroxidase, an enzyme crucial for thyroid hormone production. Understanding these antibodies and their levels can help diagnose thyroid conditions and guide treatment strategies. This test is a valuable tool for healthcare professionals in evaluating potential thyroid issues.The purpose of this test is to identify the presence of autoantibodies, specifically targeting thyroid peroxidase, an enzyme crucial for thyroid hormone synthesis.
These antibodies, if present in elevated levels, often indicate an autoimmune response, a situation where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues. The presence of these antibodies is a key indicator in diagnosing autoimmune thyroid diseases, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
Types of Thyroid Peroxidase Antibody Tests and Applications
Different laboratories may employ various techniques to detect TPO antibodies. The common methods include enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs), which measure the amount of antibodies present in the blood sample. ELISA tests are commonly used in clinical settings due to their accuracy and efficiency. The results are reported as antibody titers (often measured in IU/mL), which represent the concentration of antibodies in the blood.
Different laboratories may use different units, so it’s crucial to check the specific reporting units for each test.
Interpreting Results of the Test
The interpretation of TPO antibody test results is crucial for clinical diagnosis. Elevated TPO antibody levels often correlate with autoimmune thyroid conditions, particularly Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, a condition that frequently leads to hypothyroidism. However, the absence of antibodies doesn’t definitively rule out thyroid disease. Other factors, such as iodine deficiency, can contribute to thyroid dysfunction. A healthcare professional must consider the test results alongside other clinical findings and symptoms to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
A doctor will typically assess the TPO antibody levels in relation to other clinical parameters, including thyroid hormone levels (TSH, T3, and T4), to accurately evaluate the patient’s thyroid function.
Common Reasons for Ordering the Test
Healthcare providers might order a TPO antibody test for various reasons. Suspected autoimmune thyroid conditions, like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, are a primary concern. Individuals experiencing symptoms suggestive of hypothyroidism, such as fatigue, weight gain, or cold intolerance, may undergo this test. Family history of autoimmune diseases, including thyroid disorders, also prompts the testing. Additionally, monitoring the progress of patients with known thyroid conditions or evaluating the effectiveness of treatment can involve this test.
A significant increase in TPO antibodies might suggest a worsening of the condition, while a decrease could indicate a response to treatment. For example, a patient with a history of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis might have this test repeated periodically to monitor the antibody levels and assess the effectiveness of medication.
Test Procedure and Preparation
The thyroid peroxidase antibody (TPOAb) test is a crucial diagnostic tool for identifying autoimmune thyroid conditions, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease. Understanding the test procedure and preparation ensures accurate results and facilitates proper patient management. A correct procedure is essential for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.Accurate interpretation of the TPOAb test results is directly linked to proper sample collection and handling.
This section details the necessary steps involved in performing the test, the required patient preparation, and different methodologies used for measuring antibodies. Adherence to these protocols is critical for reliable results.
Patient Preparation
Proper patient preparation is vital for obtaining accurate TPOAb test results. Fasting is generally not required for this test, but patients should inform their healthcare provider about any medications they are taking, as certain medications may interfere with the test results. This information will be important for the laboratory to adjust their procedures accordingly and may affect the test’s accuracy.
It’s also important to inform the lab personnel of any recent illnesses or conditions that may impact the test results.
Ever wondered about a thyroid peroxidase antibody test? It’s a blood test used to help diagnose autoimmune thyroid conditions. Sometimes, these conditions can manifest in skin issues, like various skin lesions. Understanding the different types of skin lesions, their causes, and treatment options can be really helpful, especially if you’re experiencing unusual skin changes alongside thyroid problems.
Check out this resource on types of skin lesion pictures causes and treatment for a comprehensive look at the subject. Ultimately, a thorough understanding of these skin conditions can provide further context and insights into your thyroid peroxidase antibody test results.
Sample Collection Methods
Venipuncture is the standard method for collecting blood samples for TPOAb testing. A qualified phlebotomist or trained medical professional will use a sterile needle and syringe to draw a blood sample from a vein, typically in the arm. The collected blood is then placed in a specific tube containing an anticoagulant to prevent clotting. Maintaining proper blood collection technique is paramount to avoid hemolysis (breakdown of red blood cells), which can interfere with the test’s accuracy.
Measurement Methodologies
Several methodologies exist for measuring TPOAb levels in a blood sample. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a common and widely used technique. This method involves coating a surface with a known substance that binds to the antibodies. The sample is then added, and if antibodies are present, they bind to the substance. A specific enzyme is then added to detect the antibodies.
The intensity of the color change is directly proportional to the antibody concentration. Other techniques, though less common, include radioimmunoassay (RIA) and immunofluorescence. Each method has its advantages and limitations in terms of sensitivity, specificity, and cost.
Step-by-Step Procedure
| Step | Description | Materials | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Patient identification and consent. | Patient identification form, consent form | Accurate patient identification and consent for the procedure. |
| 2 | Venipuncture. | Sterile needle, syringe, collection tube with anticoagulant (e.g., EDTA), alcohol swabs, gloves, sharps container. | Collection of a blood sample without contamination or hemolysis. |
| 3 | Labeling and processing of the sample. | Sample tubes, labels, appropriate storage conditions (refrigeration), transport containers. | Correctly labeled and processed blood sample ready for analysis. |
| 4 | Antibody measurement using ELISA or other appropriate methodology. | ELISA equipment, reagents, laboratory equipment. | Quantitative result of TPOAb levels in the blood sample. |
Factors Affecting Test Results
The thyroid peroxidase antibody (TPOAb) test is a valuable diagnostic tool, but its accuracy can be influenced by various factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for interpreting the results correctly and ensuring appropriate patient management. Factors like age, sex, underlying health conditions, medications, and even the testing method itself can impact the test outcome. A comprehensive understanding of these variables helps in distinguishing between a true positive or negative result and a false one.
Age and Sex
Age and sex can subtly influence TPOAb levels. Generally, the prevalence of TPOAb positivity tends to vary across different age groups and between genders. Studies have shown higher rates of positivity in older individuals, especially women, potentially reflecting the increased prevalence of autoimmune thyroiditis in this demographic. The correlation between age and TPOAb positivity might also be linked to the general rise in autoimmune diseases with age.
Similarly, differences in hormone levels between men and women could contribute to variations in TPOAb positivity rates.
Underlying Health Conditions
Other medical conditions can impact TPOAb levels. For example, individuals with certain infections, such as viral infections, or other inflammatory conditions, may show elevated TPOAb levels. This is because these conditions can affect the immune system, potentially leading to an overreaction and higher production of antibodies. Conversely, some illnesses can dampen the immune response, which might result in lower TPOAb levels than expected.
Medications
Medications can sometimes affect TPOAb test results. Certain drugs, like those used to treat psychiatric disorders or certain types of cancer, can impact the immune system, leading to either elevated or reduced TPOAb levels. For instance, some medications can induce an inflammatory response, potentially elevating antibody levels. Conversely, immunosuppressants, which suppress the immune system, might lead to lower TPOAb readings.
This interaction with medications is crucial to consider when interpreting the results, especially if the patient is taking multiple medications.
False-Positive and False-Negative Results
False-positive results occur when the test indicates the presence of TPOAb when it’s not actually present. This could be due to laboratory errors, sample handling issues, or interference from other factors, such as certain medications or conditions. False-negative results, conversely, indicate the absence of TPOAb when it is actually present. This could also be related to the reasons mentioned above, or the presence of certain medications or the specific testing method used.
Impact of Different Factors on Test Accuracy
The impact of different factors on the accuracy of the TPOAb test can vary significantly. While age and sex might show a general trend, the influence of underlying health conditions and medications can be highly specific. For example, a particular medication might consistently influence the results, whereas a viral infection may only temporarily elevate the TPOAb levels.
Correlation Between Factors and Potential Impact on Results
| Factor | Description | Potential Impact on Results |
|---|---|---|
| Age | Age-related changes in immune system activity | Potentially higher TPOAb positivity in older individuals, especially women. |
| Sex | Differences in hormone levels and immune response | Potential variations in TPOAb positivity rates between men and women. |
| Underlying Health Conditions | Infections, inflammation, or other medical conditions | May cause elevated or lowered TPOAb levels. |
| Medications | Certain medications affecting the immune system | Can potentially elevate or reduce TPOAb levels. |
| Laboratory Errors/Sample Handling | Errors during testing or sample processing | Can cause false-positive or false-negative results. |
Interpreting Results and Clinical Significance
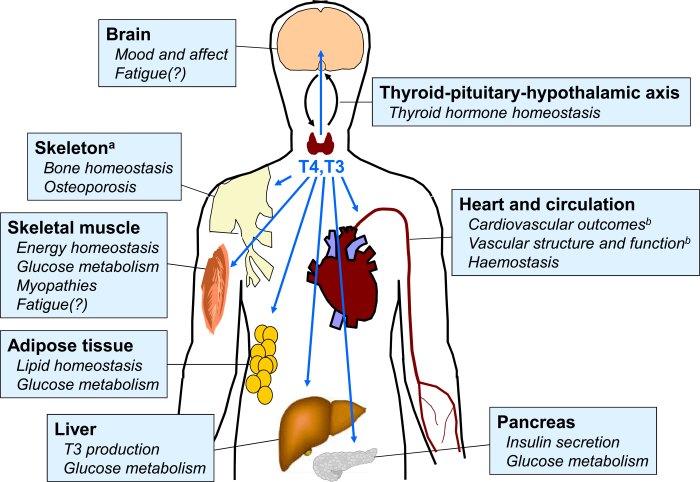
Understanding the results of a thyroid peroxidase antibody (TPOAb) test is crucial for diagnosing and managing thyroid disorders. These antibodies, produced by the immune system, can target the thyroid gland’s thyroid peroxidase enzyme, often indicating an autoimmune process. Interpreting TPOAb levels helps clinicians assess the risk of developing thyroid conditions and guide appropriate treatment strategies.
Reporting of Results and Value Ranges
TPOAb results are typically reported in units per milliliter (U/mL). The specific ranges used can vary slightly between laboratories, but generally, a result within a certain reference range suggests a healthy thyroid function. However, these reference ranges are not absolute; they should be considered in the context of the patient’s overall clinical presentation and other laboratory findings. Elevated levels often point towards an autoimmune thyroid disease, while decreased levels can sometimes suggest other underlying factors.
Significance of Elevated TPOAb Levels
Elevated TPOAb levels strongly suggest an autoimmune thyroid disease, most commonly Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. This condition is characterized by the immune system attacking the thyroid gland, leading to gradual thyroid damage and impaired hormone production. Elevated levels don’t necessarily mean the patient will develop a thyroid condition immediately, but it increases the risk significantly. In some cases, individuals with elevated TPOAb levels might not exhibit any symptoms, highlighting the importance of regular check-ups and monitoring.
For example, a 35-year-old woman with elevated TPOAb levels but no noticeable symptoms might be advised to monitor her thyroid function periodically.
Significance of Decreased TPOAb Levels
Decreased TPOAb levels are less frequently associated with specific conditions. While they don’t necessarily rule out thyroid disease, they often occur in patients who have other conditions or are undergoing treatments that affect the immune system. This doesn’t imply a complete absence of thyroid issues, and a comprehensive evaluation, including clinical symptoms and other tests, is essential for a proper diagnosis.
A 60-year-old man with a recent history of a severe illness and decreased TPOAb levels might need further investigations to rule out other potential underlying factors.
Medical Conditions Associated with Abnormal Results
Abnormal TPOAb levels can be indicative of various medical conditions. Elevated levels are strongly linked to autoimmune thyroid diseases, particularly Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, which often leads to hypothyroidism. Decreased levels might occur in individuals with certain conditions impacting the immune system, or those undergoing immune-suppressing treatments.
Comparison of Disease States and Antibody Levels
Different thyroid conditions exhibit distinct patterns in TPOAb levels. For instance, in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, the TPOAb levels are typically elevated, reflecting the autoimmune nature of the disease. In Graves’ disease, another autoimmune thyroid condition, TPOAb levels are often elevated, but another antibody, thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI), may also be elevated. Conversely, in patients with non-autoimmune thyroid disorders, such as thyroid nodules or iodine deficiency, TPOAb levels are usually normal.
Table: Thyroid Conditions and TPOAb Results
| Condition | Typical Antibody Level | Associated Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis | Elevated | Fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, constipation, dry skin, hair loss, goiter (enlarged thyroid) |
| Graves’ Disease | Elevated | Weight loss, nervousness, heat intolerance, rapid heartbeat, tremors, goiter |
| Thyroid Nodules | Normal or slightly elevated | May be asymptomatic or present with a lump in the neck, difficulty swallowing, or hoarseness |
| Iodine Deficiency | Normal | Goiter, fatigue, and other symptoms associated with hypothyroidism |
Diagnosis and Treatment Implications
The thyroid peroxidase antibody (TPO Ab) test plays a crucial role in diagnosing and managing autoimmune thyroid diseases. Understanding how these antibodies relate to the underlying conditions and how test results inform treatment is essential for effective patient care. This section delves into the diagnostic and treatment implications of TPO Ab testing, providing a clear picture of its importance in the healthcare process.
Role in Diagnosing Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases
The presence of elevated TPO antibodies strongly suggests an autoimmune thyroid condition. These antibodies attack the thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and potential dysfunction. While not a definitive diagnosis on its own, the test significantly contributes to a comprehensive evaluation, often used in conjunction with other tests, like thyroid hormone levels (TSH, T3, T4), and physical examination findings.
A positive TPO Ab result, combined with other clinical indicators, heightens the suspicion of autoimmune thyroiditis, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, and aids in differentiating it from other potential causes of thyroid dysfunction.
Using Test Results to Guide Treatment Plans
TPO Ab test results help healthcare professionals tailor treatment strategies. Elevated TPO antibodies typically indicate an ongoing autoimmune process. This information is essential in managing the progression of the condition, especially in cases of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. The treatment approach focuses on mitigating the effects of the immune response on the thyroid gland, often through medication to replace or regulate thyroid hormone levels.
The level of antibodies and the severity of the associated symptoms inform the intensity of the treatment plan.
Importance of Following Up with a Healthcare Professional
Regular monitoring is crucial after an initial TPO Ab test, particularly for individuals with elevated levels. Continued medical supervision allows for adjustments to treatment strategies based on the evolving condition. This personalized approach ensures optimal management of the disease and minimizes potential complications. Symptoms may vary, and regular check-ups allow for early detection of changes in thyroid function, preventing potential long-term health issues.
Ever wondered about those thyroid peroxidase antibody tests? They’re a crucial part of diagnosing thyroid issues, but healthy hair habits can also impact your overall well-being, including thyroid health. For example, regular scalp exfoliation can remove dead skin cells and promote healthy hair growth, which indirectly contributes to a healthier you, and thus, a better response to the thyroid peroxidase antibody test results.
Check out this guide on how to exfoliate your scalp for clean healthy hair how to exfoliate your scalp for clean healthy hair for some tips on keeping your scalp and thyroid in top shape! Ultimately, a holistic approach to health is key when considering the thyroid peroxidase antibody test.
Treatment Options Based on Diagnosis
| Condition | Treatment | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis (hypothyroidism) | Levothyroxine (synthetic thyroid hormone) | Normalization of thyroid hormone levels, reduction in symptoms, and potential slowing of disease progression. Examples include reduced fatigue, improved energy levels, and better mood regulation. |
| Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis (subclinical hypothyroidism) | Levothyroxine (synthetic thyroid hormone) – often initiated when TSH levels rise above a specific threshold, typically based on patient symptoms and risk factors. | Potential prevention of further thyroid damage, preventing progression to overt hypothyroidism. The exact outcome depends on individual factors. |
| Graves’ Disease (hyperthyroidism) | Antithyroid medications (e.g., methimazole), radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery. | Reduction in thyroid hormone production, normalization of thyroid hormone levels, and mitigation of hyperthyroid symptoms. Examples may include reduced heart rate, lower blood pressure, and improved energy regulation. |
Note: Treatment plans are personalized and depend on individual factors such as age, overall health, and severity of the condition.
Precautions and Considerations: Thyroid Peroxidase Antibody Test
The thyroid peroxidase antibody test, while generally safe, carries some potential risks and considerations. Understanding these precautions can help ensure a smooth and accurate testing process, minimizing any potential complications. Careful attention to pre- and post-test instructions is crucial for obtaining reliable results.Thorough preparation and awareness of potential issues are essential for ensuring the test’s accuracy and minimizing any adverse effects.
Adhering to the Artikeld precautions protects both the patient and the healthcare providers involved.
Potential Risks and Complications
The thyroid peroxidase antibody test itself is typically a safe procedure. However, like any medical test, there’s a slight possibility of discomfort or minor complications. These are usually temporary and resolve without intervention. Rarely, allergic reactions to the testing materials can occur, but these are typically manageable with prompt medical attention. Proper handling and administration of the test minimize these risks.
Importance of Medical History and Medications
Accurate test results depend on the patient’s complete disclosure of their medical history and current medications. This includes any known allergies, past or present thyroid conditions, other medical diagnoses, and all prescription, over-the-counter, and herbal medications. This information helps the healthcare provider interpret the results correctly and tailor any necessary follow-up care. For example, a patient with a known history of severe allergies to latex might require special handling during blood collection.
Conversely, if a patient is taking medications known to affect thyroid function, this needs to be noted.
Following Post-Test Instructions
Following post-test instructions is vital for the accuracy and safety of the results. These instructions, usually provided by the healthcare provider, may include avoiding strenuous activities for a short period or keeping the puncture site clean and dry. Adhering to these guidelines prevents potential complications, such as excessive bleeding or infection at the puncture site. For instance, applying pressure to the puncture site for a few minutes after the blood draw and keeping the area clean and dry can minimize the risk of bruising and infection.
Safety Precautions for Patients and Healthcare Providers
Safe practices are crucial during the thyroid peroxidase antibody test process, safeguarding both the patient and the healthcare provider. These practices encompass a range of procedures and precautions designed to mitigate potential risks.
- Proper Handling of Specimens: Maintaining proper handling procedures for blood samples is essential to prevent contamination and ensure accurate results. This includes using appropriate containers, labeling specimens correctly, and adhering to established protocols for transporting and storing samples.
- Sterile Techniques: Using sterile equipment and techniques throughout the procedure is crucial to prevent infections and maintain the integrity of the test. This includes using sterile needles and gloves during blood collection.
- Patient Monitoring: Monitoring the patient’s vital signs and overall condition before, during, and after the test is essential to detect any immediate adverse reactions. This helps in prompt intervention if needed.
- Allergy Precautions: Recognizing and addressing potential allergies to testing materials is crucial. A thorough allergy history from the patient and appropriate precautions are vital to minimize risks.
- Proper Disposal of Sharps: Safe disposal of sharps (needles, lancets) is a critical safety measure to prevent accidental needle sticks and potential infections for healthcare providers. Using appropriate sharps containers and disposal methods are crucial.
Alternative Tests and Comparisons
The thyroid peroxidase antibody (TPO) test is a valuable tool in diagnosing autoimmune thyroid conditions, but it’s not the only option. Understanding alternative tests and their comparative strengths and weaknesses can help healthcare providers make more informed decisions. This section delves into the various diagnostic methods available, highlighting their specific applications and limitations.Alternative tests provide crucial complementary information for a comprehensive assessment of thyroid function.
Comparing different tests based on factors like sensitivity, specificity, and cost aids in selecting the most suitable method for a particular patient or situation.
Ever wondered about that thyroid peroxidase antibody test? It’s a blood test used to help diagnose potential thyroid issues. While exploring ways to manage thyroid health, I stumbled upon a fascinating article on how adding a little sage to your diet can add flavor and lower cholesterol – a great addition to any healthy eating plan. add flavor and lower cholesterol with sage This approach might just complement managing the potential inflammation associated with thyroid peroxidase antibodies.
Ultimately, it’s always best to consult your doctor for personalized advice regarding thyroid peroxidase antibody test results.
Alternative Diagnostic Methods for Autoimmune Thyroid Disease
Various tests can assist in diagnosing conditions similar to those detected by the TPO antibody test. These methods provide alternative avenues for evaluating thyroid function and related issues. Consideration of these tests is critical for a thorough diagnostic approach.
- Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Test: This test measures the levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the pituitary gland. Elevated or suppressed TSH levels can indicate an underlying thyroid disorder. A normal TSH level doesn’t necessarily rule out thyroid issues, but it can be an initial screening tool. TSH is often used in conjunction with other tests for a more complete picture of thyroid health.
- Free T4 and Free T3 Tests: These tests assess the levels of free thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) hormones, which are biologically active forms of thyroid hormones. Imbalances in these hormones can be indicative of thyroid dysfunction. Combining these with TSH tests provides a more comprehensive evaluation of thyroid hormone production and function.
- Anti-Thyroglobulin Antibody (TgAb) Test: This test measures antibodies targeting thyroglobulin, a protein crucial for thyroid hormone production. High TgAb levels often accompany Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, a common autoimmune condition. This test is frequently used alongside TPO antibodies for a more definitive diagnosis.
- Ultrasound of the Thyroid Gland: This imaging technique allows visualization of the thyroid gland. It can identify structural abnormalities, nodules, or goiters that might contribute to thyroid dysfunction. This is especially useful for evaluating physical characteristics that may not be detectable through other tests.
- Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy (FNAB): This procedure involves extracting a small tissue sample from a thyroid nodule for microscopic examination. FNAB is essential for distinguishing benign from malignant nodules, a critical step in determining appropriate treatment.
Comparison of Diagnostic Methods
A comprehensive comparison of various diagnostic methods is presented in a table format below, offering a clear view of their strengths and weaknesses. The information below should be considered in conjunction with clinical judgment.
| Test | Sensitivity | Specificity | Cost | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPO Antibody | High | High | Moderate | Excellent for detecting autoimmune thyroiditis, early diagnosis | Doesn’t always reflect current thyroid hormone levels |
| TSH | High | Moderate | Low | Initial screening test, cost-effective | Doesn’t provide information about antibodies or thyroid gland structure |
| Free T4 & Free T3 | High | High | Moderate | Direct measure of active thyroid hormones | Doesn’t indicate the cause of hormonal imbalances |
| TgAb | High | High | Moderate | Helpful in distinguishing specific autoimmune forms | May not be as sensitive as TPO antibodies |
| Thyroid Ultrasound | Moderate to High | High | Moderate | Visualizes structural abnormalities, nodules | Doesn’t directly measure hormone levels or antibodies |
| FNAB | High | High | High | Confirms malignancy, guides treatment decisions | Invasive procedure, requires specialized expertise |
Prevention and Management Strategies
Taking proactive steps to prevent thyroid issues and effectively managing them after diagnosis is crucial for overall well-being. A combination of lifestyle choices, medical guidance, and ongoing monitoring can significantly impact the quality of life for individuals with thyroid conditions. Understanding the role of prevention and management is essential for long-term health and well-being.Adopting a healthy lifestyle is not just about preventing thyroid problems; it plays a vital role in managing them effectively.
A balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques can help maintain optimal thyroid function and minimize the severity of symptoms. Consistency in these practices is key to sustained improvement.
Preventive Measures for Thyroid Health
Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular physical activity is a significant preventive measure. A diet rich in iodine, essential for thyroid hormone production, is crucial. Foods like iodized salt, seafood, and dairy products can contribute to adequate iodine intake. Regular exercise and stress management are important components of overall health and can indirectly support thyroid function.
Reducing stress levels through techniques like yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature can have a positive effect on thyroid health.
Role of a Healthy Lifestyle in Managing Thyroid Conditions, Thyroid peroxidase antibody test
A healthy lifestyle plays a vital role in managing existing thyroid conditions. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains is essential for overall health and can support the body’s metabolic processes. Regular exercise not only improves physical health but also helps regulate mood and reduce stress, which can positively influence thyroid function. Adequate sleep is critical for hormone regulation, including thyroid hormones.
Prioritizing sleep hygiene can help optimize thyroid function. Minimizing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies, can also contribute to managing thyroid conditions effectively.
Monitoring and Managing the Condition After Diagnosis
After diagnosis, regular check-ups with a healthcare professional are critical for monitoring the condition and adjusting treatment as needed. The frequency of these check-ups will vary based on individual circumstances and the specific thyroid condition. This includes monitoring thyroid hormone levels, and other relevant markers, as well as addressing any emerging symptoms. Adhering to prescribed medications and making necessary lifestyle adjustments is crucial for managing the condition.
Open communication with the healthcare provider is vital to address concerns, adjust treatment plans, and achieve optimal management.
Lifestyle Recommendations for Managing Thyroid Conditions
- Balanced Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains is essential for overall health and can support the body’s metabolic processes. Incorporating foods rich in iodine, such as iodized salt, seafood, and dairy products, is also beneficial. Limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive caffeine can help manage symptoms.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity is beneficial for overall health and can help regulate mood and reduce stress. Finding activities you enjoy, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, can contribute to a healthier lifestyle.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact thyroid function. Employing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies, can help manage symptoms effectively.
- Adequate Sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for hormone regulation, including thyroid hormones. Prioritizing sleep hygiene, such as establishing a regular sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine, can contribute to better management.
- Regular Check-ups: Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare professionals are critical for monitoring thyroid hormone levels, addressing any emerging symptoms, and adjusting treatment plans as needed.
Closure
In conclusion, the thyroid peroxidase antibody test plays a vital role in diagnosing and managing autoimmune thyroid conditions. By understanding the test’s procedure, potential influencing factors, and interpretation of results, individuals and healthcare providers can collaborate effectively to achieve optimal health outcomes. Remember, accurate diagnosis and proactive management are key to maintaining overall well-being.




