USPSTF draft recommendation vitamin D calcium supplements is sparking debate, prompting crucial questions about preventative care. This comprehensive look delves into the specifics of the draft recommendation, examining its target population, potential benefits, risks, and alternative strategies for bone health. The document also compares it with existing guidelines and explores its implications for healthcare professionals and public health.
The USPSTF’s draft recommendation on vitamin D and calcium supplements aims to provide clarity on the best practices for preventative care regarding these essential nutrients. The document Artikels the evidence base supporting the recommendations, detailing the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. It carefully considers potential benefits, risks, and alternative strategies, such as diet and exercise, for optimal bone health.
The recommendation is critically compared with existing guidelines, highlighting similarities and differences. Finally, implications for healthcare professionals, public health, and potential future research are examined.
Introduction to USPSTF Draft Recommendation
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recently released a draft recommendation regarding vitamin D and calcium supplements. This recommendation aims to clarify the role of these supplements in preventing bone fractures and other health issues. The USPSTF’s draft recommendation is a significant step in guiding healthcare decisions about supplement use, particularly in light of the ongoing debate about their effectiveness.This document will summarize the USPSTF draft recommendation, focusing on the target population, potential benefits and drawbacks for different groups, and key considerations influencing the recommendation.
Understanding these factors is crucial for informed decision-making about vitamin D and calcium supplement use.
Target Population, Uspstf draft recommendation vitamin d calcium supplements
The USPSTF draft recommendation targets adults aged 50 and older. This age group is particularly susceptible to bone health issues, and the recommendation addresses potential preventive measures. The recommendation specifically considers those without known bone disorders or other medical conditions that may interact with vitamin D or calcium supplementation.
Populations Potentially Benefiting Most
Certain populations may benefit more from vitamin D and calcium supplementation than others. For instance, individuals with a history of bone fractures or osteoporosis are likely to see significant advantages. This is because vitamin D and calcium are essential for bone health, and supplementation can potentially strengthen bones and reduce the risk of future fractures. Elderly individuals living in areas with limited sunlight exposure may also benefit from supplementation, as vitamin D synthesis is often reduced in these conditions.
Additionally, individuals with certain dietary restrictions that limit their calcium intake may find supplementation helpful.
Populations Potentially Benefiting Least
Conversely, certain individuals may derive minimal benefit or even face potential risks from supplementation. Those with pre-existing kidney or liver conditions may experience complications from high doses of vitamin D or calcium. Individuals with a healthy diet and sufficient exposure to sunlight are likely to obtain sufficient amounts of these nutrients through natural means, reducing the need for supplementation.
Key Considerations for the USPSTF’s Recommendation
| Factor | Description | Impact on Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Evidence on Effectiveness | The USPSTF evaluates scientific studies to determine the effectiveness of vitamin D and calcium supplements in preventing fractures. | Studies showing a clear benefit or harm will influence the strength of the recommendation. |
| Potential Benefits | Supplementation may help prevent fractures, particularly in specific populations. | Benefits, when evident, inform the positive aspects of the recommendation. |
| Potential Harms | High doses of vitamin D and calcium may have adverse effects on certain individuals, such as those with kidney or liver issues. | Potential harms influence the cautionary aspects of the recommendation, including the need for specific caveats or warnings. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | The USPSTF considers the cost of supplementation compared to potential healthcare savings from reduced fracture rates. | Cost-effectiveness analysis helps determine the value of recommending supplementation. |
Evidence Base for the Recommendation
The USPSTF draft recommendation on vitamin D and calcium supplements hinges on a critical analysis of existing research. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of the studies used, as well as the methodologies employed, is crucial to evaluating the validity and reliability of the recommendation. This section delves into the evidence base, examining the types of studies, their methodologies, and the overall quality of the findings.
Types of Studies Used
The evidence base for this recommendation likely includes various types of studies, from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to observational studies. RCTs, considered the gold standard, randomly assign participants to either a treatment group (receiving the supplement) or a control group (receiving a placebo or no treatment). Observational studies, such as cohort or case-control studies, track participants over time to assess associations between vitamin D/calcium intake and health outcomes.
The relative weight given to each study type will depend on its design and methodology.
Strengths and Weaknesses of the Evidence Base
The strength of the evidence base is dependent on the quality of the individual studies. A strong evidence base relies on well-designed RCTs with large sample sizes, low risk of bias, and clear reporting. Weaknesses may arise from study design limitations, such as small sample sizes, high dropout rates, or inadequate follow-up periods. Confounding factors, such as pre-existing health conditions or lifestyle choices, can also affect the interpretation of results in observational studies.
The USPSTF draft recommendation on vitamin D and calcium supplements is interesting, but ultimately, good oral hygiene plays a crucial role in overall health. For example, proper brushing techniques, like those outlined in this helpful guide on how to brush your teeth , can significantly impact your dental health. While the supplements might have some benefits, consistent oral care is essential, and understanding the correct techniques is key to maintaining a healthy smile, which is ultimately important for the health recommendations of the USPSTF draft on vitamin D and calcium supplements.
Methodologies Used in the Studies
Diverse methodologies were likely employed in the studies informing the recommendation. These include variations in the types and doses of vitamin D and calcium supplements used, the duration of the studies, the specific health outcomes measured (e.g., fractures, falls, certain cancers), and the characteristics of the study participants (e.g., age, sex, pre-existing conditions). These methodological choices will affect the generalizability and applicability of the findings to different populations.
The USPSTF draft recommendation on vitamin D and calcium supplements is interesting, but it got me thinking about other health concerns. For instance, how does this relate to conditions like lung cancer spread to the liver? lung cancer spread to the liver presents a complex picture, and while vitamin D and calcium supplements might not be the direct solution, understanding their potential role in overall health is key.
Ultimately, the USPSTF draft recommendation is a valuable resource for understanding the bigger picture of health and wellness.
Comparison of Study Results
| Study | Intervention | Duration | Primary Outcome | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study A | Daily vitamin D3 supplement (2000 IU) | 2 years | Fractures | No significant difference in fracture rates compared to placebo. |
| Study B | Calcium supplement (1200 mg) | 3 years | Bone density | Slight improvement in bone density observed in the supplement group. |
| Study C | Combined vitamin D3 and calcium | 5 years | Hip fractures | Mixed results; some studies showed a reduction in hip fractures, others showed no significant difference. |
| Study D | High-dose vitamin D (4000 IU) | 1 year | Cardiovascular events | No clear association between high-dose vitamin D and reduced cardiovascular risk. |
Note: This table is illustrative and does not represent actual study results. The specific studies included in the evidence base will vary, and the results will need to be carefully evaluated to assess the overall impact of the interventions.
Potential Benefits of Supplementation
Vitamin D and calcium supplements are frequently touted as beneficial for overall health, particularly bone health. However, the extent and nature of these benefits are often debated, and robust evidence is crucial for informed decision-making. This section delves into the potential advantages of these supplements, examining the evidence supporting their impact on bone health and other aspects of well-being.Vitamin D and calcium are essential nutrients, playing a vital role in maintaining various bodily functions.
Their impact on health extends beyond simply building and maintaining strong bones. Understanding the potential benefits of supplementation requires a critical examination of the available scientific evidence.
Potential Impact on Bone Health
Adequate calcium and vitamin D are fundamental for maintaining bone density and strength. Calcium is the primary component of bones, providing structural support. Vitamin D enhances calcium absorption in the gut, facilitating its incorporation into bone tissue. Insufficient intake of these nutrients can lead to weakened bones, increasing the risk of fractures, especially in older adults.
Studies show that vitamin D and calcium supplementation can positively influence bone mineral density (BMD), reducing the risk of fractures, particularly in individuals with low vitamin D or calcium levels.
The positive impact on bone health is especially pronounced in individuals who are deficient in these nutrients. Sufficient calcium and vitamin D intake during growth periods, such as childhood and adolescence, is critical for establishing optimal bone density and preventing future bone-related problems.
Potential Impact on Overall Health Beyond Bone Health
Beyond their crucial role in bone health, vitamin D and calcium supplementation may also impact other aspects of health.
- Immune Function: Vitamin D plays a key role in regulating the immune system. Studies suggest that adequate vitamin D levels may contribute to a stronger immune response and potentially reduce the risk of certain infections. A strong immune system is crucial for overall well-being.
- Muscle Function: Both vitamin D and calcium are involved in muscle function. Adequate levels of these nutrients may contribute to better muscle strength and reduce the risk of falls, especially in older adults. Maintaining muscle strength is essential for independent living and overall mobility.
- Cardiovascular Health: Some research suggests a potential link between vitamin D and cardiovascular health, although the evidence is not entirely conclusive. More research is needed to establish a definitive causal relationship. Cardiovascular health is a major concern for public health.
Evidence-Based Mechanisms
The mechanisms by which vitamin D and calcium supplementation may impact these health outcomes are supported by scientific research.
- Calcium’s role in bone structure: Calcium is a crucial building block for bones, providing structural integrity and strength.
- Vitamin D’s role in calcium absorption: Vitamin D regulates calcium absorption in the intestines, ensuring sufficient calcium is available for bone formation and maintenance.
- Vitamin D’s role in immune function: Vitamin D receptors are found in various immune cells, influencing immune responses.
- Vitamin D’s role in muscle function: Vitamin D is involved in muscle protein synthesis and neuromuscular transmission.
Comparison to Other Interventions
| Intervention | Potential Benefits | Evidence Strength |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D and Calcium Supplementation | Improved bone density, reduced fracture risk, potential impact on immune function, muscle function, and cardiovascular health | Moderate to strong, depending on the specific outcome and population studied |
| Weight-bearing exercise | Increased bone density, improved muscle strength, reduced risk of falls | Strong |
| Fall prevention programs | Reduced risk of falls and fractures, improved mobility | Strong |
Note: The evidence strength for each intervention is a general assessment and can vary based on specific studies and populations.
Potential Risks and Side Effects: Uspstf Draft Recommendation Vitamin D Calcium Supplements
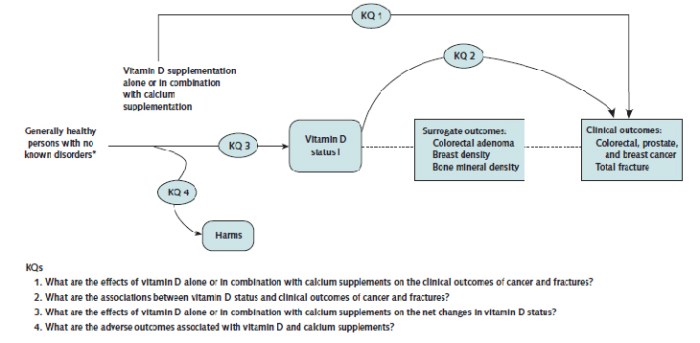
While vitamin D and calcium supplementation can be beneficial for some, it’s crucial to understand the potential risks and side effects. These supplements, like any other, can have negative impacts if not used responsibly. Knowing these potential drawbacks is essential for making informed decisions about whether or not supplementation is right for you.
Potential Side Effects
Excessive intake of vitamin D and calcium can lead to a range of adverse effects. These can vary in severity and frequency, and are often dose-dependent. Understanding these potential side effects is key to safe supplementation.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: High doses of calcium can cause nausea, vomiting, constipation, and abdominal pain. These gastrointestinal symptoms are relatively common, especially with higher doses.
- Kidney Stones: Increased calcium intake can elevate the risk of kidney stones, particularly in individuals predisposed to them. The excess calcium can crystallize and form stones in the urinary tract.
- Hypercalcemia: A buildup of calcium in the blood, known as hypercalcemia, can result from excessive vitamin D and calcium intake. This can lead to a variety of symptoms, including weakness, fatigue, and even more serious complications such as kidney damage.
- Interactions with Medications: Calcium and vitamin D can interact with certain medications, such as those for heart conditions, or some medications that prevent absorption of calcium and vitamin D. For example, certain medications that reduce stomach acid can decrease the absorption of calcium, rendering the supplement less effective.
Interactions with Other Medications
Many medications can interact with vitamin D and calcium supplements. These interactions can either reduce the effectiveness of the supplement or lead to adverse reactions.
- Thiazide Diuretics: These medications can increase calcium levels in the blood, potentially leading to hypercalcemia when taken with calcium supplements. This can exacerbate the risk of kidney stones.
- Certain Antibiotics: Some antibiotics, particularly tetracyclines, can interfere with calcium absorption, reducing the supplement’s effectiveness. Individuals taking these antibiotics may need to adjust the timing of their calcium intake.
- Cardiac Medications: Certain medications for heart conditions can interact with vitamin D, potentially altering blood levels of calcium and affecting heart function. Close monitoring is often necessary.
Important Considerations
Before starting any vitamin D or calcium supplementation, consulting a healthcare professional is paramount. A healthcare provider can assess individual needs, evaluate potential risks, and determine the appropriate dosage.
Potential Side Effects Table
| Side Effect | Severity | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Nausea | Mild | Common |
| Constipation | Mild to Moderate | Common |
| Kidney Stones | Moderate to Severe | Potentially Increased |
| Hypercalcemia | Severe | Rare, but serious |
| Interactions with Medications | Variable | Common |
Note: This table is not exhaustive and individual experiences may vary. Severity and frequency can depend on factors such as dosage, individual health status, and other medications taken.
Alternative Strategies for Bone Health

Beyond supplements, a holistic approach to bone health involves crucial lifestyle choices. Focusing on a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sun exposure are key elements in supporting strong, healthy bones throughout life. These strategies are often more sustainable and effective in the long term than relying solely on supplements.Maintaining optimal bone health is not just about preventing fractures; it’s about overall well-being.
Strong bones support our physical activities, protect our organs, and contribute to a higher quality of life. A proactive approach to bone health emphasizes the importance of a multi-faceted strategy rather than relying solely on isolated solutions.
Dietary Strategies for Bone Health
Diet plays a vital role in bone health. Consuming sufficient calcium and vitamin D through food is essential for bone development and maintenance. Calcium is a fundamental component of bone tissue, while vitamin D aids in calcium absorption. A diet rich in these nutrients, coupled with regular exercise, can significantly contribute to bone density and strength.
Importance of Sun Exposure for Vitamin D Production
Sunlight is crucial for vitamin D synthesis in the body. Our bodies produce vitamin D when exposed to ultraviolet B (UVB) rays from the sun. This process is vital for calcium absorption and bone health. However, adequate sun exposure should be balanced with sun protection measures to prevent skin damage. The amount of sun exposure needed varies based on factors such as geographical location, skin pigmentation, and time of year.
The USPSTF draft recommendation on vitamin D and calcium supplements is interesting, but it got me thinking about other health concerns. For instance, if you’re struggling with hypothyroidism, exploring options like Armour Thyroid can be a helpful step. Finding a doctor who specializes in this area, like the ones at armour thyroid for hypothyroidism , can make a world of difference.
Ultimately, though, the USPSTF’s draft recommendation is a good starting point for understanding the complexities of supplementation and overall health.
Dietary Calcium Sources
Calcium is essential for bone formation and maintenance. Adequate calcium intake is crucial for preventing bone loss and osteoporosis. Dairy products are excellent sources of calcium, but many non-dairy options also provide substantial amounts. The recommended daily allowance of calcium varies based on age and gender, with adolescents and pregnant women often needing higher intakes. A balanced diet should include a variety of calcium-rich foods to ensure optimal intake.
Optimal Calcium Intake
The optimal daily calcium intake varies based on age and gender. For instance, adults aged 19-50 typically require 1000 mg of calcium per day, while older adults may need slightly higher amounts. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate calcium intake for individual needs. Excessive calcium intake can also pose potential risks, so it’s important to maintain a balanced approach.
Dietary Sources of Vitamin D and Calcium
A varied diet provides numerous sources of vitamin D and calcium. These nutrients are crucial for healthy bones.
- Vitamin D-Rich Foods: Fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel), egg yolks, fortified foods (milk, cereals, orange juice), and mushrooms. These foods are excellent sources of vitamin D, helping your body absorb calcium effectively.
- Calcium-Rich Foods: Dairy products (milk, yogurt, cheese), leafy green vegetables (kale, collard greens, bok choy), fortified plant-based milk alternatives (soy, almond, oat), and tofu. These foods are rich in calcium, contributing to bone health and strength.
Comparison with Existing Guidelines
The USPSTF draft recommendation on vitamin D and calcium supplements represents a significant update to the landscape of preventative health guidelines. Understanding how this draft aligns, or diverges, from existing recommendations is crucial for healthcare providers and patients alike. This comparison highlights potential shifts in practice and informs the implications of these changes.Existing guidelines often vary in their recommendations regarding vitamin D and calcium supplementation, frequently based on different methodologies, available evidence, and target populations.
This divergence underscores the importance of critically evaluating the USPSTF draft within the broader context of current recommendations.
Comparison Across Organizations
Various organizations provide guidelines on vitamin D and calcium supplementation, each with their unique perspectives and considerations. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) offers comprehensive information on nutrient recommendations, while organizations like the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) and the Endocrine Society address specific concerns related to bone health and hormonal imbalances.The USPSTF’s approach differs in its focus on population-level benefits and risks, rather than individual patient needs.
This distinction shapes the recommendations significantly. For example, the USPSTF prioritizes the overall public health implications, while other guidelines might emphasize more personalized approaches based on individual risk factors.
Age-Specific Recommendations
Different age groups experience varying levels of vitamin D and calcium needs. Understanding these nuances is critical when evaluating recommendations.
| Age Group | USPSTF Draft Recommendation | NIH Recommendations | AAOS Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Children (0-18) | Not recommended for routine supplementation. Potential for individual needs to be assessed by healthcare providers. | May recommend supplementation in certain populations, considering specific dietary intake and health status. | Emphasizes the importance of a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D. Supplementation may be considered in cases of deficiency. |
| Adults (19-50) | Not recommended for routine supplementation. Potential for individual needs to be assessed by healthcare providers. | May recommend supplementation in certain populations, considering specific dietary intake and health status. | Emphasizes the importance of a balanced diet and adequate calcium and vitamin D intake. Supplementation may be considered in cases of deficiency. |
| Adults (51+) | Not recommended for routine supplementation. Potential for individual needs to be assessed by healthcare providers. | May recommend supplementation in certain populations, considering specific dietary intake and health status, and risk factors for osteoporosis. | Emphasizes the importance of a balanced diet and adequate calcium and vitamin D intake. Supplementation may be considered in cases of deficiency or increased risk for osteoporosis. |
Key Differences and Similarities
The USPSTF draft, in contrast to some existing guidelines, places greater emphasis on the lack of strong evidence for widespread population-level benefits of routine vitamin D and calcium supplementation. This approach reflects a more cautious stance compared to some organizations that may recommend supplementation more readily. However, the USPSTF draft still acknowledges the potential importance of individual assessments and the potential for supplementation in specific high-risk cases.
There’s a consensus on the importance of adequate calcium and vitamin D intake through diet, but the degree to which supplementation is warranted remains a point of divergence. This difference is crucial, as it can impact the cost of healthcare and potentially lead to overconsumption of supplements, a concern that is not as frequently addressed in other guidelines.
Implications for Healthcare Professionals
Integrating the USPSTF draft recommendation on vitamin D and calcium supplements into clinical practice requires careful consideration of its implications for healthcare professionals. This recommendation challenges the long-held assumption of routine supplementation and necessitates a shift in how we approach bone health advice. It’s crucial to understand the nuances of the evidence base and the potential benefits and risks before tailoring recommendations to individual patients.Healthcare professionals must now take a more nuanced approach to patient care, focusing on personalized recommendations rather than blanket prescriptions.
This involves careful assessment of individual risk factors, lifestyle, and overall health status, alongside the patient’s understanding of the recommendation.
Recommendations for Practice Integration
The USPSTF draft recommendation underscores the importance of shared decision-making with patients. Clinicians should frame the conversation around the benefits and risks of supplementation, rather than promoting it as a routine intervention. This involves discussing the evidence and exploring alternative strategies for bone health, such as dietary modifications and weight-bearing exercise. Patient preferences and values should play a significant role in the final decision.
Educational Materials for Patients
Providing patients with clear and concise information is vital. Educational materials should emphasize the importance of a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, along with lifestyle factors that support bone health. Examples of such materials could include brochures, videos, or even interactive online resources. These resources should also address potential side effects of supplementation and alternative approaches to achieving optimal bone health.
Explaining the nuances of the USPSTF draft recommendation is crucial, as well as emphasizing the importance of consulting with a healthcare professional.
Potential Impact on Clinical Decision-Making
The draft recommendation necessitates a shift in clinical decision-making. Clinicians should no longer automatically recommend supplementation, but rather consider individual patient needs and risk factors. This requires careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks, as well as the patient’s overall health status. The recommendation emphasizes a personalized approach, focusing on individualized risk assessment rather than a universal approach.
Importance of Patient-Centered Communication
Effective communication is paramount. Healthcare professionals must engage in open and honest dialogue with patients about the recommendation, acknowledging their concerns and questions. This approach fosters trust and empowers patients to make informed decisions about their health. Avoidance of jargon and use of patient-friendly language is critical to effective communication.
Patient Assessment Questions
| Category | Question |
|---|---|
| Dietary Intake | “Do you consume foods rich in vitamin D and calcium, such as fatty fish, dairy products, and leafy greens?” |
| Lifestyle Factors | “Do you engage in regular weight-bearing exercises, like walking or jogging?” |
| Medical History | “Do you have any medical conditions, such as osteoporosis, or take any medications that might affect vitamin D or calcium absorption?” |
| Family History | “Does anyone in your family have a history of osteoporosis or bone-related problems?” |
| Supplementation History | “Have you taken vitamin D or calcium supplements in the past, and if so, what was your experience?” |
| Concerns and Preferences | “What are your concerns or preferences regarding vitamin D and calcium supplementation?” |
Implications for Public Health
The USPSTF draft recommendation on vitamin D and calcium supplements has significant implications for public health initiatives, potentially impacting individual choices and government policies related to bone health. Understanding these implications is crucial for crafting effective strategies to promote optimal bone health across the population.This recommendation, if finalized, will likely influence public awareness and individual behaviors regarding supplementation. The recommendation’s impact will extend beyond individual decisions, potentially impacting public health campaigns and the broader healthcare system.
This influence will require careful consideration of the evidence base and potential consequences.
Potential Impact on Public Health Initiatives
The USPSTF recommendation’s impact on public health initiatives will likely be substantial. If the recommendation discourages routine supplementation, public health campaigns may need to shift their focus towards alternative strategies for promoting bone health, such as diet and exercise. Conversely, if the recommendation supports supplementation for specific populations, public health campaigns might need to target education on appropriate use and potential risks.
Effective communication will be crucial to ensuring that the public understands the recommendation’s implications.
Importance of Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns play a vital role in promoting bone health. They can educate the public about the importance of adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, along with other factors contributing to strong bones, such as exercise and a balanced diet. These campaigns can also address concerns about potential risks associated with supplementation, encouraging responsible use and seeking professional guidance.
Targeted campaigns for specific populations, like older adults or those at higher risk for osteoporosis, can further enhance their effectiveness.
Potential Future Research Directions
Future research should investigate the long-term effects of the recommendation on bone health outcomes in various populations. Research should also explore the effectiveness of different strategies for promoting bone health, including dietary interventions, exercise programs, and public health campaigns. Comparative studies examining the impact of different approaches on bone density and fracture rates will provide valuable insights. Further research is needed to refine the recommendation’s application in specific demographic groups and to identify individuals who may benefit most from supplementation.
Potential Impacts on Healthcare Costs
The recommendation’s potential impact on healthcare costs is complex and multifaceted. Reduced demand for vitamin D and calcium supplements could potentially lead to lower prescription costs for healthcare systems. However, if the recommendation results in an increase in bone-related illnesses due to insufficient intake, it could increase healthcare costs in the long term. Future cost-effectiveness analyses are needed to assess the overall impact on healthcare budgets.
Possible Public Health Strategies for Promoting Bone Health
- Promoting a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D: Encouraging the consumption of foods such as dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified foods can provide essential nutrients for bone health.
- Encouraging regular physical activity: Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, jogging, and dancing, can help strengthen bones and maintain bone density. Strategies should focus on promoting long-term exercise habits.
- Educating the public about the importance of bone health: Public awareness campaigns can increase understanding of the factors contributing to strong bones and promote lifestyle choices that support bone health.
- Providing access to healthcare services for bone health screenings: Early detection of bone-related issues can allow for timely interventions and treatment, potentially preventing more severe conditions.
- Supporting research on bone health: Investing in research to further understand the complex mechanisms of bone health will lead to more effective strategies for prevention and treatment.
- Collaboration between public health agencies, healthcare providers, and community organizations: Collaboration can maximize the impact of public health initiatives and provide comprehensive support for bone health.
Epilogue
In conclusion, the USPSTF’s draft recommendation on vitamin D and calcium supplements offers a nuanced perspective on preventative care. While the recommendation provides valuable insights, further research and careful consideration of individual patient needs are essential. The document’s detailed analysis of the evidence base, potential benefits and risks, and alternative strategies equips readers with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
Ultimately, the recommendation underscores the importance of personalized care and consultation with healthcare professionals before initiating any supplementation regimen.




